
(3) Indifference Curve Economic Theories Microeconomics
The slope of an indifference curve is the negative of the ratio of the marginal utility of X over the marginal utility of Y. To see this, imagine that the quantities of X and Y change by small amounts. The change in utility specified in Equation 1 can then be expressed mathematically as. 3. dU = ∂U (X , Y)/∂X dX + ∂U (X , Y)/∂Y dY = ∂.

8 Properties of Indifference Curve with Diagram and Examples
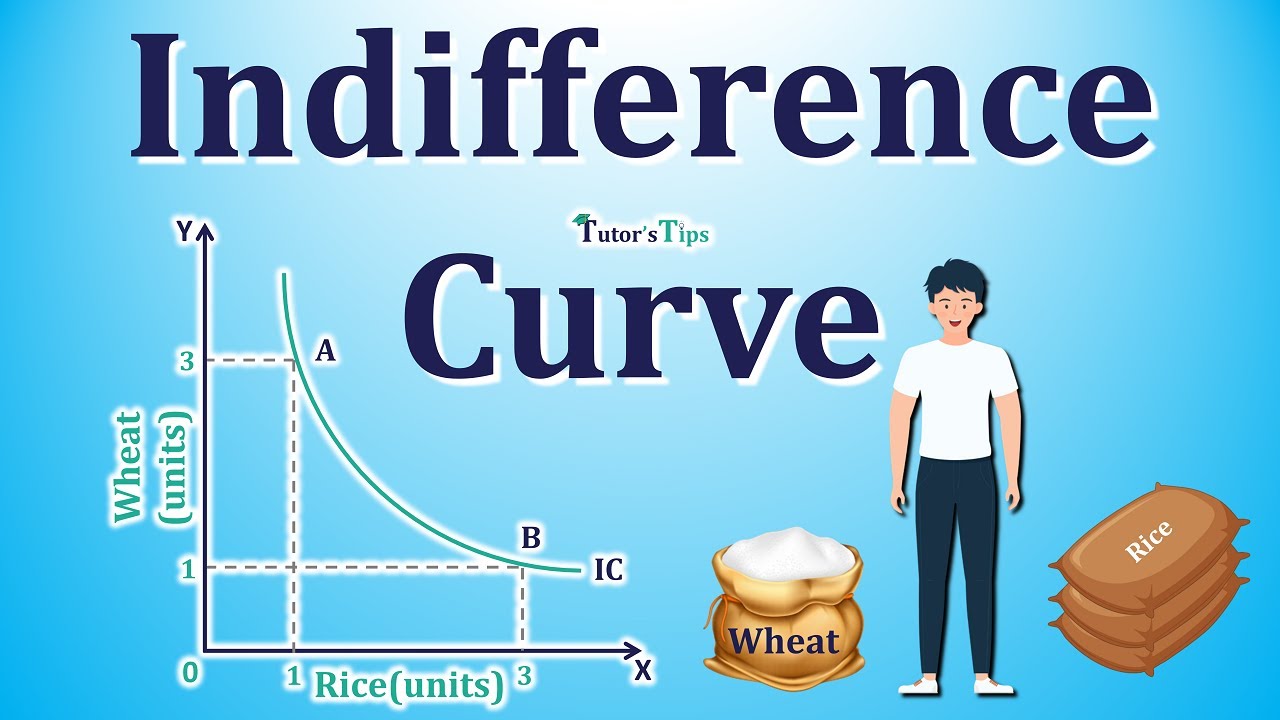
Indifference Curve: An indifference curve represents a series of combinations between two different economic goods, between which an individual would be theoretically indifferent regardless of.
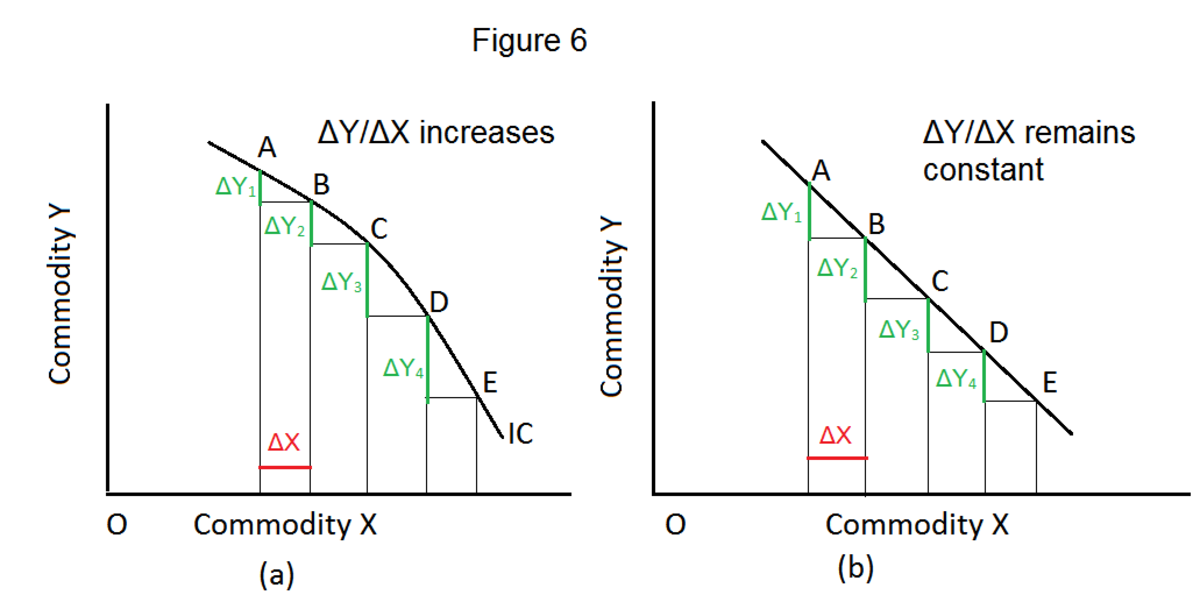
What Are the Properties of the Indifference Curves? Owlcation
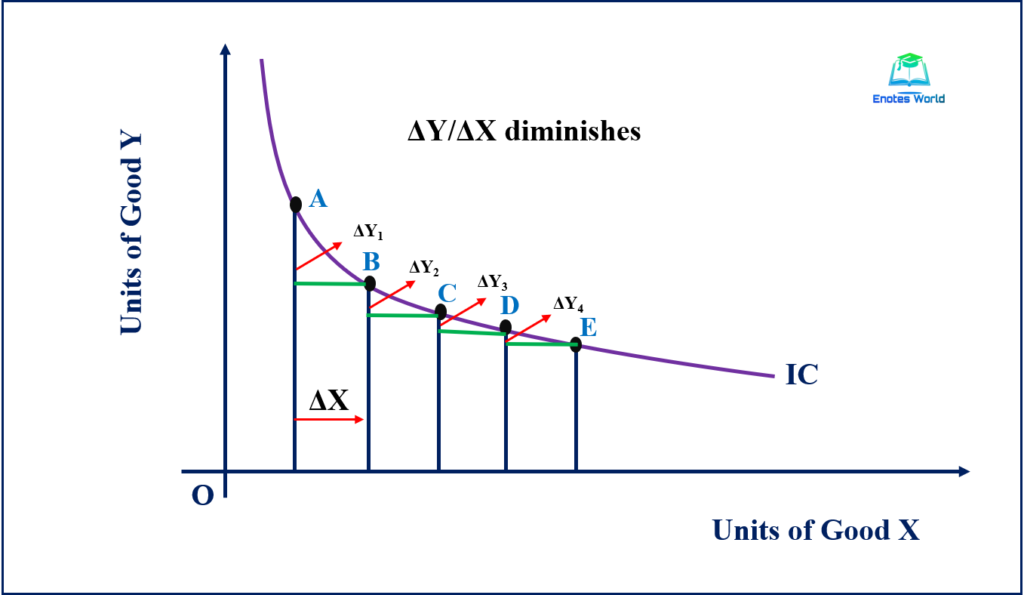
The Marginal Rate of Substitution is the amount of of a good that has to be given up to obtain an additional unit of another good while keeping the satisfaction the same. As some amount of a good has to be sacrificed for an additional unit of another good it is the Opportunity Cost. The MRS is basically a way of mathematically representing the.

Indifference Curve Meaning and Properties Tutor's Tips
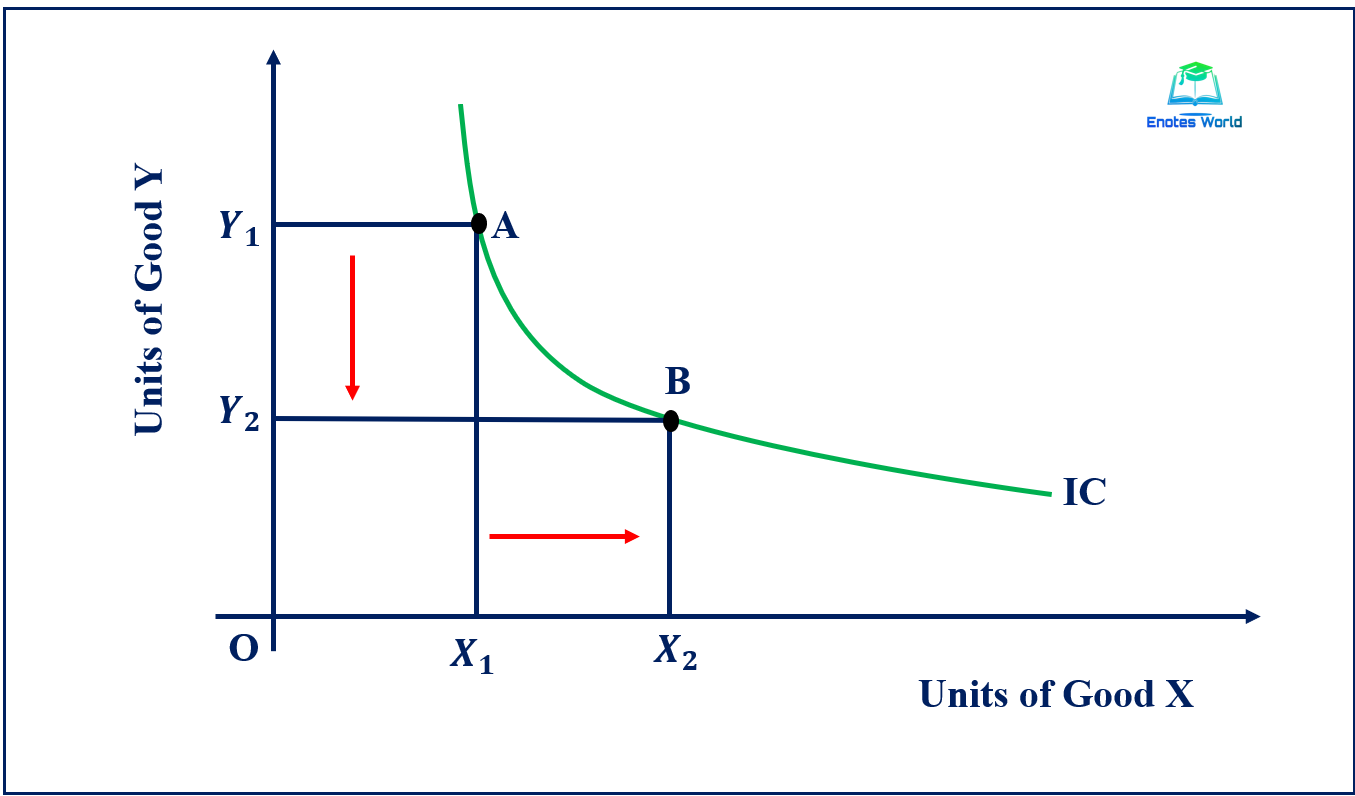
The indifference curve shows that she could obtain the same level of utility by moving to point W, skiing for 7 days and going horseback riding for 1 day. She could also get the same level of utility at point Y, skiing just 1 day and spending 5 days horseback riding. Ms. Bain is indifferent among combinations W, X, and Y.
Indifference Curve and its properties with diagrams
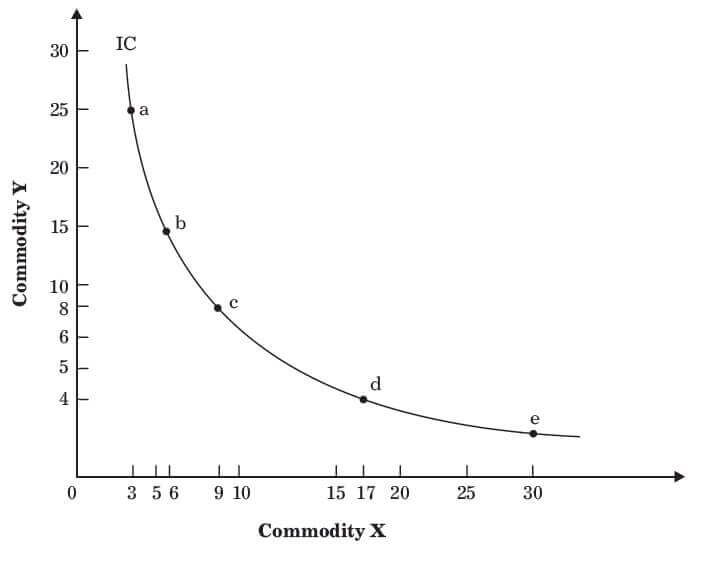
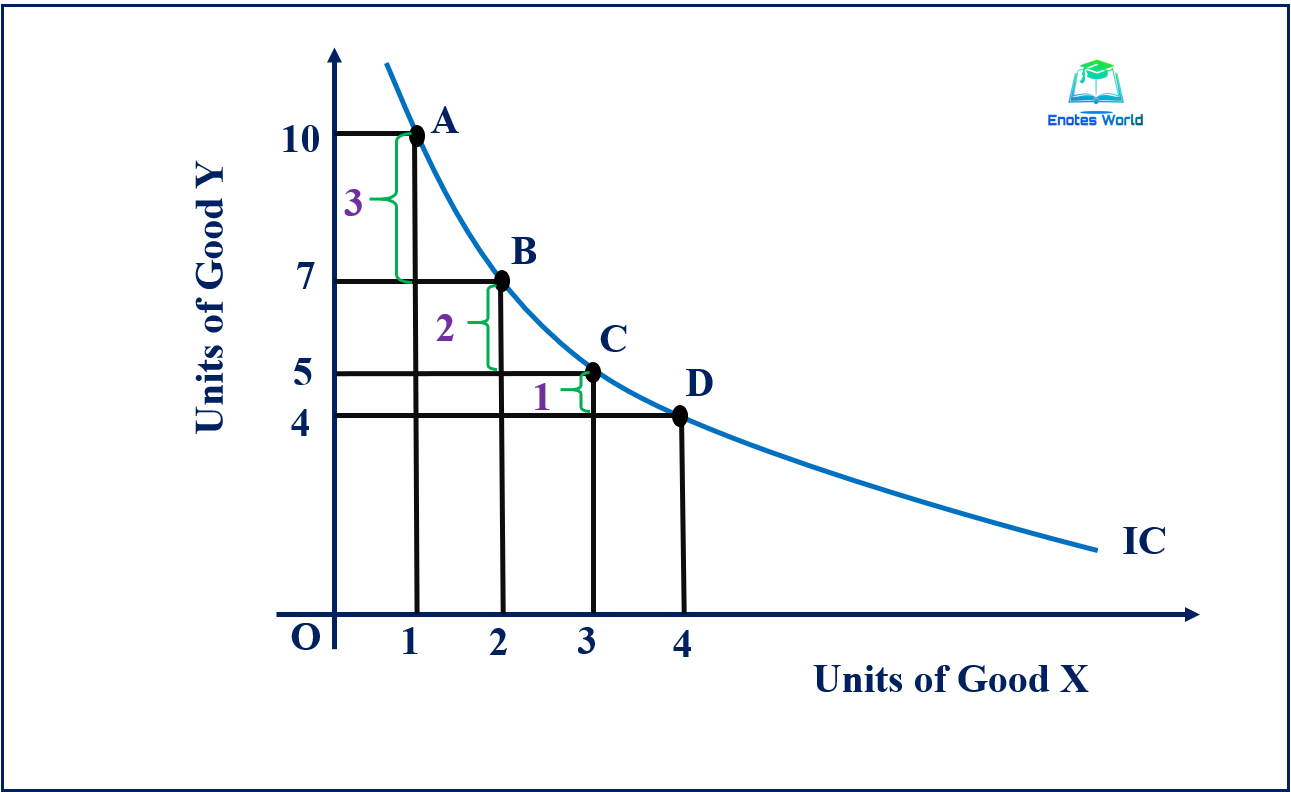
The Shape of an Indifference Curve. The indifference curve Um has four points labeled on it: A, B, C, and D. Since an indifference curve represents a set of choices that have the same level of utility, Lilly must receive an equal amount of utility, judged according to her personal preferences, from two books and 120 doughnuts (point A), from three books and 84 doughnuts (point B) from 11 books.
PPT TEORI PERILAKU KONSUMEN DAN PERMINTAAN PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6009506
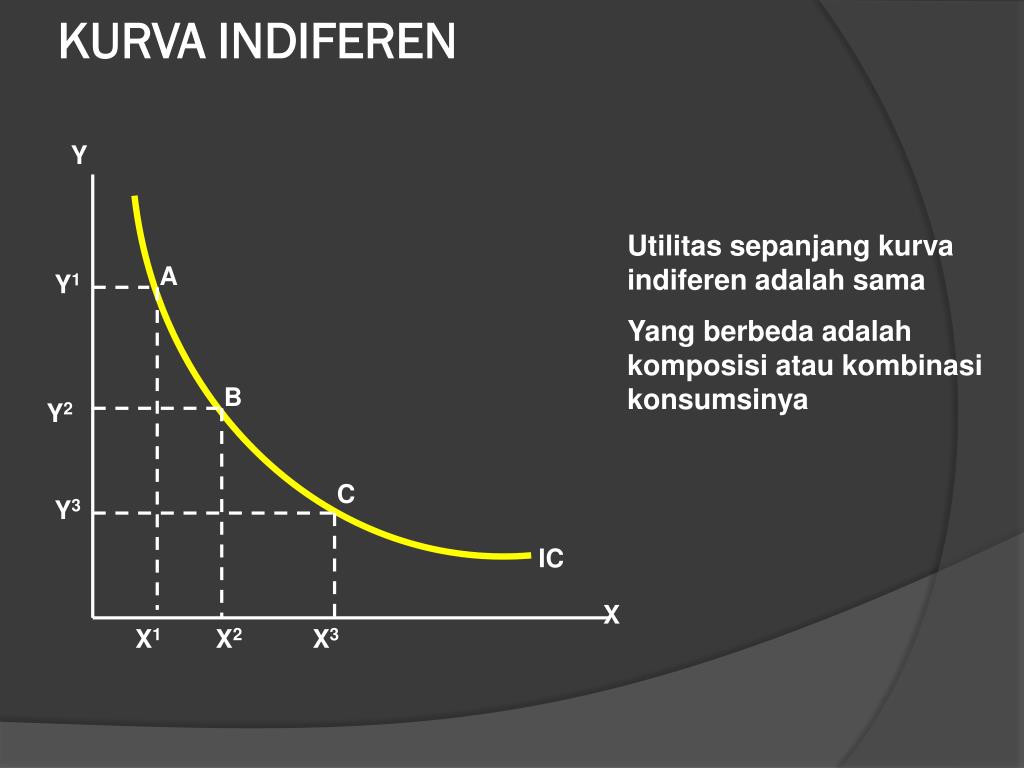
Indifference Curve (IC) adalah kurva yang menggambarkan kombinasi konsumsi dua macam barang/jasa yang menghasilkan tingkat kepuasan yang sama. Setiap titik dalam kurva ini melambangkan tingkat kepuasan yang tidak berbeda ( indifference ), meski kombinasi konsumsi barang/jasanya berbeda-beda. Indifference Curve digunakan pertama kali oleh.
What Is Indifference Curve? Properties, Assumption, Analysis
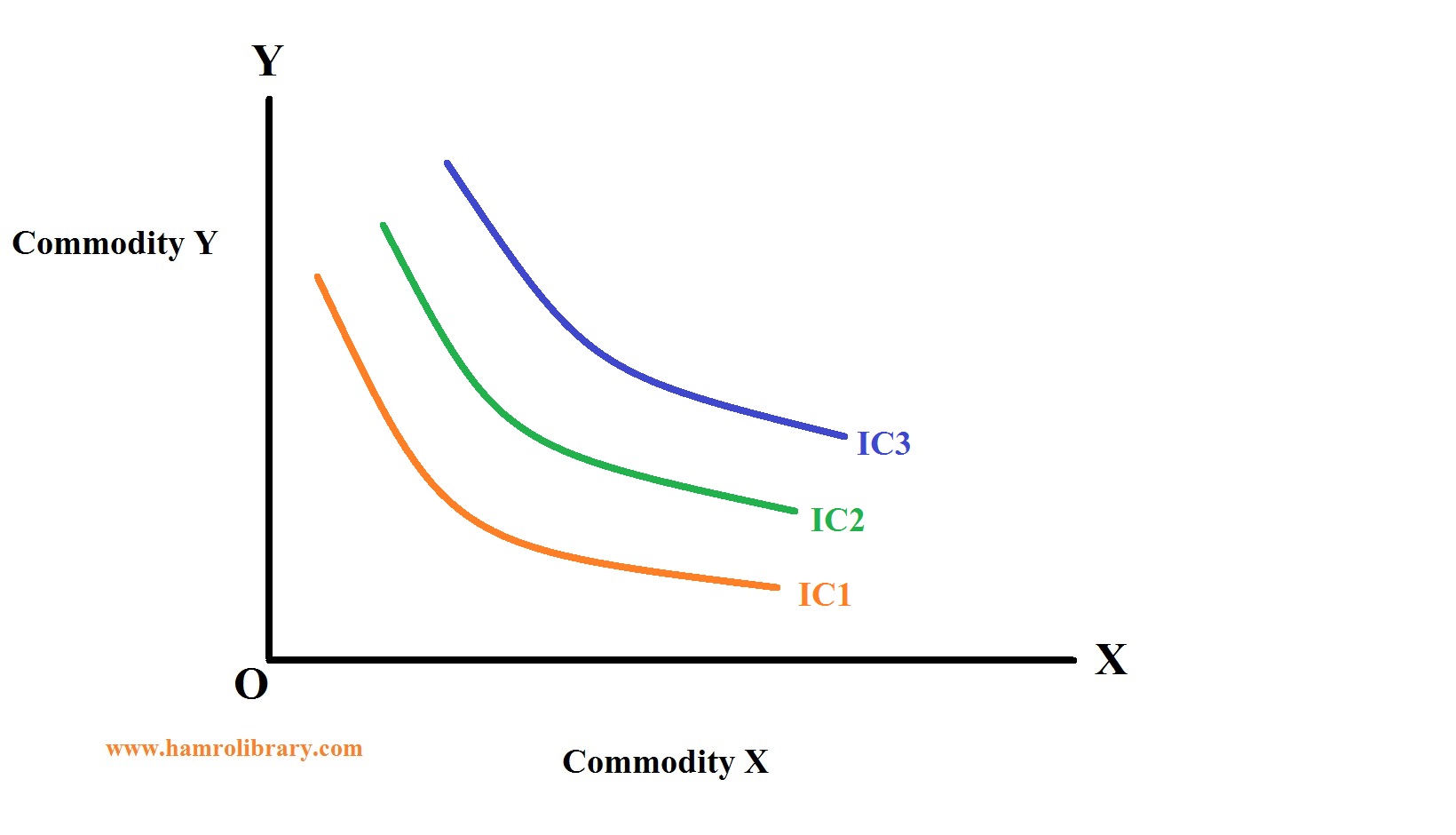
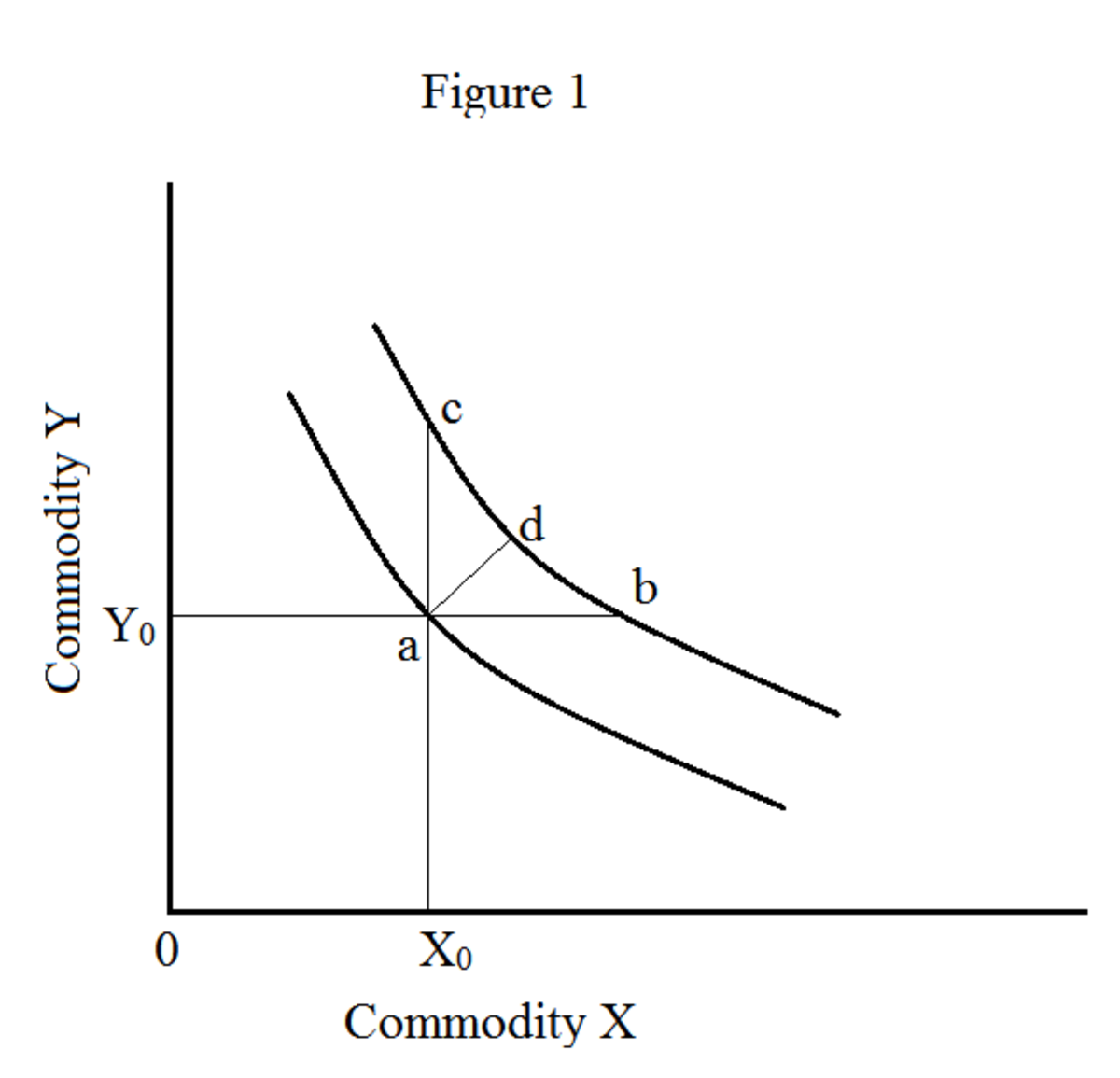
Higher indifference curves represent a greater level of utility than lower ones. In Figure 1, indifference curve Ul can be thought of as a "low" level of utility, while Um is a "medium" level of utility and Uh is a "high" level of utility. All of the choices on indifference curve Uh are preferred to all of the choices on.
Indifference Curve Meaning and Properties Explained with Animated Examples YouTube
An indifference curve is a contour line where utility remains constant across all points on the line. The four properties of indifference curves are: (1) indifference curves can never cross, (2) the farther out an indifference curve lies, the higher the utility it indicates, (3) indifference curves always slope downwards, and (4) indifference.
Assumptions and Properties of Indifference CurveMicroeconomics
Kurva indiferen adalah teori yang dibuat oleh seorang ekonom dan ahli statistic asal Irlandia bernama Francis Ysidro Edgeworth pada tahun 1881. Dilansir dari The Economic Times , kurva indiferen adalah grafik yang menunjukkan kombinasi dua barang yang memberikan kepuasan atau utilitas yang sama kepada konsumen.
Assumptions and Properties of Indifference CurveMicroeconomics
An indifference curve is a graphical representation of various combinations or consumption bundles of two commodities. It provides equivalent satisfaction and utility levels for the consumer. It makes the consumer indifferent to any of the combinations of goods shown as points on the curve. Also, it means the consumer cannot prefer one bundle.

Indifference Curve and its properties with diagrams
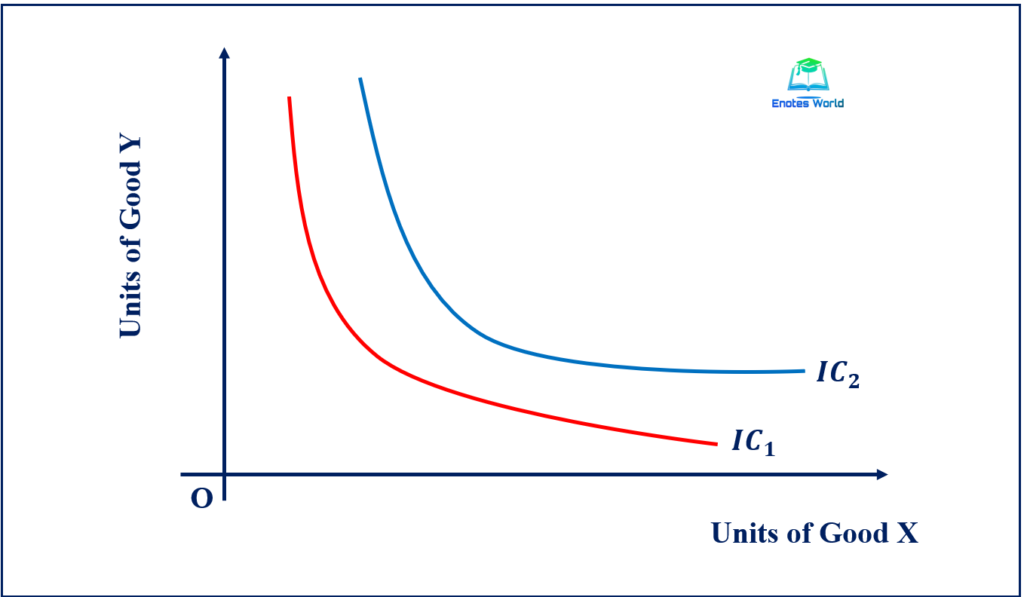
Dalam hal ini, ciri-ciri kurva indiferen (indifference curve) yaitu menghubungkan titik-titik kombinasi sejumlah barang yang dikonsumsi, di mana hasilnya memberikan kesamaan pada tingkat kepuasan konsumen.. IC2 adalah kurva indiferen yang lebih tinggi dari IC1. KurvaIndiferenX&Y.jpg. Sumber: Byju's.com. Sementara itu, pada contoh gambar di.
Assumptions and Properties of Indifference CurveMicroeconomics
Kurva Indiferen (Indifference Curve) adalah kurva yang menggambarkan berbagai kombinasi dari barang yang dikonsumsi oleh konsumen dengan manfaat atau kepuasan yang sama (Prof.Dr.Soeharno, 2006:40. Misalkan saja konsumen ingin mengonsumsi dua jenis produk yang berbeda kita bisa ambil contoh teh dan susu.Ketika konsumen lebih menyukai susu maka,konsumsi teh lebih rendah daripada susu.
Assumptions and Properties of Indifference CurveMicroeconomics
Marginal Rate of Substitution: The marginal rate of substitution is the amount of a good that a consumer is willing to give up for another good, as long as the new good is equally satisfying. It's.
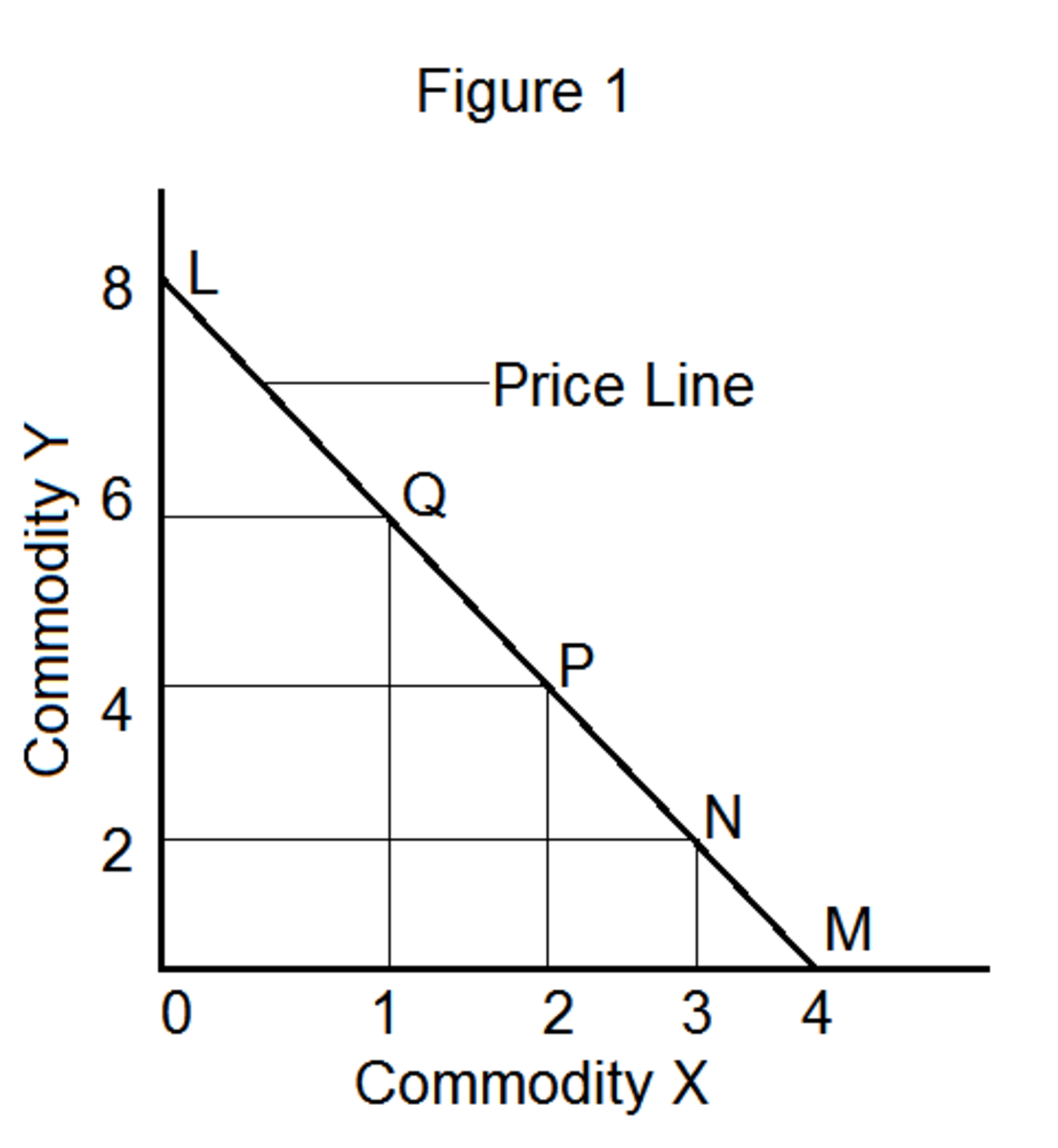
How to Derive Consumer's Equilibrium Through the Techniques of Indifference Curve and Budget
By definition, in economics when we consider indifference curves, we say "more is better", that is the farther of the indifference curve is, the better. So we would always chose the one that is farthest given a choice. Now back to the example, cold coffee and ice cream. If the two indifference curves crossed, they would have a common point, say.
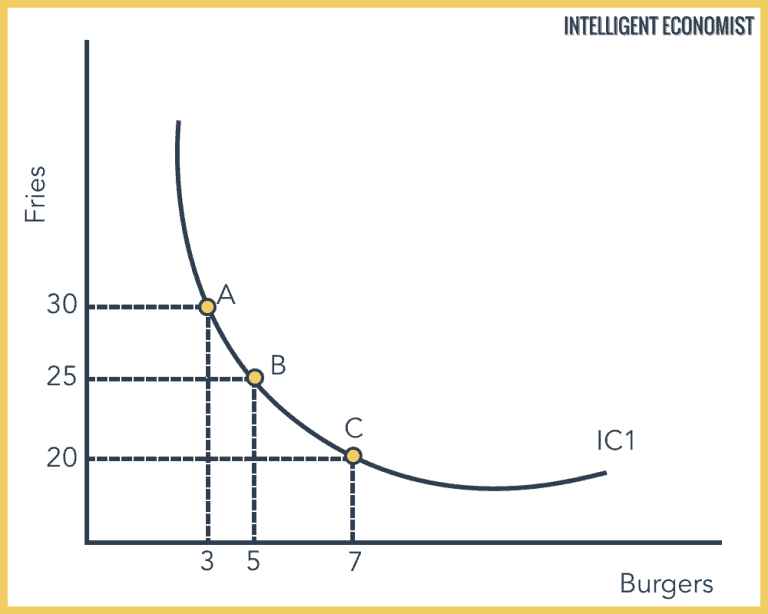
Indifference Curve Intelligent Economist
Menurut Prof. Dr.Soeharno (2006:43-44) sifat-sifat Kurva Indiferen (Indifference Curve) dapat dijelaskan sebagai berikut: 1. Terdapat banyak kurva indiferen U1,U2,U3,., Un. Susunan kurva indiferen disebut peta indiferen. 2. Kurva indiferen yang letaknya lebih tinggi menunjukkan kepuasan yang lebih tinggi. 3.
What are the Properties of the Indifference Curves? Owlcation
Pendekatan kurva indiferen (indifference curve) adalah cara menilai perilaku konsumen dalam suatu bisnis dengan menggunakan kurva. Grafik atau garis lengkung tersebut menghubungkan titik-titik kombinasi dari beberapa jumlah barang tertentu yang dikonsumsi, sehingga memberikan tingkat kepuasan yang sama. ADVERTISEMENT.