Fibromatosis colli, causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment & prognosis
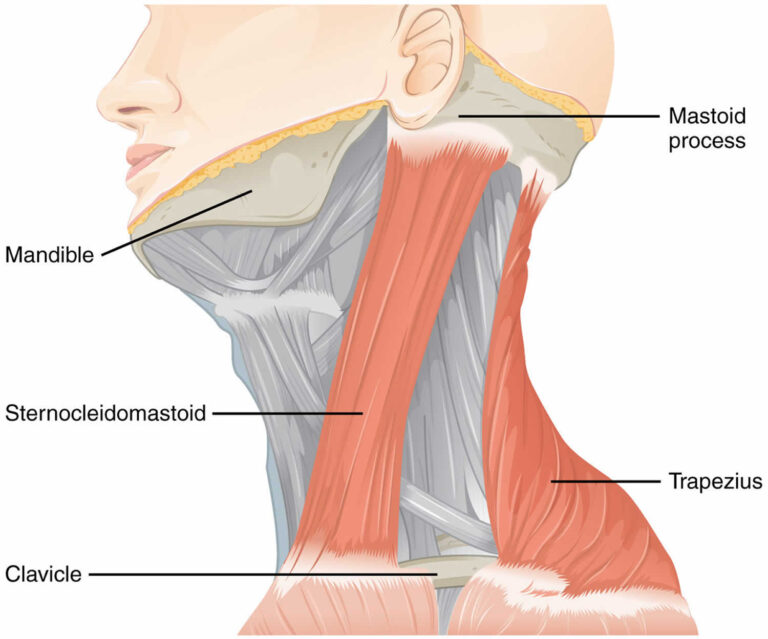
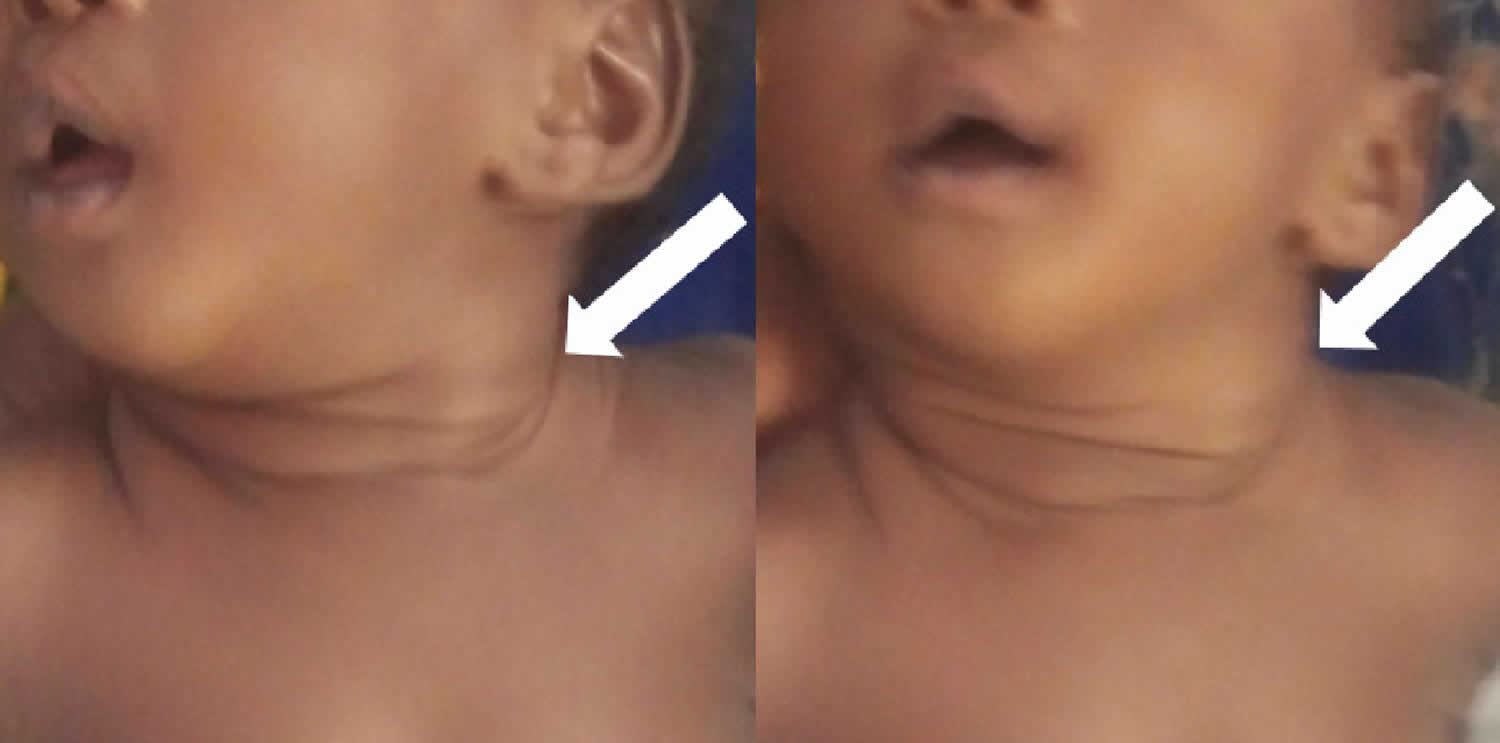
Introduction. Fibromatosis colli (FC) also known as sternocleidomastoid tumor, a self limiting lesion, presents as a firm to hard, immobile, fusiform swelling in the lower or middle portion of the sternocleidomastoid muscle and usually appears within the first few weeks of life. Most of the cases present with torticollis but there are exceptions.

Fibromatosis Colli Eurorad
Fibromatosis colli (FMC) was first described as the sternocleidomastoid tumor of childhood (SCMT). [ 1] It is a unique form of perinatal fibromatosis resulting in the development of a tough mass in the sternocleidomastoid muscle (SCM) of the newborn. [ 2] It is a rare condition that is particularly seen in newborns and infants. [ 3]

Fibromatosis colli Image
Pathology. Fibromatosis colli is thought to be related to birth trauma (e.g. forceps delivery and difficult labor) or malposition (e.g. breech) in the womb. Resulting hemorrhage eventually results in fibrosis. The importance of fibromatosis colli, above all else, is that it must be recognized for its benign nature.
Fibromatosis colli, causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment & prognosis
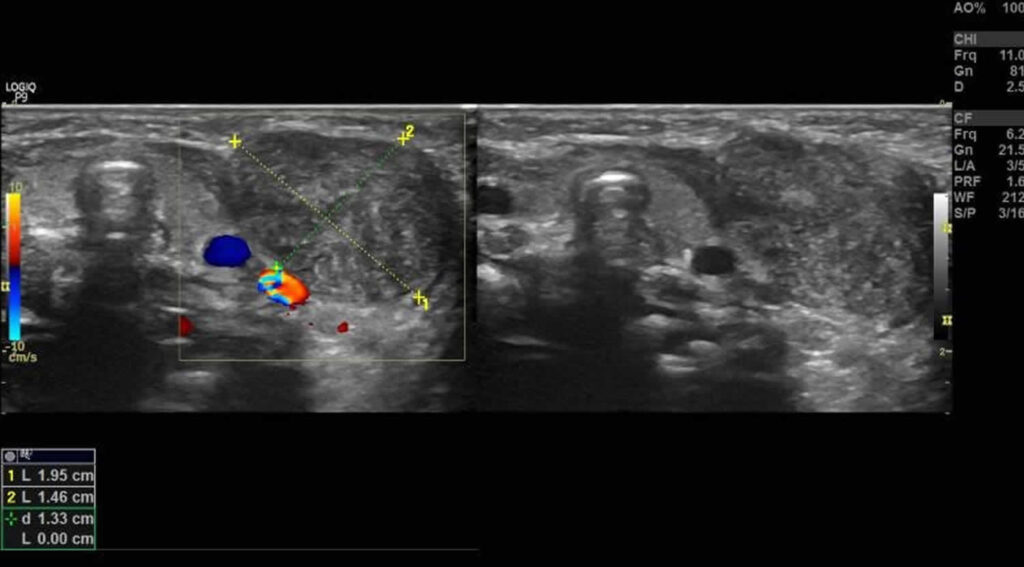
F ibromatosis colli is a condition of benign proliferation of fibrous tissue within the sternocleidomastoid muscle leading to focal or diffuse enlargement. Clinically, it presents as neck mass with restriction of neck movement, usually in infancy. Though the exact etiology is not known, it is mostly attributed to ischemia of the muscle likely.
Fibromatosis colli, causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment & prognosis
The presentation and management of fibromatosis colli. 2010 Sep;89 (9):E4-8. doi: 10.1177/014556131008900902. Department of Otolaryngology and Communication Enhancement, Children's Hospital, Boston, MA 02115, USA. We conducted a systematic chart review to identify all infants with fibromatosis colli who had been seen at Children's Hospital in.

Fibromatosis colli of infancy Eurorad
Search All ICD-10 Toggle Dropdown. Search All ICD-10; ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Codes; ICD-10-PCS Procedure Codes; ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Index; ICD-10-CM External Causes Index; ICD-10-CM Table of Drugs; ICD-10-CM Table of Neoplasms; HCPCS Codes; ICD-9-CM Diagnosis Codes; ICD-9-Vol-3 Procedure Code; Search All Data

Fibromatosis Colli pediatric ultrasound Dr.Mohamed Soliman YouTube
ICD coding. ICD-10: D48.1 - neoplasm of uncertain behavior of connective and other soft tissue. 2F7C & XH13Z3 - neoplasm of uncertain behavior of connective or other soft tissue & desmoid type (aggressive) fibromatosis. 2F7C & XH6116 - neoplasm of uncertain behavior of connective or other soft tissue & abdominal (mesenteric) fibromatosis.

Fibromatosis colli Image
Congenital muscular torticollis (CMT), also known as fibromatosis colli, is recognized as unilateral contracture and shortening of the sternocleidomastoid (SCM) muscle due to muscle atrophy and interstitial fibrosis, causing ipsilateral head tilt and turn ().Its frequency ranges from 0.3 to 2% in newborns with history of perinatal injury, but it is far less common in adults, who are often.
Fibromatosis colli pacs
Fibromatosis colli (FMC), also termed sternocleidomastoid tumor of infancy, pseudotumor of infancy, and infancy sternocleidomastoid pseudotumor, is an uncommon (incidence: 0.4%-1.3% of live births), congenital tumor in one of the two sternocleidomastoid neck muscles although rare cases have presented with a FMC tumor in both.

Fibromatosis colli Image
The term fibromatosis refers to a group of soft tissue tumors which have certain characteristics in common,. Aggressive infantile fibromatosis; Fibromatosis colli: benign sternocleidomastoid muscle tumor developing in infants within 8 weeks (average: 24 days) of delivery. It generally does not require resection and responds well to.

Fibromatosis Colli
Search Results. 500 results found. Showing 1-25: ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code J15.5 [convert to ICD-9-CM] Pneumonia due to Escherichia coli. Bronchopneumonia due to escherichia coli; E coli bronchopneumonia; E coli pneumonia. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code M72.2 [convert to ICD-9-CM] Plantar fascial fibromatosis. Bilateral plantar fasciitis; Fibromatosis.

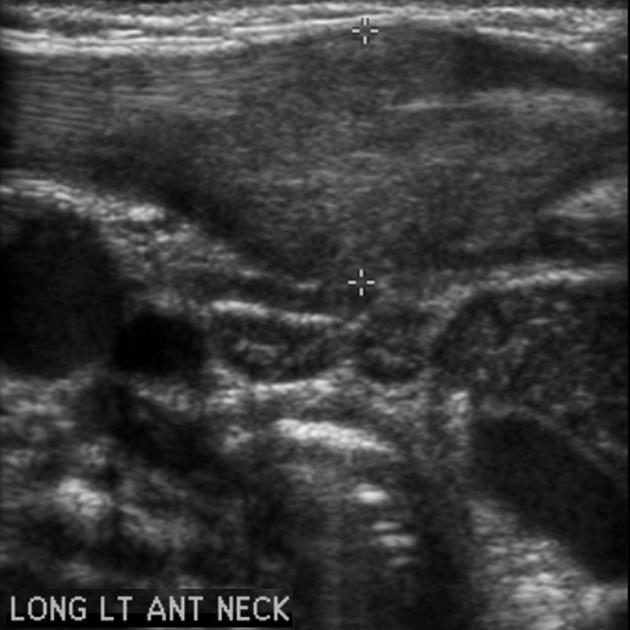
Fibromatosis colli pacs
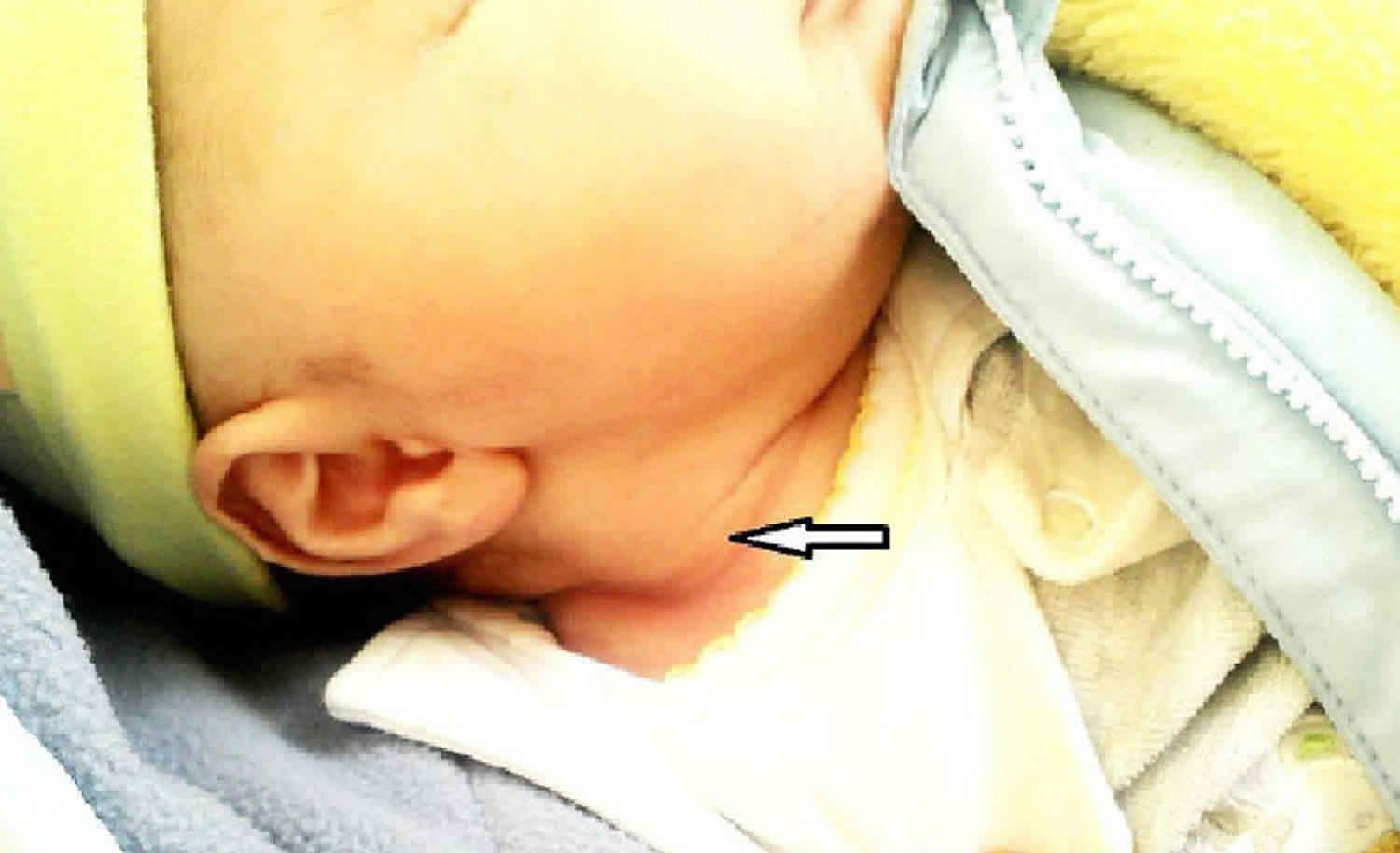
A sternocleidomastoid tumor of infancy, also known as fibromatosis colli of infancy, is a rare benign mass in the muscle on the side of the neck. The tumor is usually on the right side, and is firm, measuring a couple centimeters in diameter. It appears in a newborn, usually between the second and fourth weeks of life.
Fibromatosis colli, causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment & prognosis
Q68.0 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2024 edition of ICD-10-CM Q68.0 became effective on October 1, 2023. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of Q68.0 - other international versions of ICD-10 Q68.0 may differ. Applicable To.

Fibromatosis colli leading to positional plagiocephaly with gross anatomical and sonographic
ICD-10-CM D48.1 is a new 2024 ICD-10-CM code that became effective on October 1, 2023. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of D48.1 - other international versions of ICD-10 D48.1 may differ. Applicable To

Sternocleidomastoid tumour in neonate fibromatosis colli BMJ Case Reports
Fibromatosis Colli is a rare condition, with a prevalence estimated at 0.4%. It is categorized as a benign fibroblastic proliferation of the sternocleidomastoid muscle [1] . Newborns are usually normal at birth and present with a unilateral neck mass associated to restricted motion, occurring two to four weeks after birth.

Fibromatosis colli leading to positional plagiocephaly with gross anatomical and sonographic
Case Discussion Fibromatosis colli is also called congenital muscular torticollis, sternocleidomastoid tumor, or pseudotumor of infancy. It is due to the benign fibroblastic proliferation of the affected sternocleidomastoid muscle. The exact pathogenesis is unclear, however, there is an association between fibromatosis colli and birth injury during breech delivery, instrumental delivery, and.