
Interleukins, from 1 to 37, and interferonγ Receptors, functions, and roles in diseases
Interleukin 6 (IL-6) is an interleukin that acts as both a pro-inflammatory cytokine and an anti-inflammatory myokine.In humans, it is encoded by the IL6 gene.. In addition, osteoblasts secrete IL-6 to stimulate osteoclast formation. Smooth muscle cells in the tunica media of many blood vessels also produce IL-6 as a pro-inflammatory cytokine.IL-6's role as an anti-inflammatory myokine is.

IL23 (Interleukin23)Producing Conventional Dendritic Cells Control the Detrimental IL17
Circulating concentrations of the pleiotropic cytokine interleukin-6 (IL-6) are known to be increased in pro-inflammatory critical care syndromes, such as sepsis and acute respiratory distress syndrome. Elevations in serum IL-6 concentrations in patients with severe COVID-19 have led to renewed interest in the cytokine as a therapeutic target. However, although the pro-inflammatory properties.
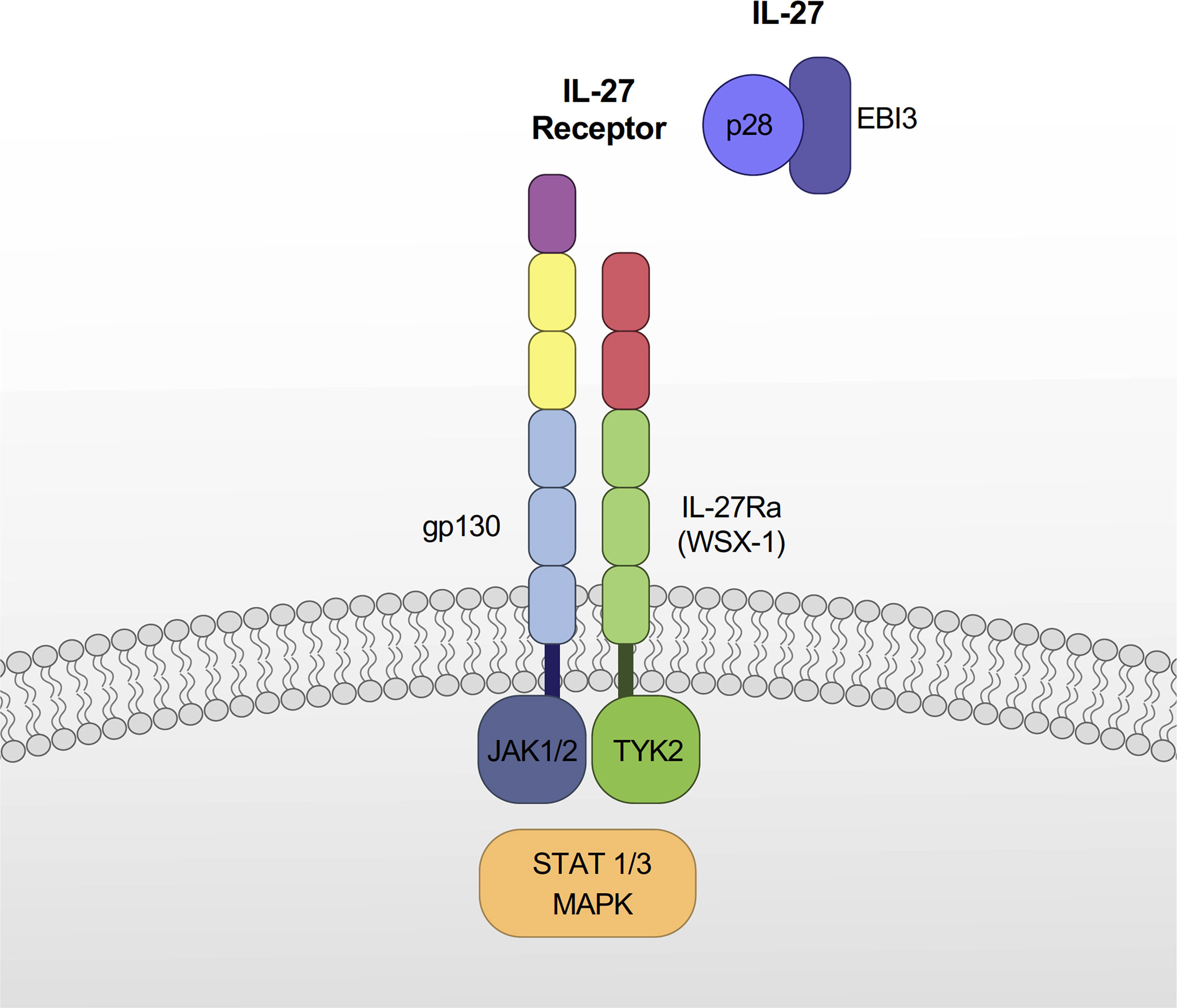
Frontiers Interleukin27 and Its Diverse Effects on Bacterial Infections
Interleukin is a protein that mediates communication between cells, especially in the immune system. Learn about the 15 types of interleukins, their roles in inflammation, infection, and disease, and how they differ from other cytokines.

Interleukin1 function and role in rheumatic disease Semantic Scholar
Interleukin-6 (IL-6) is a proinflammatory cytokine produced by cells during COVID-19 infection. Interleukin-6 inhibitors are drugs that block IL-6 activity and can be used to treat hospitalized patients with COVID-19 who have systemic inflammation and hypoxemia. The web page provides information on the clinical data, recommendations, adverse effects, drug availability, and pregnancy and lactation considerations of tocilizumab and sarilumab, two interleukin-6 inhibitors for COVID-19 treatment.

Interleukin 4 Binding To Its Receptor Photograph by Juan Gaertner/science Photo Library Fine
Interleukin-6 (IL-6) is a member of the pro-inflammatory cytokine family, induces the expression of a variety of proteins responsible for acute inflammation, and plays an important role in the proliferation and differentiation of cells in humans. IL-6 signaling is mediated by building a complex of IL-6, the transmembrane IL-6 receptor (mIL-6R.

Interleukin2 Receptor Signaling At the Interface between Tolerance and Immunity Immunity
Interleukins are cytokines produced and secreted mainly by CD3+ and CD4+ T lymphocytes. Interleukins promote development and differentiation of natural killer cells, T and B lymphocytes and.

Interleukin21 Signaling Functions in Cancer and Autoimmunity
Interleukin-33 (IL-33) — a member of the IL-1 family — was originally described as an inducer of type 2 immune responses, activating T helper 2 (T H 2) cells and mast cells. Now, evidence is.

Interleukin2 Biology, Design and Application Trends in Immunology
Soluble receptors in cancer: mechanisms, clinical significance, and therapeutic strategies. Interleukins and associated cytokines serve as the means of communication for innate and adaptive immune.

Role of interleukin 33 in human immunopathology Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases
Interleukin-2 (IL-2) is an interleukin, a type of cytokine signaling molecule in the immune system.It is a 15.5-16 kDa protein that regulates the activities of white blood cells (leukocytes, often lymphocytes) that are responsible for immunity.IL-2 is part of the body's natural response to microbial infection, and in discriminating between foreign ("non-self") and "self".

Interleukin‐18 Biological properties and role in disease pathogenesis Kaplanski 2018
Interleukin-4 (IL-4) CD4+T cells (Th2) synthesize IL-4, and it acts on both B and T cells. It is a B-cell growth factor and causes IgE and IgG1 isotype selection. It causes Th2 differentiation and proliferation, and it inhibits IFN gamma-mediated activation on macrophages. It promotes mast cell proliferation in vivo. Interleukin-5 (IL-5)

Interleukin1 Beta as a Target for Atherosclerosis Therapy Biological Basis of CANTOS and
2. Characteristics, Biological Role and Mechanism of Action of Interleukins in the Human Body. Interleukins, apart from interferons and chemokines, belong to a group of cytokines (Figure 1 A) showing very complex and broad actions in the human body, interacting with all cells of the immune system and other cells and tissues and creating a network of connections—a cytokine network [].
What is Interleukin6? HealthMatters.io Lab results explained
Interleukin (IL)-15, a member of the immunoregulatory cytokines family, is a pluripotent molecule with therapeutic potential. It is predominantly expressed by the myeloid cells, as well as other cell types. IL-15 serves multiple functions including dictating T cell response, regulating tissue repair.

Therapeutic Targeting of the Interleukin4/Interleukin13 Signaling Pathway In Allergy and
Here, the authors discuss the biological role of interleukin-2 (IL-2) in the immune system, focusing on recent advances in our understanding of how IL-2 signals have different effects on various T.
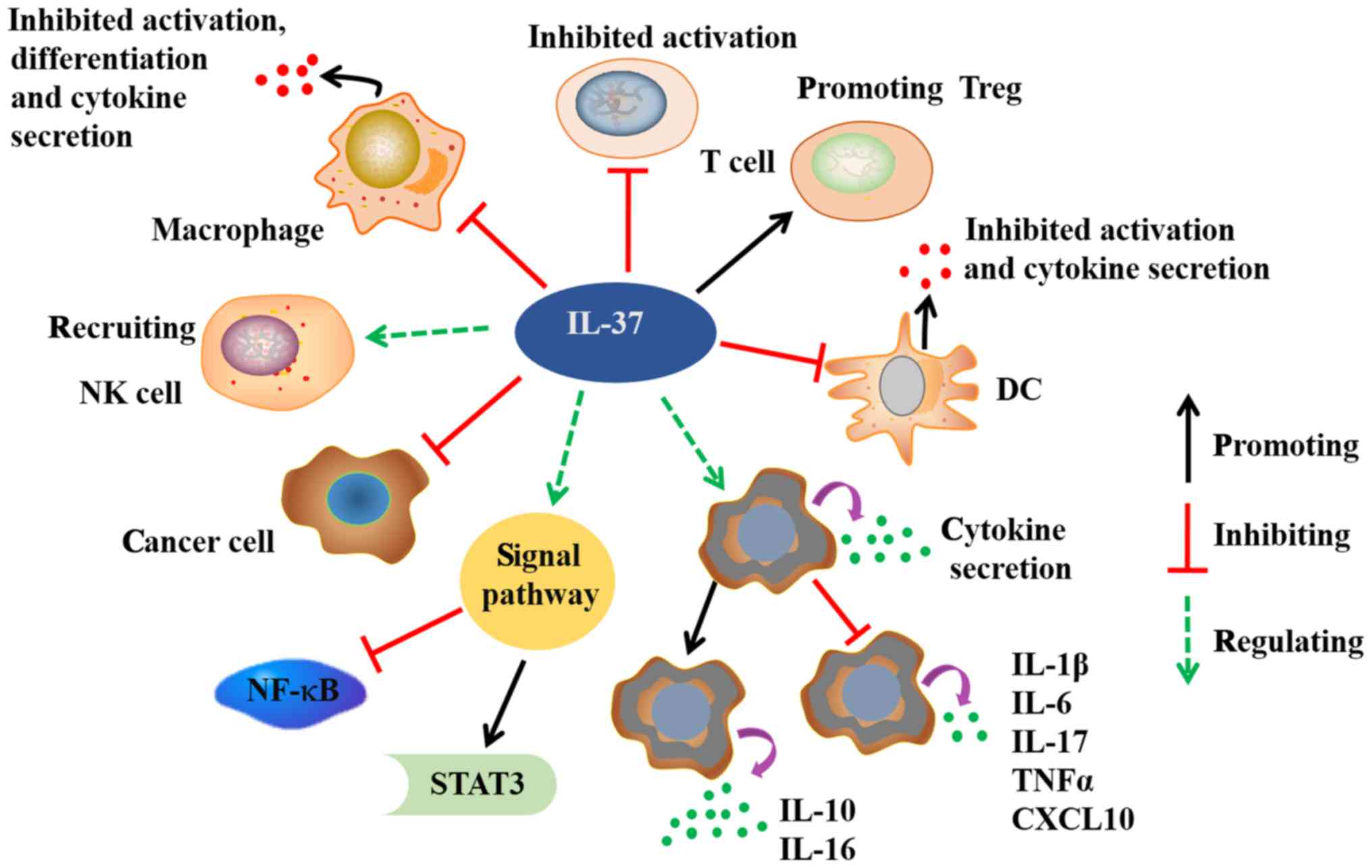
Interleukin37 A crucial cytokine with multiple roles in disease and potentially clinical
Abstract. Interleukin 6 (IL-6), promptly and transiently produced in response to infections and tissue injuries, contributes to host defense through the stimulation of acute phase responses, hematopoiesis, and immune reactions. Although its expression is strictly controlled by transcriptional and posttranscriptional mechanisms, dysregulated.

Interleukin1 Receptor 2 Keeps the Lid on Interleukin1α Immunity
Interleukins often influence other interleukin synthesis and actions. For instance, IL-1 promotes lymphocyte activation that leads to the release of IL-2. Cellular responses to cytokines are stimulated and regulated by external signals or high-affinity receptors. For example, stimulation of B-cells by pathogens leads to increased expression of.

IJMS Free FullText An Update on Interleukin9 From Its Cellular Source and Signal
Interleukins are a type of cytokines that were first seen to be expressed by leukocytes. The term 'interleukin' was first coined in 1979 in a letter to the editor of the Journal of Immunology to describe a number of secreted molecules produced by leukocytes, a variety of polypeptides that act specifically as mediators between leucocytes.