
Virus replication cycle and the steps which are targeted by antiviral... Download Scientific
VIRUS DOMAIN. "DOMAIN" OF THE VIRUS. Viruses are the most difficult organisms to consider in this parade of all living things. Most of them are made of a protein jacket surrounding a nucleic acid. Their structure and organization, even of the most complex viruses, is non cellular. Thus, their relationships with all other living groups are.

Profil dan Biodata Dea Onlyfans Umur, Agama, Instagram, Viral Diundang Podcast Deddy Corbuzier
The hierarchical sequence clustering of the VgrG domains, DUF2345 domains and other toxin domains were individually conducted by the CD-HIT v4.6.5 51 following the protocol described previously 43.

Virus structure, classification and antiviral therapy (Virology) (Medical Microbiology and
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) modulates host cellular signaling pathways and immune responses to maintain persistent infection 1, 2.The prominent feature of HCV infection is the development of.
The Viruses General Microbiology
Figure 1. Viral respiratory infections are accompanied by a specific pattern of natural cytotoxicity receptor (NCR) expression.Nucleic acids were extracted from nasal wash samples, obtained from patients with respiratory viral infections, respectively, respiratory syncytial virus, adenovirus, human metapneumovirus, and influenza A, along with healthy controls and then were tested for mRNA.

Virus Definition,Evolution,Taxonomy,Morphology,Replication,Pathology & more.
The human genome encodes 37 DEAD-box and 16 DEAH-box RHs that exhibit diverse biological functions, including the regulation of embryonic development, cell proliferation, hematopoiesis, metabolism.
Frontiers From Entry to Egress Strategic Exploitation of the Cellular Processes by HIV1
6.1. Ferroptosis in Viral Infection. Ferroptosis is a type of non-apoptotic regulated and autonomous cell death pathway that is largely dependent on iron (Fe)-mediated formation and accumulation of free lipid radicals [24,220]. It results from oxidative alterations of the cellular microenvironment marked by the lipid peroxide radicals formed.
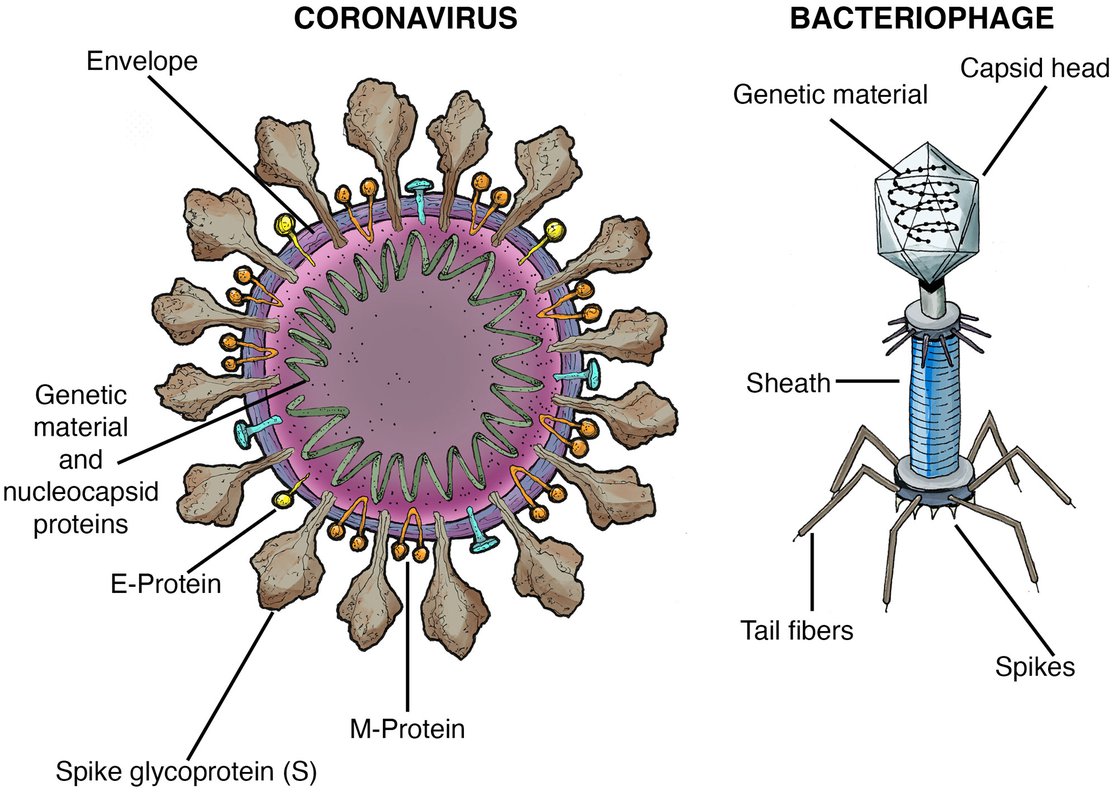
What is the coronavirus? Virus science explained Caltech Science Exchange
We first identified genes that are expressed downstream of VND6 but not downstream of SECONDARY WALL-ASSOCIATED NAC DOMAIN PROTEIN1 (SND1), a master regulator of xylem fiber cells, using transformed suspension culture cells in microarray experiments.. At 6 h, the level of transcripts for VND6 and SND1 increased over 2000- and 400-fold.

Influenza virus replication. The binding of influenza virus to the host... Download Scientific
2. Identification of L Domains within HIV-1 p6 Domain of Pr55 Gag Precursor. All retroviruses express structural Gag polyproteins that drive the assembly and the release of v irus-l ike p articles (VLPs), even in the absence of other viral components (for reviews, see [33,34]), and all retroviral Gag precursors contain the three structural domains of matrix (MA), capsid (CA), and nucleocapsid.

Structure of SARS Coronavirus Spike ReceptorBinding Domain Complexed with Receptor Science
Abstract. Late assembly (L) domains are conserved sequences that are necessary for the late steps of viral replication, acting like cellular adaptors to engage the ESCRT membrane fission machinery that promote virion release. These short sequences, whose mutation or deletion produce the accumulation of immature virions at the plasma membrane.

The Viral Life Cycle Microbiology Course Hero
The spike protein in SARS-CoV-2 (SARS-2-S) interacts with the human ACE2 receptor to gain entry into a cell to initiate infection. Both Pfizer/BioNTech's BNT162b2 and Moderna's mRNA-1273 vaccine candidates are based on stabilized mRNA encoding prefusion SARS-2-S that can be produced after the mRNA is delivered into the human cell and.

COVID19 Serology Testing Explained
In recent years, the RNA modification N6-methyladenosine (m 6 A) has been found to play a role in the life cycles of numerous viruses and also in the cellular response to viral infection. m 6 A has emerged as a regulator of many fundamental aspects of RNA biology. Here, we highlight recent advances in techniques for the study of m 6 A, as well as advances in our understanding of the cellular.
Fusion NIH
A productive infection results in an explosive viral population, cell death, and development of disease signs, during which neurons are infected. A latent infection develops in the neurons, allowing the virus to remain undetected in the host. If the viral genome is reactivated, a productive infection results, leading to viral replication and.
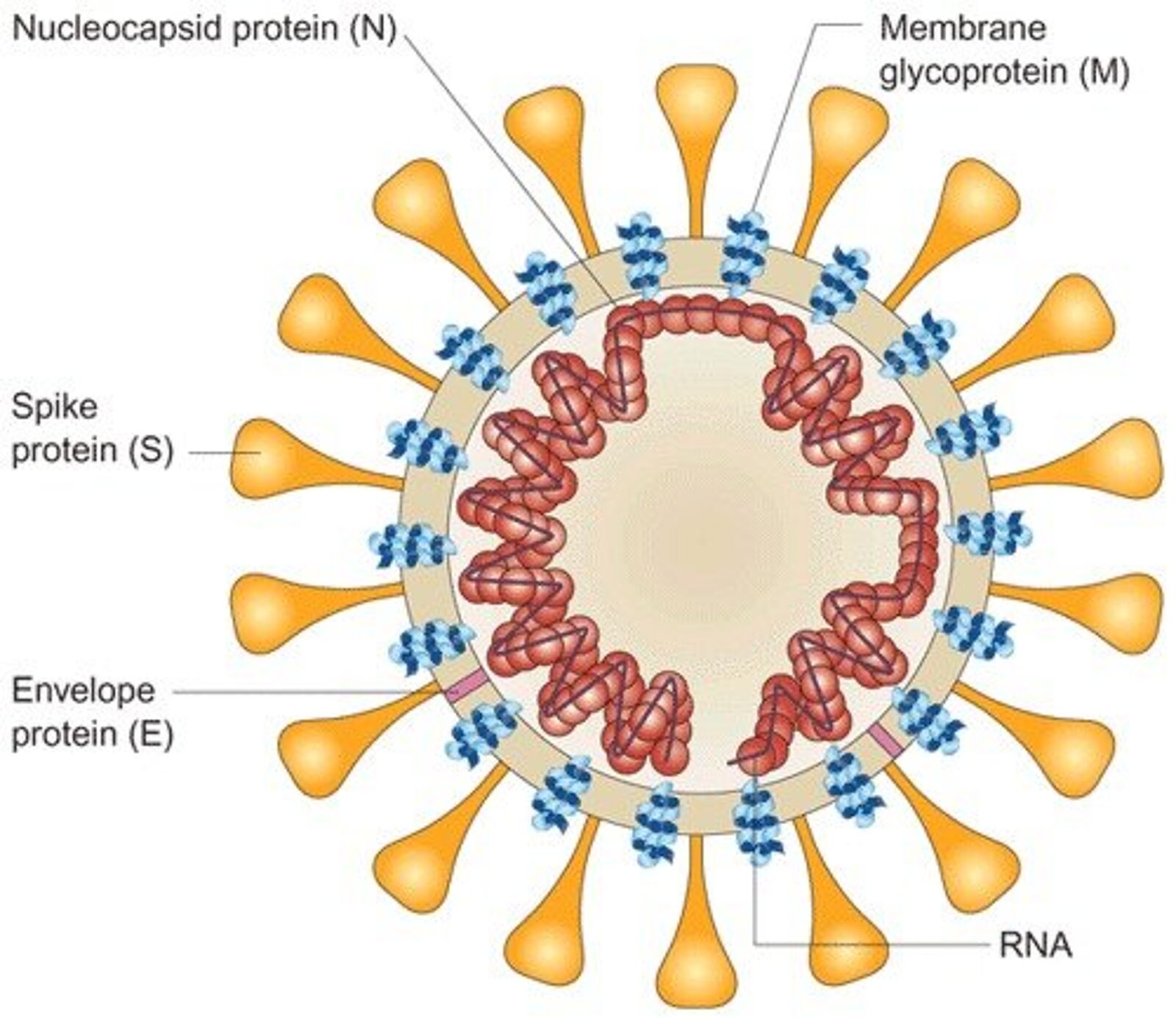
SARSCoV2 coronavirus proteins
The human genome encodes 37 DEAD-box and 16 DEAH-box RHs that exhibit diverse biological functions, including the regulation of embryonic development, cell proliferation, hematopoiesis, metabolism.

Strand swapping regulates the ironsulfur cluster in the diabetes drug target mitoNEET PNAS
ABSTRACT Poxvirus virion biogenesis is a complex, multistep process, starting with the formation of crescent-shaped viral membranes, followed by their enclosure of the viral core to form spherical immature virions. Crescent formation requires a group of.
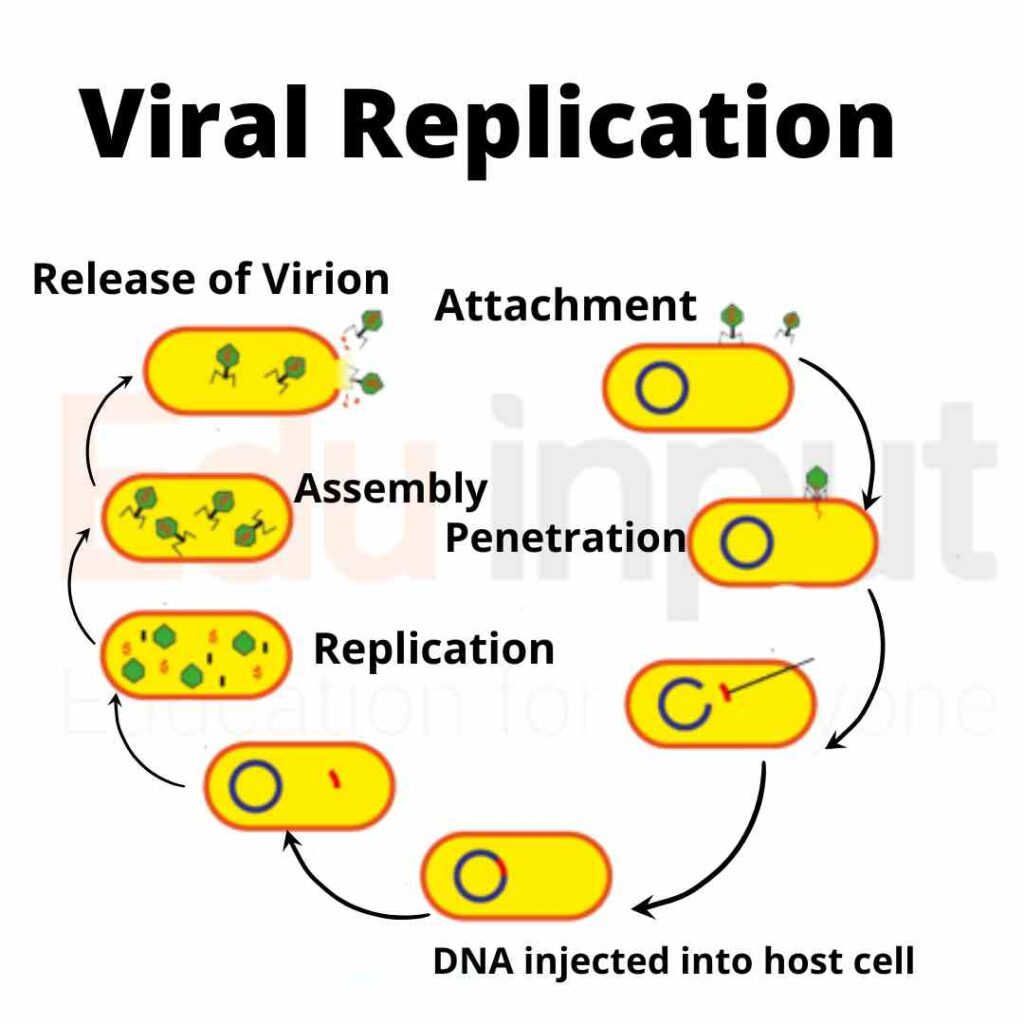
Reproduction in Viruses StepbyStep Guide to Viral Replication
DEAD-box/DEAH-box helicases (DEAD/H-box helicases), a subfamily of helicase superfamily 2 (SF2), are the enzymes that recognize and unwind RNA duplexes or displace bound protein complexes in an ATP-dependent manner (Cordin et al., 2006).The helicases' core has covalently linked two peculiar Rec-A like globular domains separated by a flexile linker region, with at least eight conserved motifs.
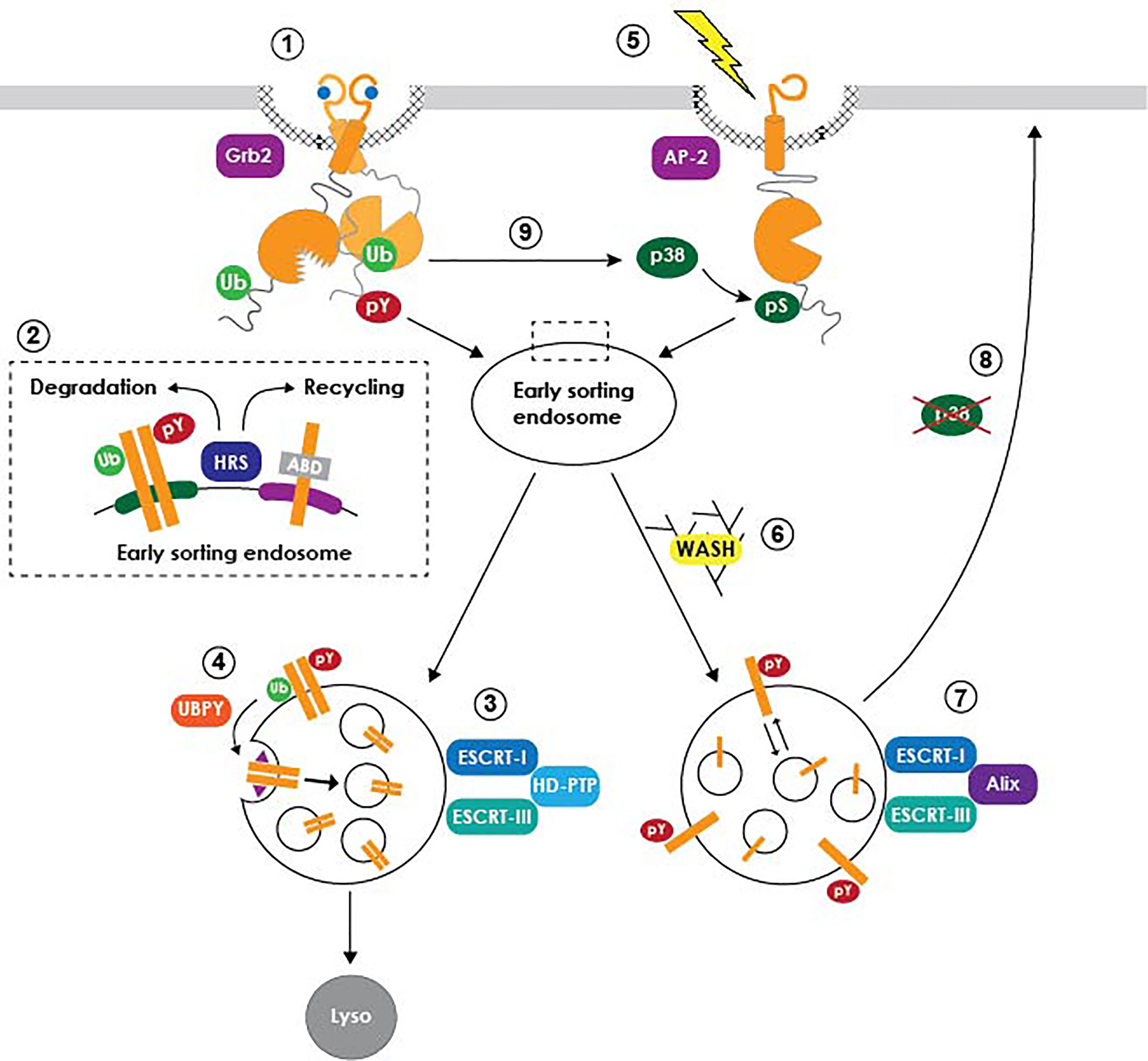
Frontiers Role of EGF Receptor Regulatory Networks in the Host Response to Viral Infections
Domains were identified from viral whole-genome sequence using automated profile Hidden Markov Models (pHMM). This study also describes the framework for constructing "domain neighborhoods.