Inferior vena cava anatomy, function, filter & inferior vena cava syndrome
Function Clinical Significance The inferior vena cava (also known as IVC or the posterior vena cava) is a large vein that carries blood from the torso and lower body to the right side of the heart. From there the blood is pumped to the lungs to get oxygen before going to the left side of the heart to be pumped back out to the body.
O que é a veia cava inferior?
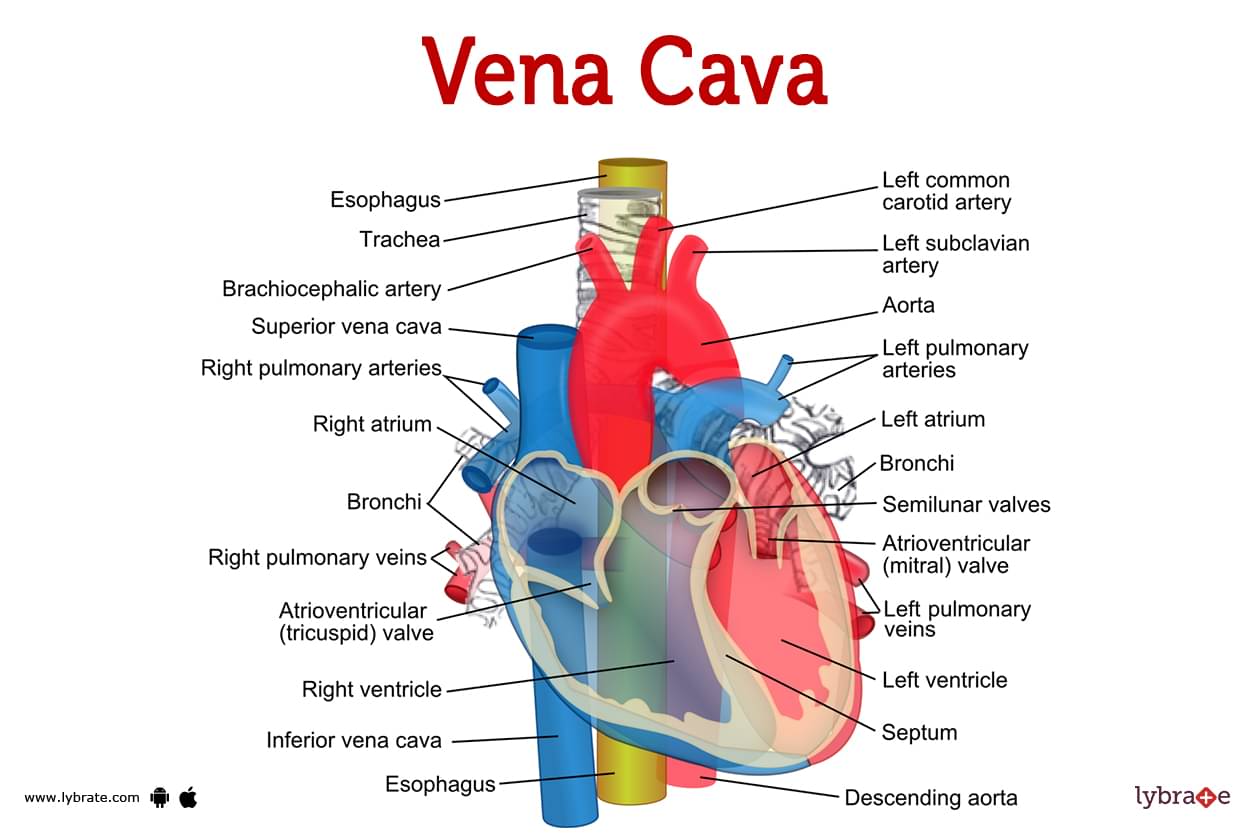
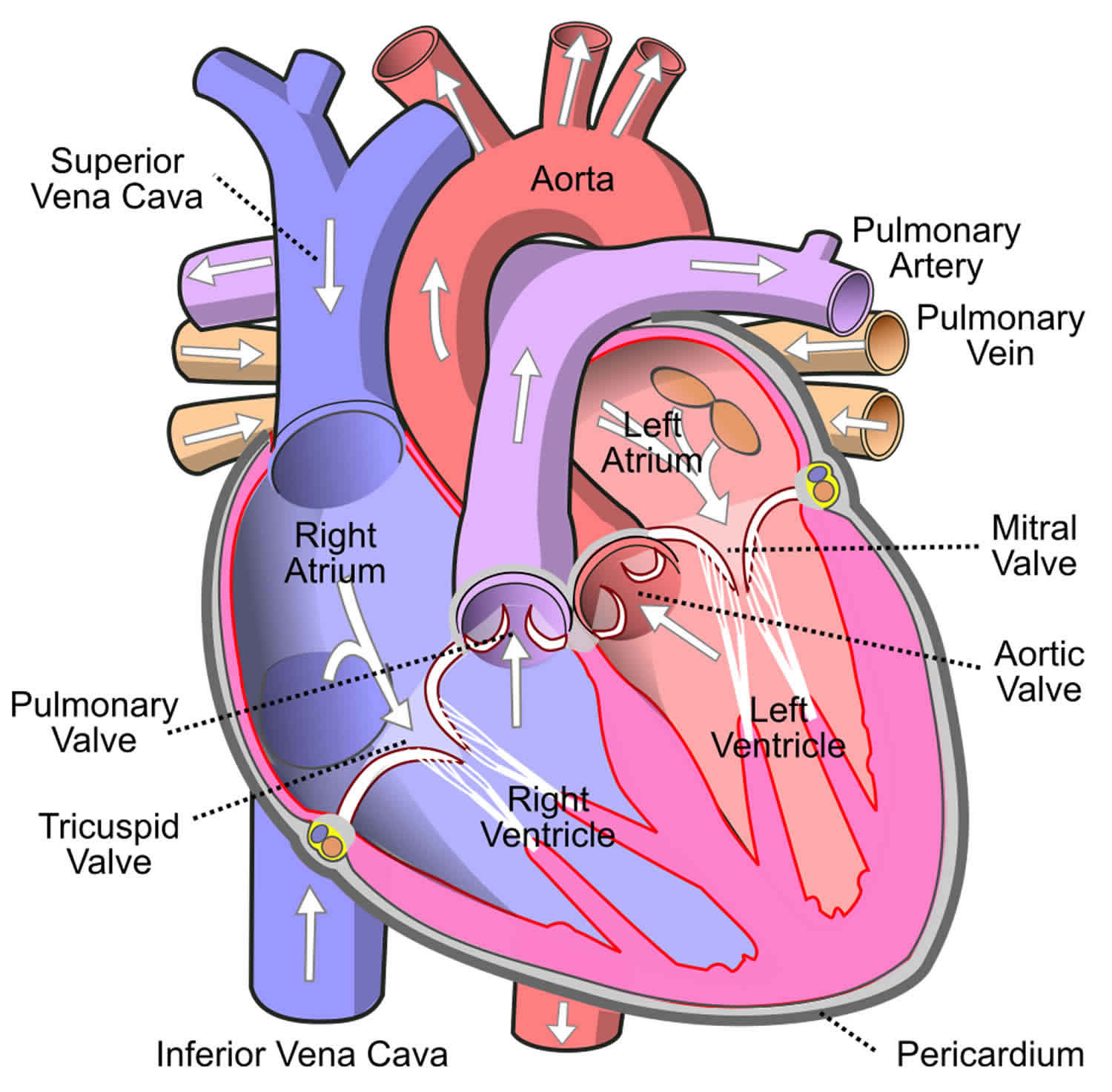
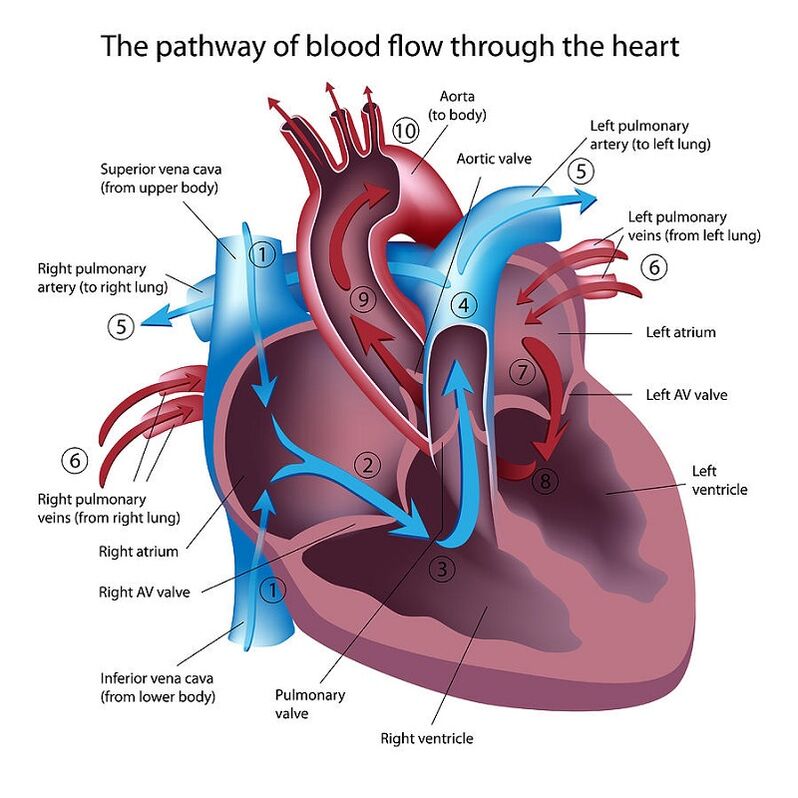
Your superior vena cava and inferior vena cava have the important function of carrying oxygen-poor blood to your heart's right atrium, where it moves into your right ventricle and then to your lungs (through your pulmonary artery) to trade in carbon dioxide for oxygen.
Vena cava (Human Anatomy) Image, Functions, Diseases and Treatments
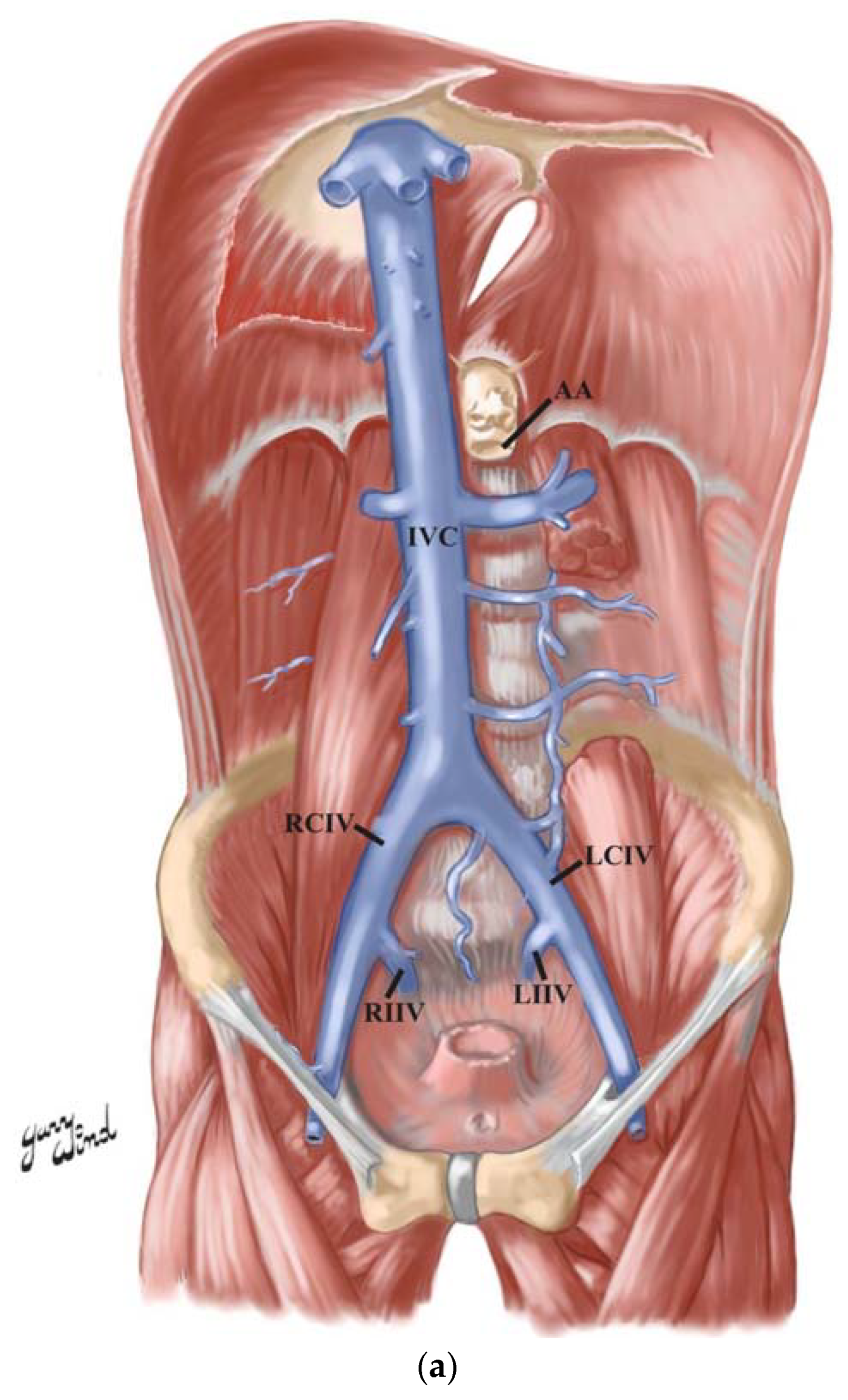
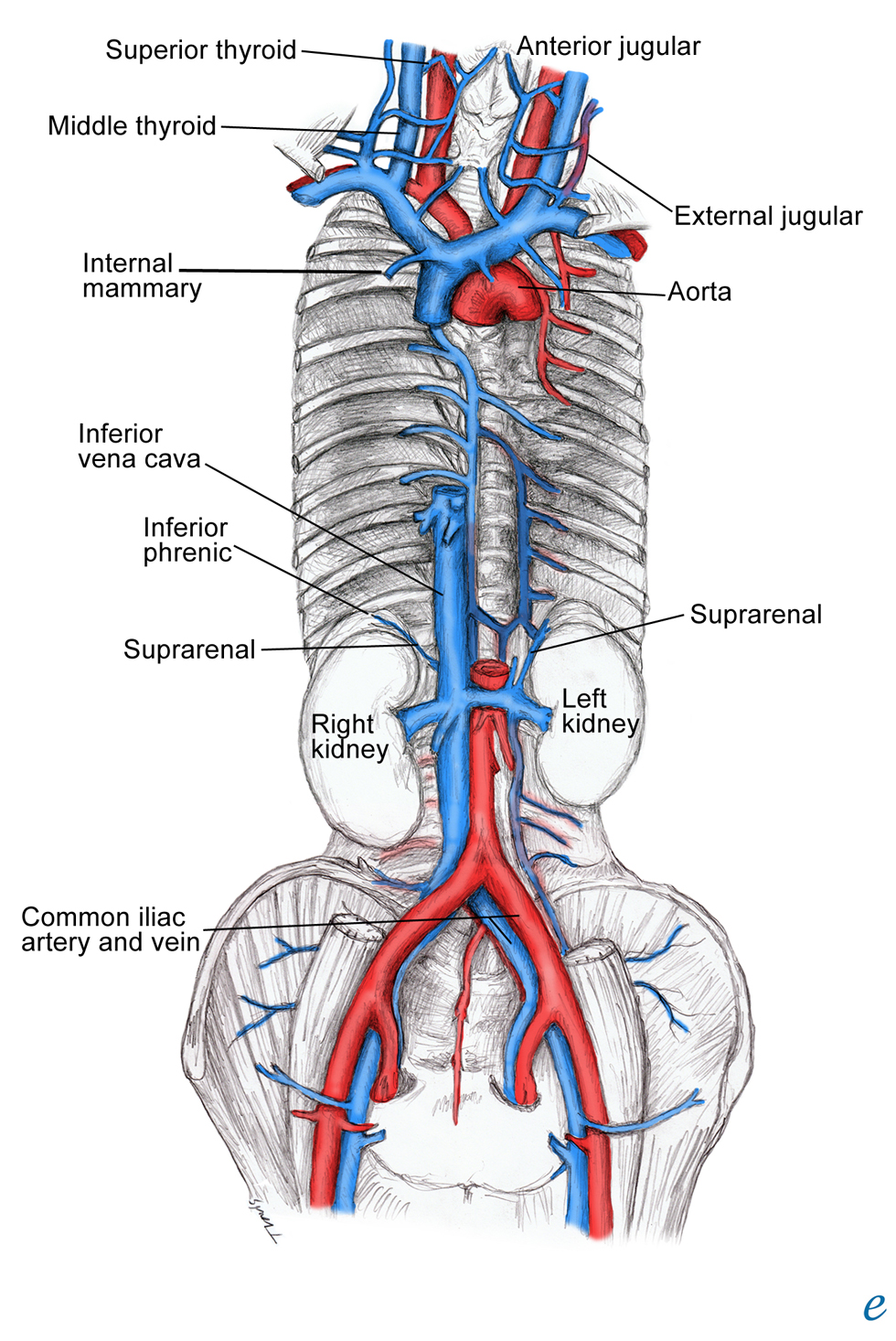
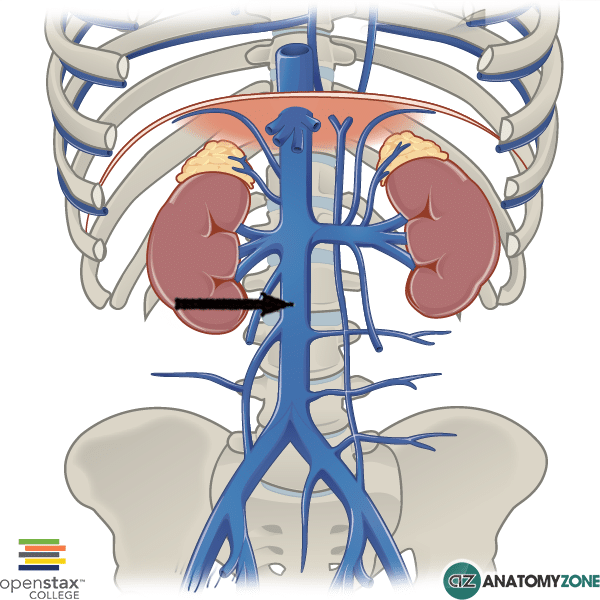
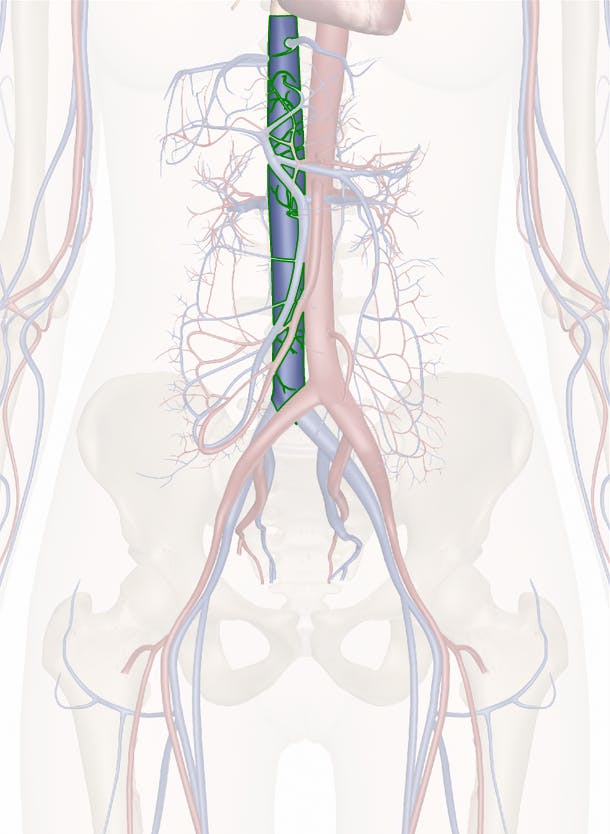
The inferior vena cava is the result of two major leg veins coming together. These leg veins are called iliac veins. The iliac veins come together at the small of the back, at the fifth lumbar.
Anatomia Free FullText Duplicated Inferior Vena Cava in a 69YearOld White Female Donor
The superior vena cava is located in the upper chest region and is formed by the joining of the brachiocephalic veins. These veins drain blood from the upper body regions including the head, neck, and chest. It is bordered by heart structures such as the aorta and pulmonary artery. The inferior vena cava is formed by the joining of the common.
inferior vena cava location
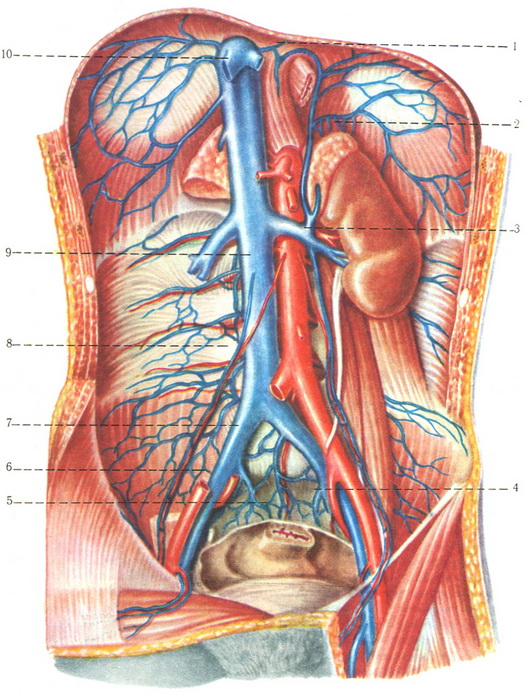
The inferior vena cava (IVC) is a large retroperitoneal vessel formed by the confluence of the right and left common iliac veins. Anatomically this usually occurs at the L5 vertebral level. The IVC lies along the right anterolateral aspect of the vertebral column and passes through the central tendon of the diaphragm around the T8 vertebral level. The IVC is a large blood vessel responsible.

Inferior Vena Cava M1 Duodenum, Pancreas and Abdominal Aorta YouTube
The inferior vena cava (IVC) is the largest vein in the body, draining blood from the abdomen, pelvis and lower extremities. This pictorial review summarises normal anatomy and embryological development of the IVC. In addition, we highlight a wide range of anatomical variants, acquired pathologies and a common pitfall in imaging of the IVC..
Inferior vena cava Anatomy, Branches & Function Human Anatomy Kenhub YouTube
The anterior vena cava, also known as the precava, drains the head end of the body, while the posterior vena cava, or postcava, drains the tail, or rear, end. In humans these veins are respectively called the superior and inferior venae cavae. Whereas many mammals, including humans, have only one anterior vena cava, other animals have two.
inferior vena cava agenesis
The IVC's function is to carry the venous blood from the lower limbs and abdominopelvic region to the heart . The inferior vena cava anatomy is essential due to the vein's great drainage area, which also makes it a hot topic for anatomy exams. For that reason, this page will cover the IVC anatomy in a way that's easy to read and understand.
Inferior Vena Cava AnatomyZone
From its origin, the inferior vena cava travels superiorly along the right side of the anterior aspect of the lower lumbar vertebrae, their associated intervertebral discs and the anterior longitudinal ligament. Along its course, it travels: - anterior to the right crus of the diaphragm and right renal artery; - posterior to the pancreas.

Sistema de la vena Cava Inferior, Nombre NOEMY KARLA FERNANDEZ PATON
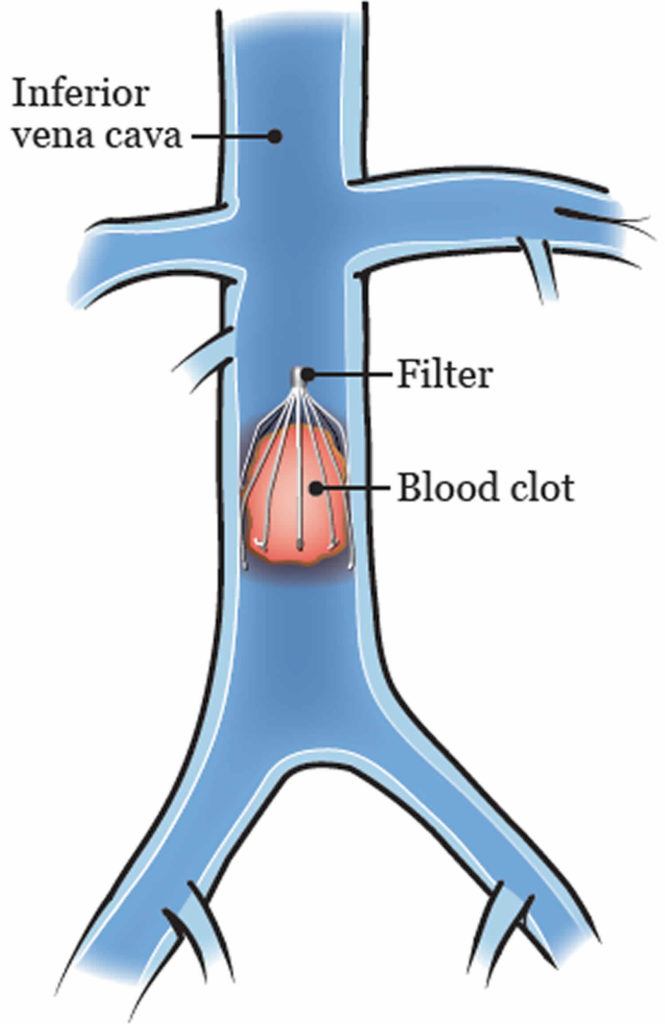
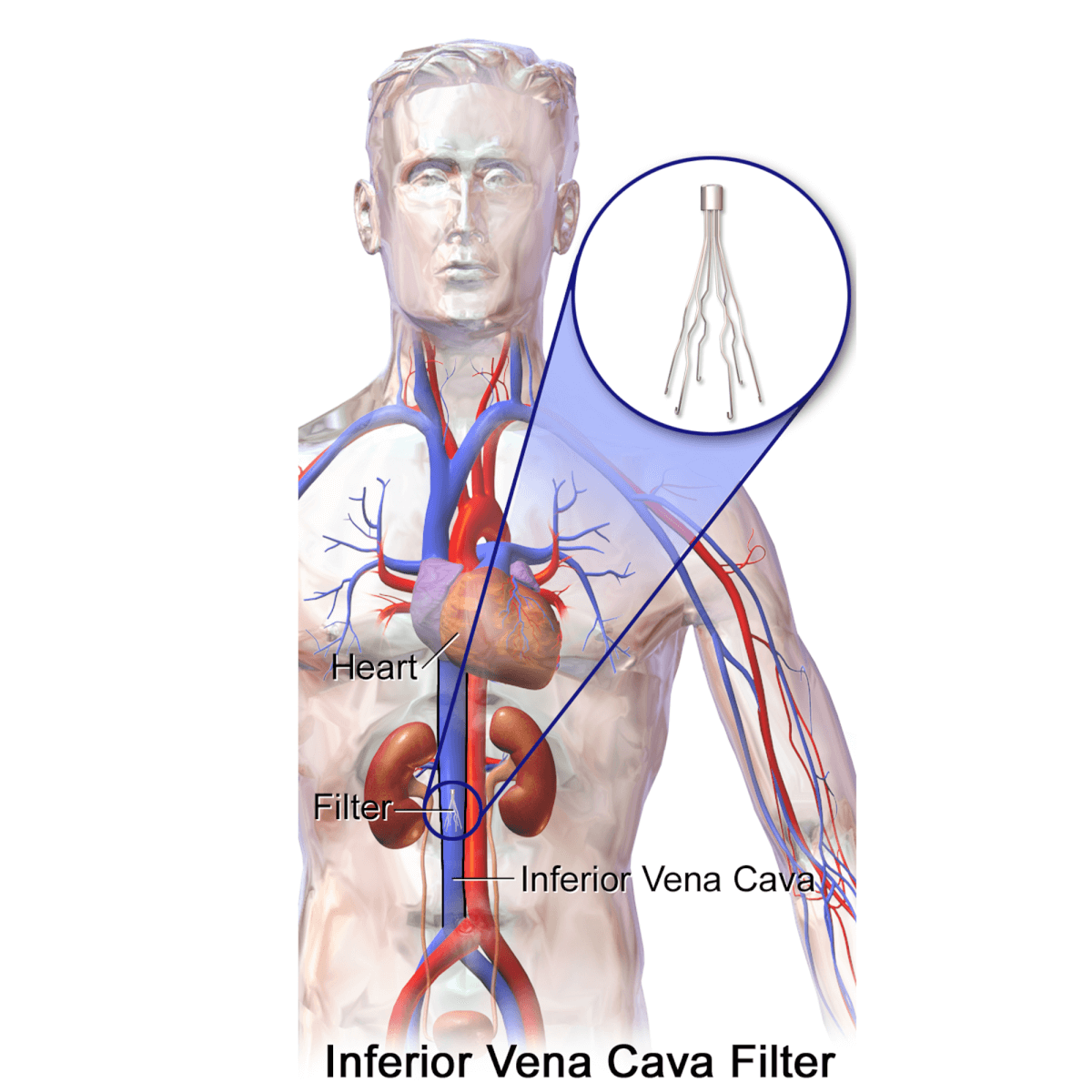
This study proposes a novel inferior vena cava filter (IVCF) design, "Lotus," aiming to enhance release stability and endothelialization. A catheter-filter-vessel model was established for IVCF property analysis, validated by comparing numerical simulations and in vitro tests. Lotus's mechanical properties were analyzed, and optimization.

INFERIOR VENA CAVA Anatomy and Function YouTube
Fungsi Vena Cava dan Anatominya Baca berita tanpa iklan. Gabung Kompas.com+ Hitung Cepat Pemilihan Presiden 2024 Update Terakhir: 17 Februari 2024, 12:14 WIB Suara Masuk: 99.80% 0 0 0 Hasil hitung cepat bukanlah hasil resmi pemilu. Hasil resmi tetap menunggu perhitungan suara secara manual oleh KPU. Lihat Lembaga Survey Lainnya
Inferior vena cava anatomy, function, filter & inferior vena cava syndrome
A vena cava (plural: venae cavae) is a large vein that carries blood to the heart. You have two venae cavae: the superior vena cava and the inferior vena cava. Together, these large.
The Inferior Vena Cava Anatomy and 3D Illustrations
The inferior vena cava is a large vein that carries the deoxygenated blood from the lower and middle body into the right atrium of the heart.It is formed by the joining of the right and the left common iliac veins, usually at the level of the fifth lumbar vertebra.. The inferior vena cava is the lower ("inferior") of the two venae cavae, the two large veins that carry deoxygenated blood from.
Vena Cava Physiopedia
Fungsi Vena Cava Inferior Fungsi utama dari IVC adalah untuk mengangkut darah terdeoksigenasi yang telah beredar melalui bagian bawah tubuh kembali ke atrium kanan jantung. IVC bertanggung jawab untuk memindahkan semua darah di bawah diafragma, sedangkan vena pengganti menangani darah di atas diafragma. Signifikansi Klinis Vena Cava Inferior

Difference Between Superior and Inferior Vena Cava
The inferior vena cava, the largest vein in the human body, transports blood from the lower limbs, most of the back, the abdominopelvic viscera and the abdominal walls to the right atrium.It is formed by the union of the common iliac veins at the level of the body of L5. During its course, it receives many veins referred to as tributaries of the inferior vena cava.

Inferior Vena Cava Overview,Structure & Clinical Significance » How To Relief
The inferior vena cava (IVC) is the largest venous conduit below the diaphragm. Although this structure is often overlooked both clinically and radiographically, it can be involved in many different pathologic processes. A thorough understanding of the IVC will assist the radiologist in recognizing anatomic variants, identifying abnormalities, and providing accurate differential diagnoses. In.