
Glasgow Coma Scale Poster PDF
The Glasgow Coma Scale was first published in 1974 at the University of Glasgow by neurosurgery professors Graham Teasdale and Bryan Jennett.[1] The Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) is used to objectively describe the extent of impaired consciousness in all types of acute medical and trauma patients. The scale assesses patients according to three aspects of responsiveness: eye-opening, motor, and.
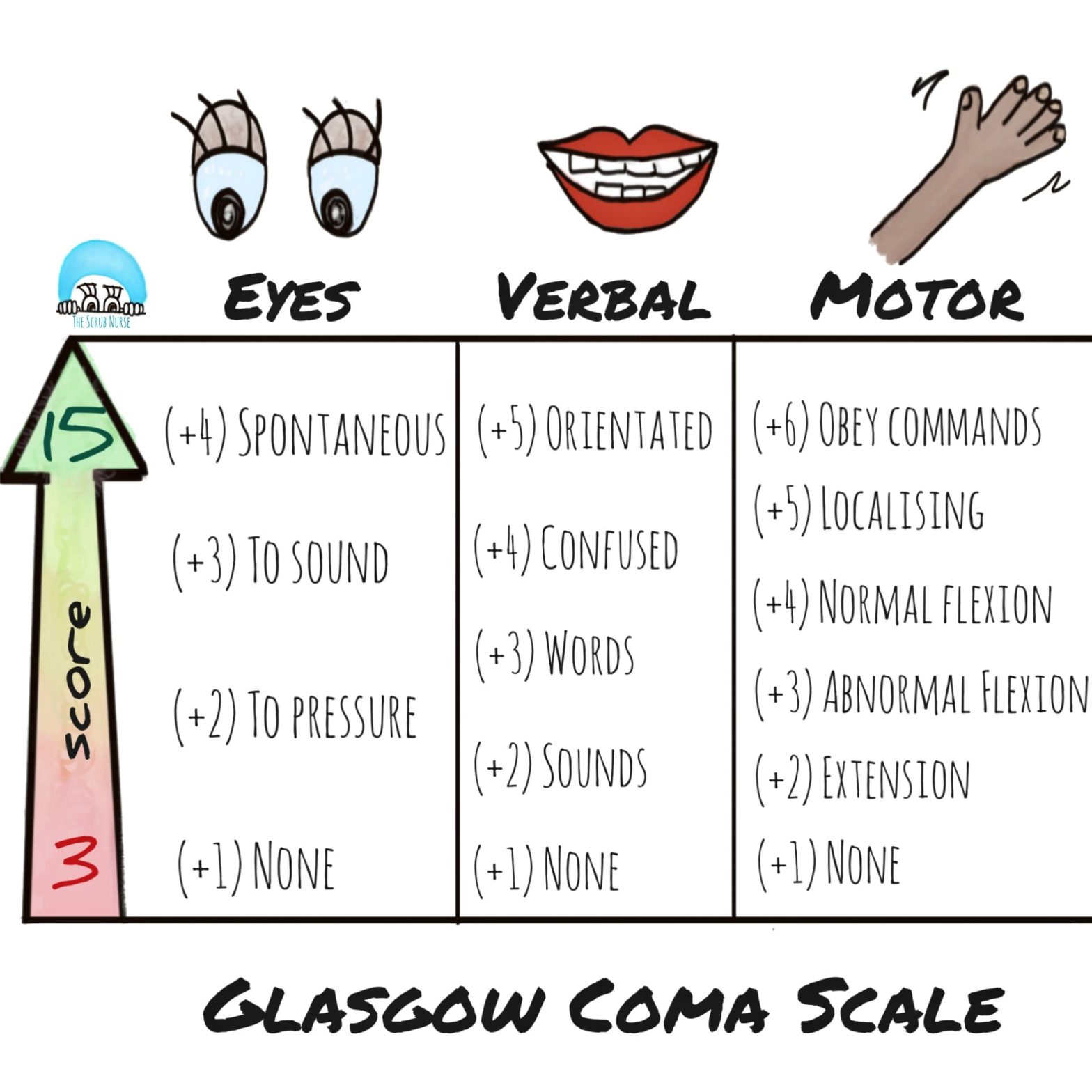
What is the Glasgow coma scale? The Scrub Nurse
Last modified: Oct 4, 2022. Synonyms: CRPS, Sudeck's atrophy, Reflex sympathetic dystrophy, RSD, Causalgia. Chronic regional pain syndrome (CRPS) is a persistent neuropathic pain syndrome of an inappropriate intensity due to sustained sympathetic activity with the absence of impending or ongoing tissue damage. There are 2 types of CRPS:
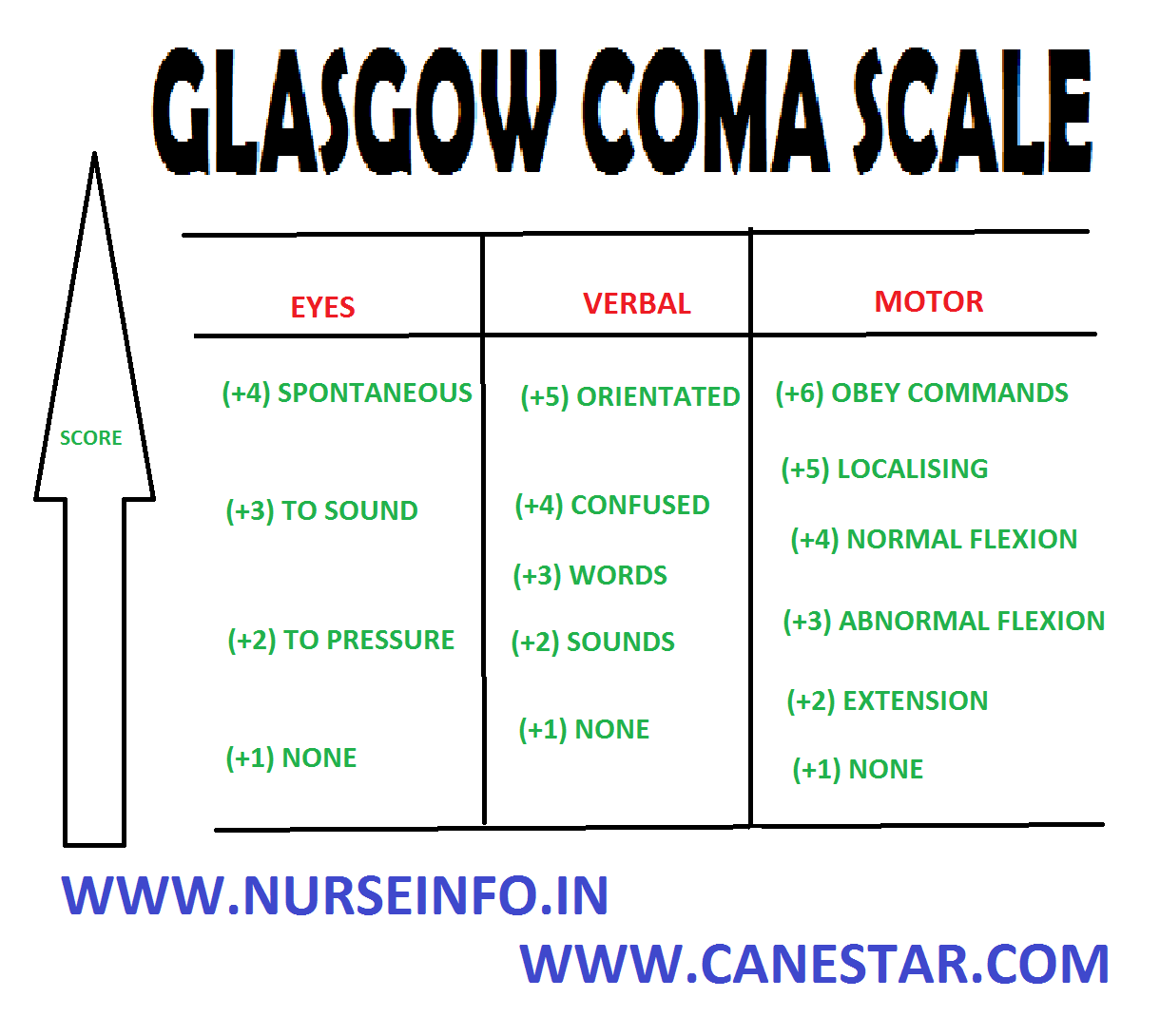
GLASGOW COMA SCALE Nurse Info
Nilai GCS yang tertinggi atau GCS normal adalah 15 yaitu E 4 V 5 M 6 , sedangkan yang terendah adalah 3 yaitu E 1 V 1 M 1. Berikut beberapa penilaian GCS dan interpretasinya terhadap tingkat kesadaran : Nilai GCS (15-14) : Composmentis. Nilai GCS (13-12) : Apatis. Nilai GCS (11-10) : Delirium.

Figure 1 from Improving Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) Competency of Nurses in One Acute Stroke Unit
The Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS), designed in 1974, is a tool that has the ability to communicate the level of consciousness of patients with acute or traumatic brain injury. Developed by Graham Teasdale and Bryan J. Jennett, professors of neurosurgery at the University of Glasgow's Institute of Neurological Sciences, this scale is the gold.

The Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) for first aiders First Aid for Free
Motor response (M) A maximum possible score of 6 points. The final part of the GCS assessment involves assessing a patient's motor response.. You should score the patient based on the highest scoring response you were able to elicit in any single limb (e.g. if they were unable to move their right arm, but able to obey commands with their left arm, they'd receive a score of 6 points).

How to calculate a Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) score First Aid for Free
The Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) was first created by Graham Teasdale and Bryan Jennett in 1974. It is a clinical scale to assess a patient's "depth and duration of impaired consciousness and coma" following an acute brain injury.. Healthcare practitioners can monitor the motor responsiveness, verbal performance, and eye-opening of the patient in the form of a simple chart.

INFO KESEHATAN GCS (GLASGOW COMA SCALE)
The Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) is a system to "score" or measure how conscious you are. It does that by giving numbered scores for how awake you are, your level of awareness and how you respond to basic instructions. Experts at the University of Glasgow in Scotland developed the GCS in 1974. Despite " coma " being part of the name, the.
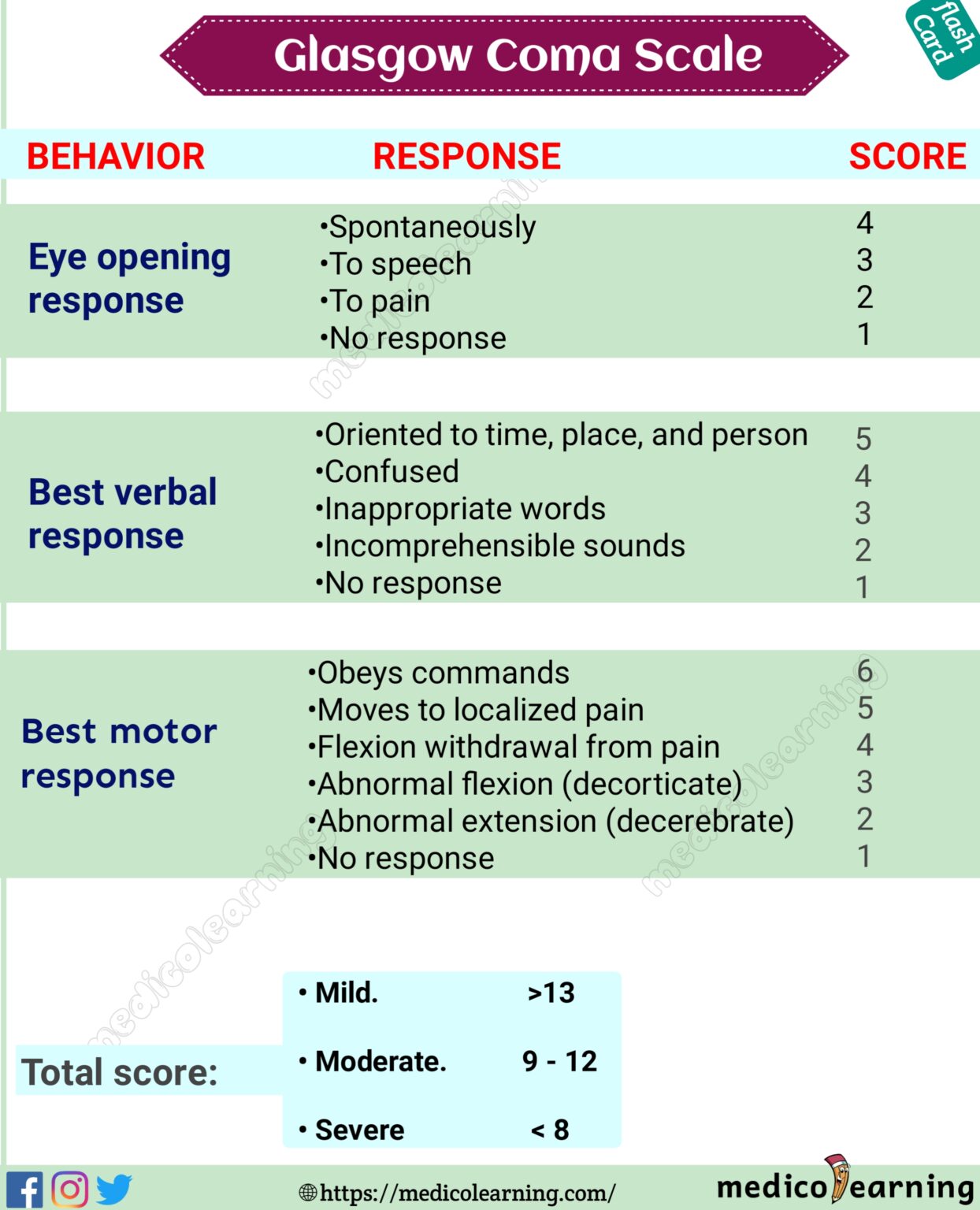
Glasgow Coma Scale MedicoLearning
The Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) score is the primary method of assessing consciousness after traumatic brain injury (TBI), and the clinical standard for classifying TBI severity. There is scant literature discerning the influence of circadian rhythms or emergency department (ED) arrival hour on this important clinical tool.
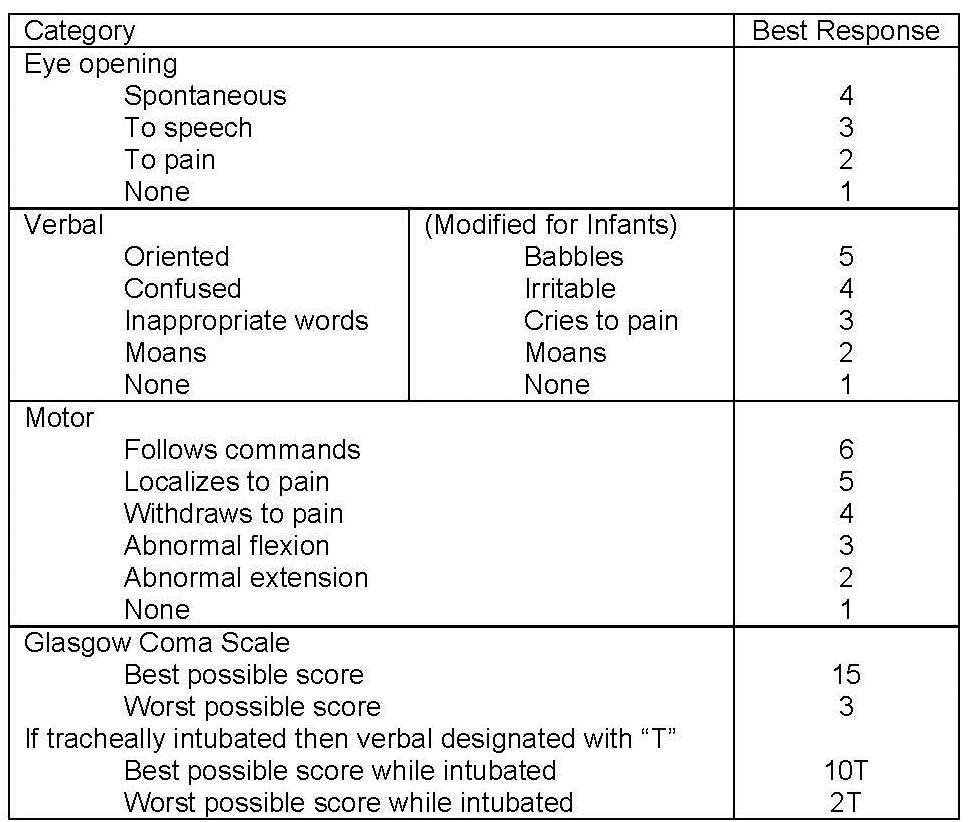
Printable Glasgow Coma Score
The Glasgow coma scale (GCS) is a tool used to assess and calculate a patient's level of consciousness. It was developed more than 40 years ago by two neurosurgeons in Glasgow and is widely applied today.1 The GCS uses a triple criteria scoring system: best eye opening (maximum 4 points), best verbal response (maximum 5 points), and best motor response (maximum 6 points). These scores are.

Easy Way To Learn Glasgow Coma Scale How To Learn Glasgow Coma Scale Glasgow Coma Scale
The same GCS score will predict different TBI mortality depending on the components — GCS of 4 with the components 1+1+2 (E+V+M) predicts a mortality rate of 48%. Baltussen A, Walder B. The use of Glasgow Coma Scale in injury assessment: a critical review. Brain Inj. 2009 May;23(5):371-84. PMID: 19408162. FOAM and web resources. Glasgow.

Glasgow Coma Scale Printable
First: distinguish between the use of the Scale and its derived total or sum Score. The purpose of the Scale is to describe and communicate the condition of an individual patient by separate, multidimensional rating of their eye, verbal and motor responses. It remains the appropriate method for this purpose.
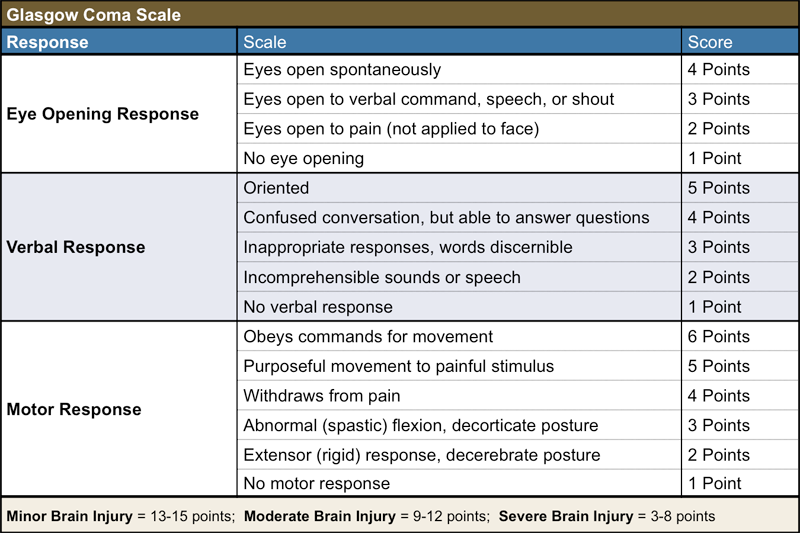
The Glasgow Coma Scale A guide to Neurological Functioning — Firstclass
An example of such a scale is the Glasgow Coma Scale . In this scale the normal state merits a score of 15, and as level of consciousness deteriorates, the score becomes less. Table 57.2. Glasgow Coma Scale. Technique. The technique of evaluation of the patient with an altered level of consciousness can be divided into three phases..

GLASGOW COMA SCALE(GCS) Neurological Examination, Raju Sir, Nursing Arena YouTube
From the results of the study, the p value was 0.00, subjects with GCS score somnolence (12-14) had six times higher risk in mortality (P = 0.02, RR = 6.38) and subjects with GCS score sopor and.
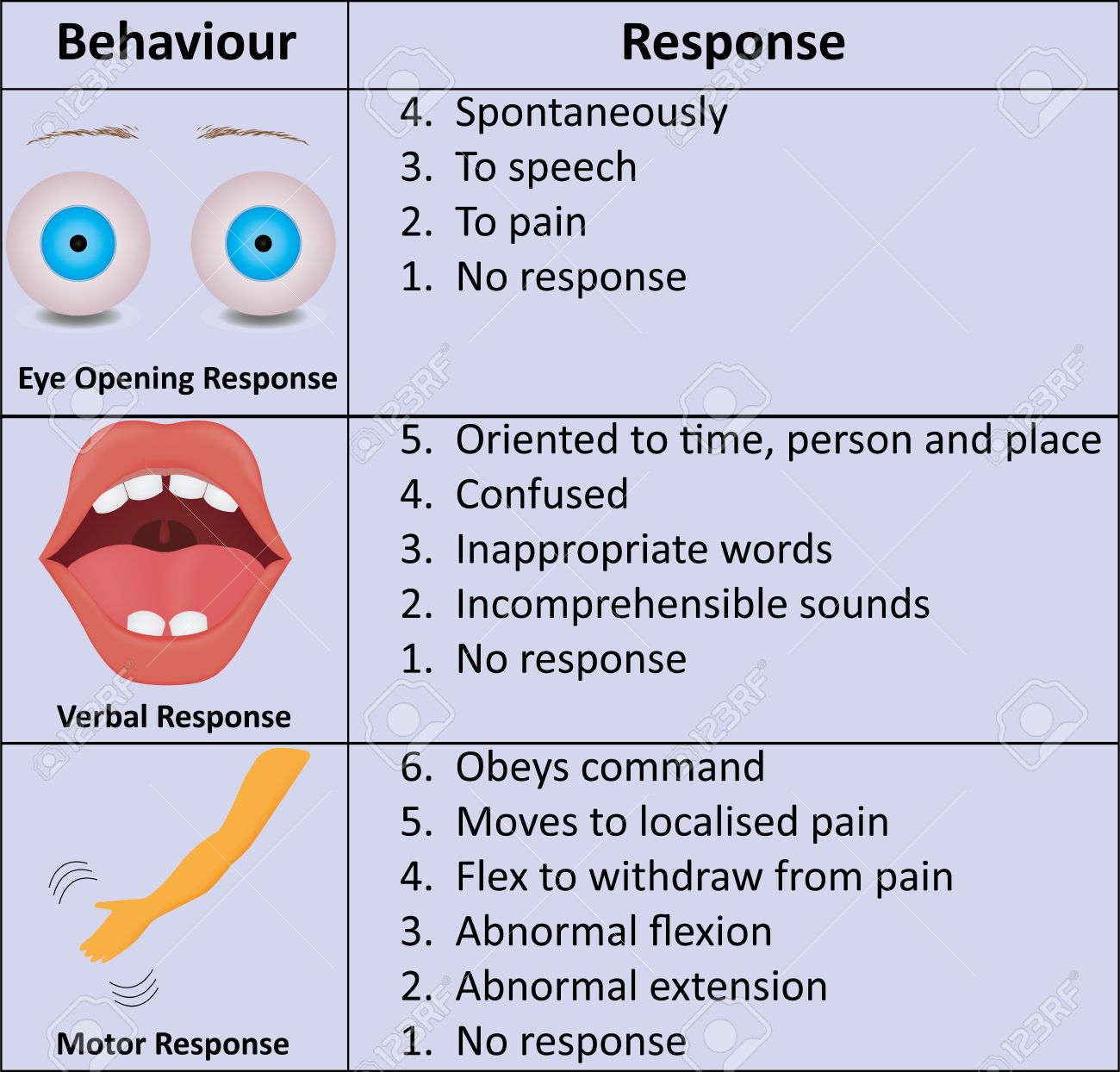
Updated Glasgow Coma Scale Brain Injury Is Big
Glasgow Coma Scale atau GCS adalah skala neurologi untuk penilaian tingkat kesadaran. Ketahui cara mengukur CGS dan nilai CGS normal pada dewasa dan anak!. Nilai GCS adalah 11-10. Somnolen adalah kondisi mengantuk yang cukup dalam namun masih bisa dibangunkan dengan menggunakan rangsangan. Ketika rangsangan tersebut berhenti, maka pasien.

Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS Score) Explained YouTube
The Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) is a clinical scale used to reliably measure a person's level of consciousness after a brain injury.. These three behaviours make up the three elements of the scale: eye, verbal, and motor. A person's GCS score can range from 3 (completely unresponsive) to 15 (responsive).

Glasgow Coma Scale jaselasyn
Complex Regional Pain Syndrome, also known as reflex sympathetic dystrophy, is an idiopathic condition caused by an aberrant inflammatory response that leads to sustained sympathetic activity in a perpetuated reflex arc. Patients present with extremity pain out of proportion to physical exam findings. Diagnosis is made clinically with the.