
Artemia Plankton Isolated On White Background Stock Photo 390464062 Shutterstock
Basic and Applied Zooplankton Biology Chapter Introduction to Artemia Culture T. Veeramani, P. Santhanam, N. Manickam & C. Rajthilak Chapter First Online: 24 July 2018 1572 Accesses 2 Citations 1 Altmetric Abstract Artemia, the brine shrimp, is an excellent live food for cultivable aquatic species.
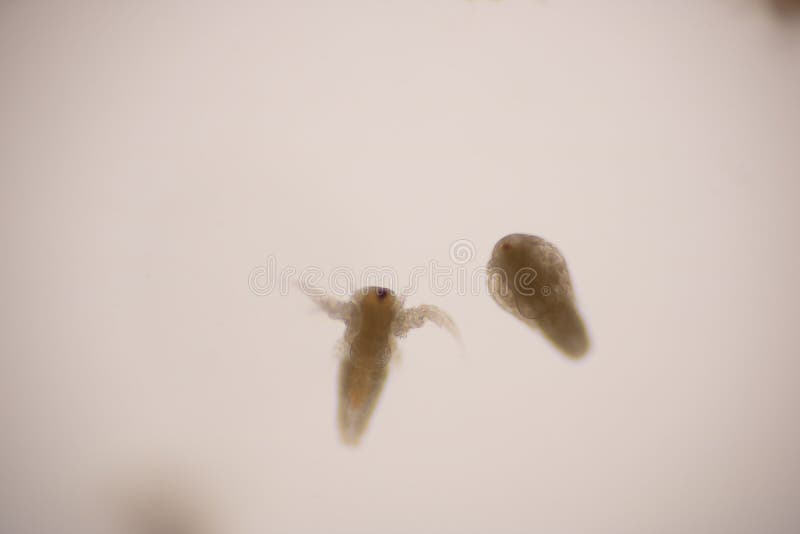
Artemia Larvae in Light Microscope, Artemia Plankton Under a Microscope Stock Photo Image of
The brine shrimp Artemia salina (hereafter "Artemia") became luminescent after swimming for only 10 s in a liquid culture of P. leiognathi, as well as after swimming for 2.5 h in the suspension of small particles of bioluminescent P. leiognathi colonies. As revealed by long-exposure photographs, the luminescence in the guts of Artemia was clearly visible from outside, with additional glow.

Artemia Plankton Isolated On White Background Stock Photo 390464092 Shutterstock
Introduction. Artemia franciscana nauplii are used as live food for the rearing of marine fish larvae. High mortalities often occur during the early life stages under intensive cultivation. Although specific pathogenic bacteria are rarely isolated during such events, bacteria seem to be one main reason for these mortalities (Vadstein et al., 1993; Munro et al., 1994).

Artemia plankton isolated on white background — Stock Photo © bluehand 11317363
Artemia salina is a natural plankton extract that helps protect skin against environmental stressors, including heat and UV-rays, and works to improve the skin's strength and elasticity. What does plankton extract do for skin?

Artemia Plankton Isolated On White Background Stock Photo 379989517 Shutterstock
In June-July 2019, adult Artemia were at all sites with salinity higher than 82 g/L when there was no suppression by predators. A self‐sustaining Artemia population in the bay may recover in 2 or 3 years, when the average salinity would reach 80-90 g/L; total abundance of the active Artemia stages may reach 3000-5000 ind. M −3 between.

Artemia Plankton Isolated On White Background Stock Photo 400590211 Shutterstock
Artemia are in wide use because they are a "convenience food." Artemia cysts (resting eggs) are harvested in bulk from the wild and preserved by canning. They therefore have a very long shelf-life, so may be stored at the hatchery and the cysts are hatched as needed. However, Artemia have several shortcomings.

Artemia Plankton Isolated On White Background Stock Photo 478265467 Shutterstock
Read more about plankton collection below, and watch the videos.. (Artemia). Artemia cysts (i.e. eggs) are commercially available and easy to hatch yourself. For the best hatching results, add your cysts to a separatory funnel that is filled with seawater (about ½ teaspoon of cysts per 400 mL seawater). The funnel should be well bubbled and.
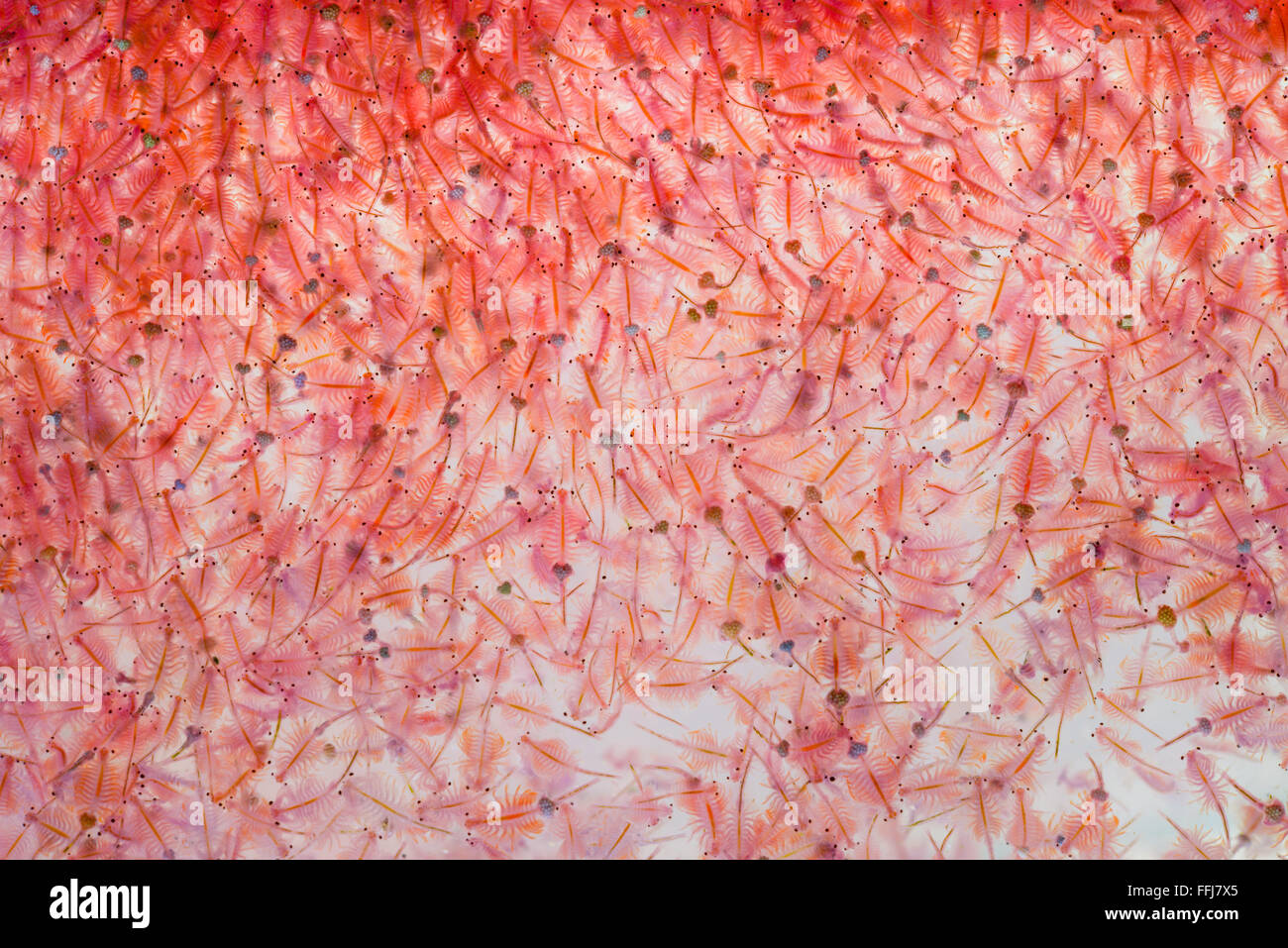
Artemia plankton Brine shrimp Stock Photo Alamy
ARTEMIA (PLANKTON) EXTRACT . This ingredient is not currently on EWG's Restricted or Unacceptable Lists. Asthma/Respiratory . No Data, Some Concern . Skin Allergies & Irritation . No Data, Some Concern . Developmental & Reproductive Toxicity . No Data, Some Concern . Cancer .

artemia plankton isolated on black background xFotosearchxLBRFx xbajita1111x ESY 036626308
Artemia has been found to be a suitable food for the most diversified group of organisms of the animal kingdom, e.g. foraminifers, coelenterates, flatworms, polychaetes, squids, insects, chaetognaths, many freshwater and marine crustaceans and fishes.

Artemia Plankton Isolated On White Background Stock Photo 105809798 Shutterstock
Plankton Artemia Extract is an extract from Artemia Salina strains with diguanoside tetraphosphate (DT) at a minimum 145mg / Kg, suitable for use as a functional ingredient. anti-pollution Or protect the skin from various environmental conditions as well

Artemia Plankton Isolated On Black Background Stock Photo 379991782 Shutterstock
An extract from the plankton Artemia salina protects DNA from UV damage and decreases UV-induced inflammatory cytokines, suggesting a way to help sunscreens protect skin from UV damage. More in Actives Anti-aging/Face Layering Efficacies to Reverse Photoaging: A Multifunctional Serum Case Study

Artemia plankton Brine shrimp Stock Photo Alamy
Artemia are known for their propensity to swarm, but little attention has been given to swarming mechanisms and the reasons for it. However, the effect of swarming in larvicultures of fish is that fewer Artemia will actually be ingested ( Gulbrandsen, 1996 ).

Artemia Plankton Isolated On Black Background Stock Photo (Edit Now) 379993519
INCI/chemical name: Water (and) Artemia Extract. SDS Link >. Gp4g sp™ biofunctional is a unique aquatic energizing and protecting plankton extract that helps the skin absorb environmental aging shocks. preservative system: phenoxyethanol, potassium sorbate. recommended use level: 1% - 2% (clinically tested at 2%)

Artemia larvae in light microscope, Artemia plankton under a microscope. 9761847 Stock Photo at
The specialty of Artemia sp. as plankton is to have tolerance (the ability to adapt and defend themselves) in a very wide range of salt levels. At very high salt levels where no organism can survive, it turns out that Artemia sp. can tolerate it. The method used is an experimental method with the experimental design used is a Completely.

Artemia Plankton Isolated On Black Background Stock Photo 386767471 Shutterstock
Artemia (Anostraca) is among the most primitive and ancient groups of crustaceans. Artemia spp. play a dominant role in the ecosystems of hypersaline waters, and often they are the only animals in these extreme biotopes. Most ethological studies on Artemia have been conducted on nauplii and metanauplii.

Artemia Plankton Isolated On White Background Stock Photo 386767492 Shutterstock
Saltern phytoplankton is dominated by microalgae such as Dunaliella sp., Rhodomonas sp., and halophitic purple sulfur bacteria, and cyanobacteria (Torrentera, unpublished data). Salterns are inhabited by the Caribbean flamingo Phoenicopterus ruber and other birds feeding on Artemia, the dominant zooplankter.Some Corixidae and Notonectidae insects are adapted to these salt pools and are also.