
Mammary gland dysplasia from a 20monthold mouse treated neonatally... Download Scientific
Benign breast disease in women is a very common finding and results in a diagnosis in approximately one million women annually in the United States (1). An understanding of the hormonal and growth factor control of breast development and function is key to the rational and systematic evaluation and treatment of patients. A firm understanding of benign breast disease is important since.

dysplasia แปลว่า คือ หมายถึง ตัวอย่าง การใช้ Dr. Krok
Benign breast diseases constitute a heterogeneous group of lesions arising in the mammary epithelium or in other mammary tissues and they may also be linked to vascular, inflammatory or traumatic pathologies.. This paper will not deal with mammary dysplasia or fibrocystic mastopathy which is the most common breast lesion in women of.

Mammary gland dysplasia in regressed, multiparous MMTVCK2α transgenic... Download Scientific
INTRODUCTION. Benign breast disease represents a spectrum of disorders that come to clinical attention because of patient symptoms (such as breast pain), palpable lesions or other findings on physical examination, or as imaging abnormalities. Following establishment of a benign diagnosis, treatment in general is aimed at symptomatic relief and.
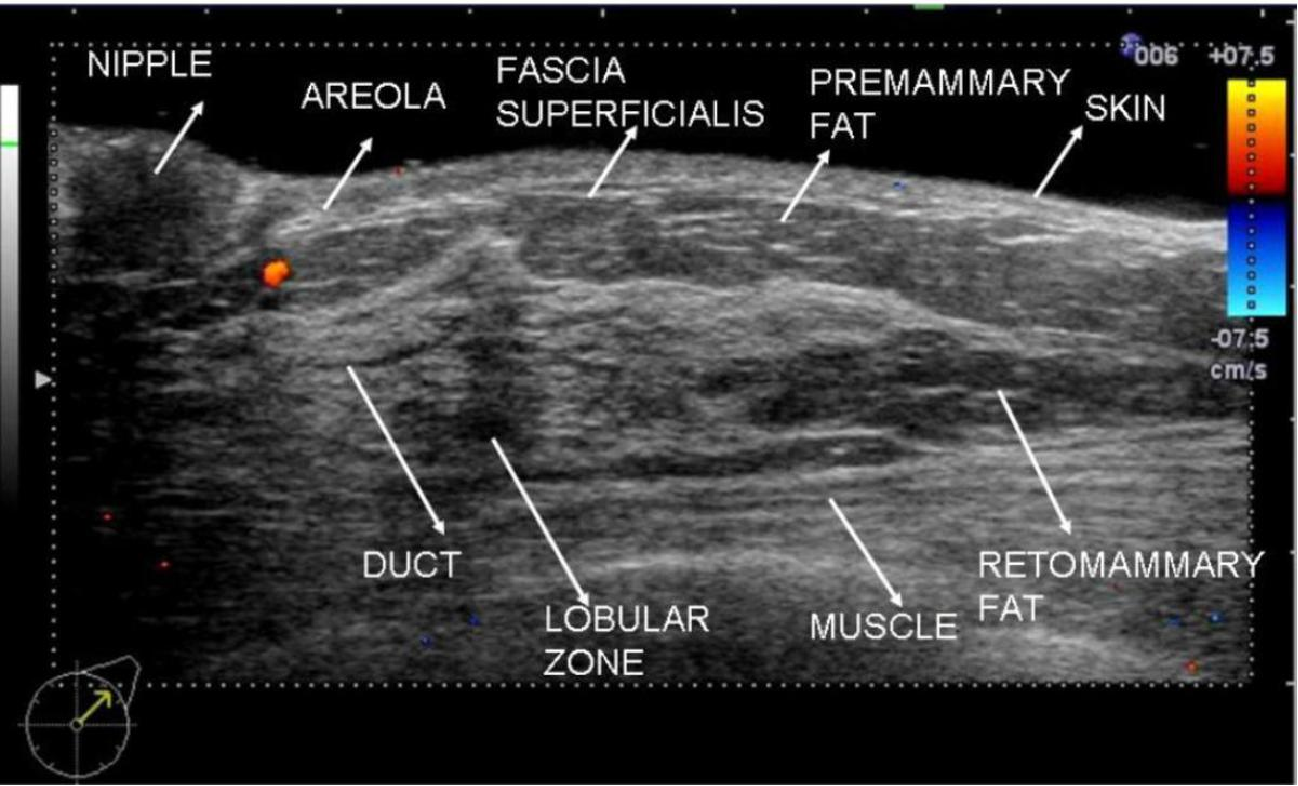
The differential diagnosis between breast cancer and fibromicrocystic dysplasia by full breast
Symptoms. Signs and symptoms of fibrocystic breasts may include: Breast lumps or areas of thickening that tend to blend into the surrounding breast tissue. Generalized breast pain or tenderness or discomfort that involves the upper outer part of the breast. Breast nodules or lumpy tissue change in size with the menstrual cycle.
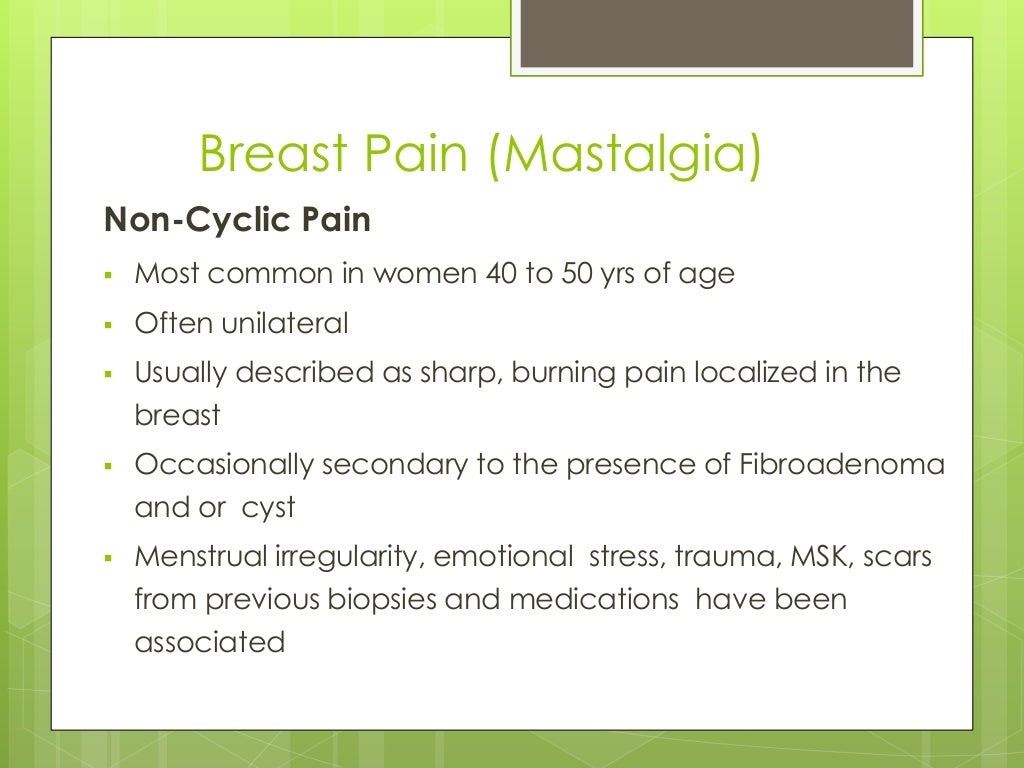
Benign Breast Diseases
I ntroduction. The vast majority of the lesions that occur in the breast are benign. Much concern is given to malignant lesions of the breast because breast cancer is the most common malignancy in women in Western countries; however, benign lesions of the breast are far more frequent than malignant ones [1-9].With the use of mammography, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging of the.

Fig 13.2, [Multicentric invasive ductal carcinoma III...]. Diseases of the Chest, Breast
Breast cancer is a multifactorial disease. 4,5 Benign breast disease (BBD) is one of the most important risk factors for breast cancer. 6-11 Breast cancer is more frequent in women with BBD than in the general population. 9 Previous studies have indicated that 90% of breast lesions are benign. 12 The etiology of BBD is unknown. 1,9

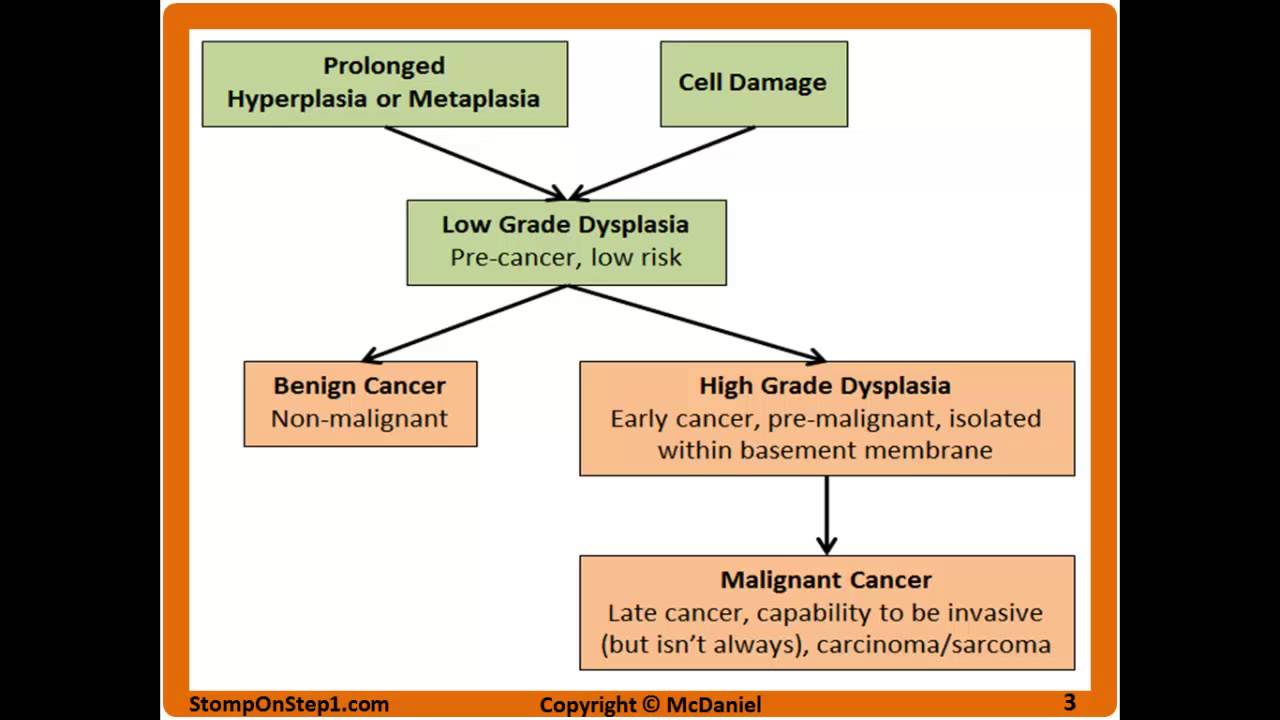
Dysplasia & the Difference between Benign and Malignant Stomp On Step1
It is a structural disorder of the mammary glands due to different degrees of hyperplasia and subinvolution of the mammary parenchyma and stroma. In the literature, HMG is also called mastopathy, fibroadenosis, fibrocystic breast disease, mastalgia, fibrocystic change, benign mammary dysplasia, or sclerosing adenosis.

(PDF) Change of angiogenesis in the nodular form of benign mammary dysplasia during treatment
To diagnose a breast condition, your healthcare provider will take your complete health history. Your provider may also: Do a complete physical exam to: Locate any lump and feel its features (for example, texture, size, and relationship to the skin and chest muscles) Look for changes in the nipples or the skin of the breast.

Breast dysplasia what it is, symptoms and treatment
Papillomas. Papillomas (first described by Warren in 1905 []) are found in around 1-3% of all biopsy tissue samples taken from the breast [4,5] (figs. (figs.1, 1, ,2). 2).The relevance of milk duct papillomas is not to be underestimated despite this relatively low incidence, as they are deemed to be a risk factor for malignant processes regardless of whether it is a solitary or a multiple.

Benign breast lesions that mimic malignancy Pathology
Hyperplasia is an overgrowth of the cells that line the lobules (milk-producing glands) or ducts (small tubes) inside the breast. It is not cancer, but some types of hyperplasia are linked with a higher risk of developing breast cancer (see below). Hyperplasia can be described as either usual or atypical, based on how the cells look under a.
Difference between Benign and Malignant, Dysplasia, poorly differentiate well differentiated
Benign breast conditions (also called benign breast diseases) are noncancerous disorders of the breast. They can occur in both women and men. There are many types of benign breast conditions. Your health care provider may use the term fibrocystic change to describe a range of benign breast conditions. This section discusses benign breast.

Raman spectra of the normal (a) and the benign (b) tissues (dysplasia... Download Scientific
Duct ectasia. Columnar alteration with prominent apical snouts and secretions (CAPSS) Papillomatosis. Fibrocystic changes. All of these are benign (non-cancerous) changes that the pathologist might see. These conditions generally do not need to be treated unless they're causing bothersome symptoms.

Benign breast diseases images. (A) Breast hyperplasia, scale bar... Download Scientific Diagram
There are many different types of benign breast disease. Benign breast disorders refer to any lump, cyst or other change in your breast tissue that isn't cancerous. Most of the following types don't increase your cancer risk and don't require treatment: Breast cysts: Up to 25% of breast lumps are fluid-filled cysts.

Fibroepithelial neoplasms of the breast Diagnostic Histopathology
Breast Lumps and Cancer. While a common breast complaint and concern is a newly discovered breast lump, only a small percentage turn out to be cancer. In fact, many women have lumpy breasts, or a condition called fibrocystic breast disease that is benign. If you have this condition, examining your breasts can be confusing and, at times, alarming.
New Zealand hospitalisations for benign mammary dysplasia Figure.NZ
Overview. Atypical hyperplasia is a precancerous condition that affects cells in the breast. Atypical hyperplasia describes an accumulation of abnormal cells in the milk ducts and lobules of the breast. Atypical hyperplasia isn't cancer, but it increases the risk of breast cancer. Over the course of your lifetime, if the atypical hyperplasia.
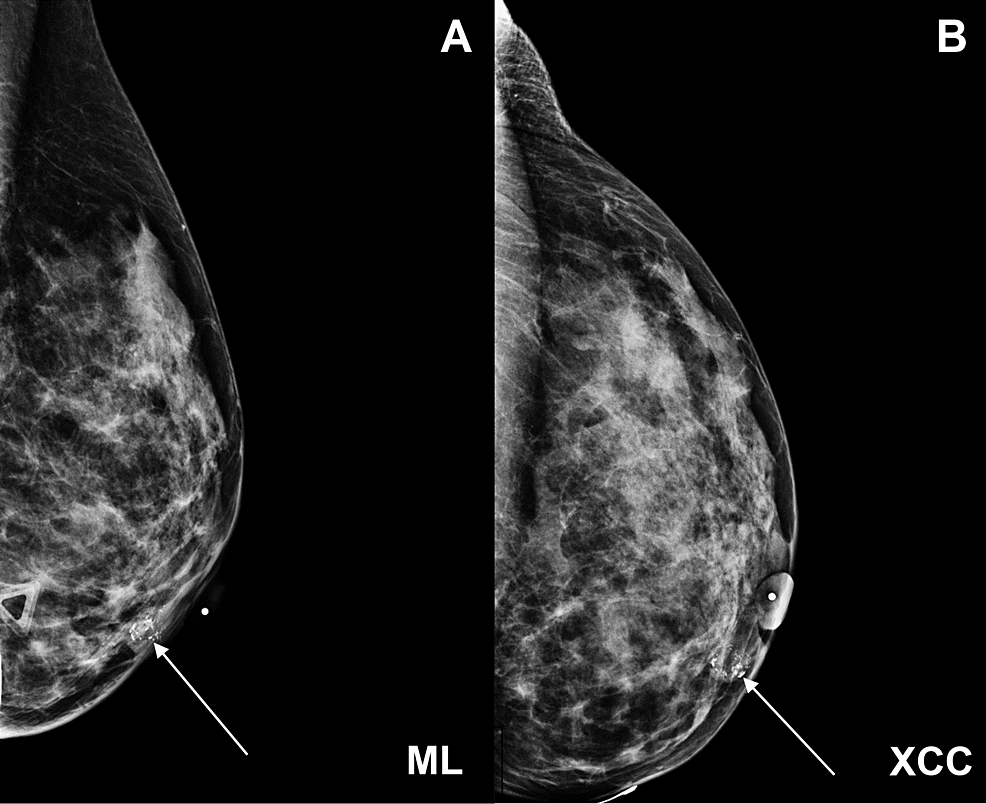
Cureus MucoceleLike Lesion of the Breast
Fibrocystic breast changes and associated risk of developing breast cancer, adapted from (12, 13) From the age of 30, about 50% of women develop fibrocystic breast disease, and in 20% of them.