
Carboxyhemoglobin joining the hemoglobin carbon Vector Image
Carbon dioxide is an important side product of the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle). This oxidized carbon represents an end product of metabolism that, ultimately, needs to be removed using transport to the lungs and subsequent expiration out into the surrounding environment. Together with renal regulation, this complex process of carbon dioxide production, transport, and elimination is the.

PPT Oxygen Transport PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID3308672
Carbaminohemoglobin (carbaminohaemoglobin BrE) (CO 2 Hb, also known as carbhemoglobin and carbohemoglobin) is a compound of hemoglobin and carbon dioxide, and is one of the forms in which carbon dioxide exists in the blood. Twenty-three percent of carbon dioxide is carried in blood this way (70% is converted into bicarbonate by carbonic anhydrase and then carried in plasma, 7% carried as free.

What is mostly present in our blood carbaminohaemoglobin or carboxyhaemoglobin? Socratic
Equilibration durations were varied between 30 and 45 min, in 3 min steps, whereas measuring the absorbance at the 759-nm peak of the spectra of and HHb. A Pearson correlation coefficient test was then performed, searching for an influence of the tonometry duration on the measured absorbance values. 2.2.

PPT BLOOD 2 RED BLOOD CELLS JAUNDICE ANEMIA & POLYCYTHEMIA PowerPoint Presentation ID1867420
Carboxyhemoglobin ( carboxyhaemoglobin BrE) (symbol COHb or HbCO) is a stable complex of carbon monoxide and hemoglobin (Hb) that forms in red blood cells upon contact with carbon monoxide. Carboxyhemoglobin is often mistaken for the compound formed by the combination of carbon dioxide ( carboxyl) and hemoglobin, which is actually.

Blood1
car·ba·mi·no·he·mo·glo·bin. ( kahr-bam'i-nō-hē'mŏ-glō'bin) Carbon dioxide bound to hemoglobin by means of a reactive amino group on the latter; approximately 20% of the total carbon dioxide in blood is combined with hemoglobin in this manner. Synonym (s): carbaminohaemoglobin. Medical Dictionary for the Health Professions and Nursing.

PPT Dr.S.Chakravarty MBBS,MD PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID3059302
The first mechanism of carbon dioxide transport is by blood plasma, as some carbon dioxide molecules dissolve in the blood. The second mechanism is transport in the form of bicarbonate (HCO 3- ), which also dissolves in plasma. The third mechanism of carbon dioxide transport is similar to the transport of oxygen by erythrocytes ( Figure 22.5.4 ).
PPT Carbon dioxide and Oxygen transport PowerPoint Presentation ID3561670
Description. Also known as. English. carbaminohemoglobin. compound of hemoglobin and carbon dioxide; one form in which carbon dioxide exists in the blood.
PPT KREV IMUNITA PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5060571
Key Points. Carbon dioxide is more soluble in blood than is oxygen; about 5 to 7 percent of all carbon dioxide is dissolved in the plasma. Carbon dioxide has the ability to attach to hemoglobin molecules; it will be removed from the body once they become dissociated from one another.
What is the common element in hemoglobin and myoglobin?(a) Fe(b) Cu(c) Mn(d) Mg
Karbaminohemoglobin kallas hemoglobin med en koldioxidmolekyl bunden till sig. Karbaminohemoglobin förskjuter syre-hemoglobindissociationskurvan åt höger, eftersom den har högre affinitet till deoxyhemoglobin. Detta är ursprunget till Haldaneeffekten. (sv)

Carboxyhaemoglobin molecule Stock Image C025/2139 Science Photo Library
Karbaminohemoglobin. Karbaminohemoglobin je hemoglobin, na kterém je navázaný CO 2. Oxid uhličitý se váže na globinový řetězec hemoglobinu. Vazba CO 2 na hemoglobin snižuje afinitu hemoglobinu ke kyslíku.
PPT Cardiovascular system Blood Anatomy Chapter20 PowerPoint Presentation ID867505
A carboxyhemoglobin test is a blood test to check the amount of carbon monoxide in your blood. Your doctor will use a needle attached to a syringe to collect a blood sample from a vein or artery.
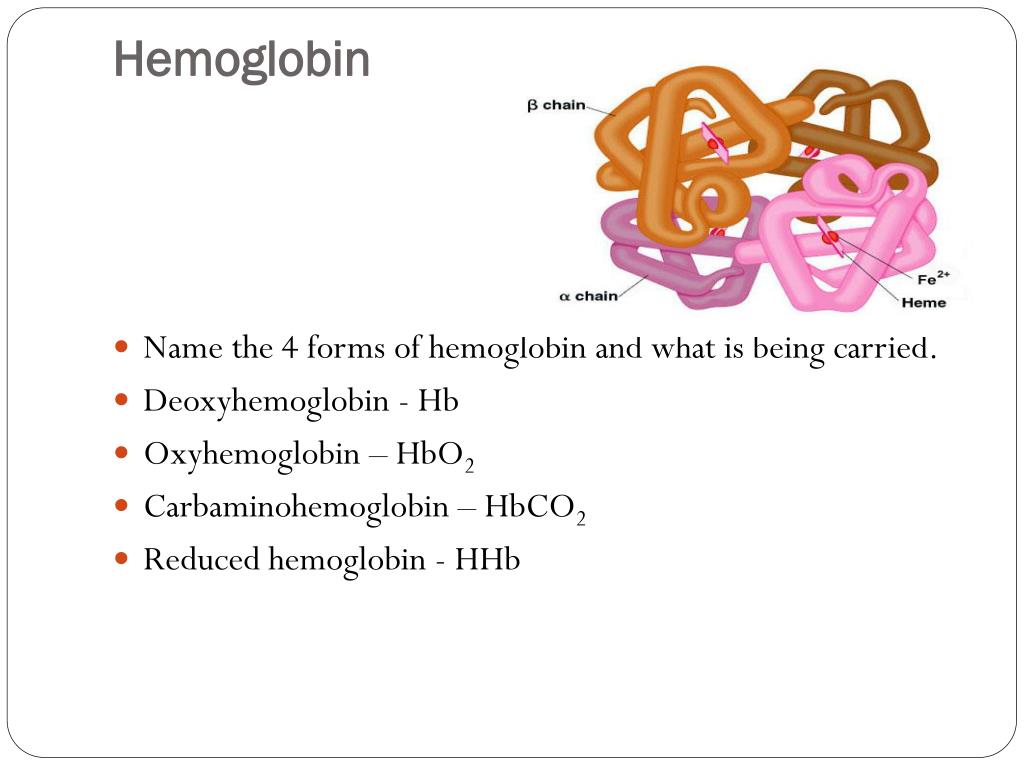
PPT Respiration external and internal PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2866648
Carboxyhemoglobin, or carboxyhaemoglobin, (symbol COHb or HbCO) is a stable complex of carbon monoxide and hemoglobin (Hb) that forms in red blood cells upon contact with carbon monoxide. Carboxyhemoglobin is often mistaken for the compound formed by the combination of carbon dioxide (carboxyl) and hemoglobin, which is actually.
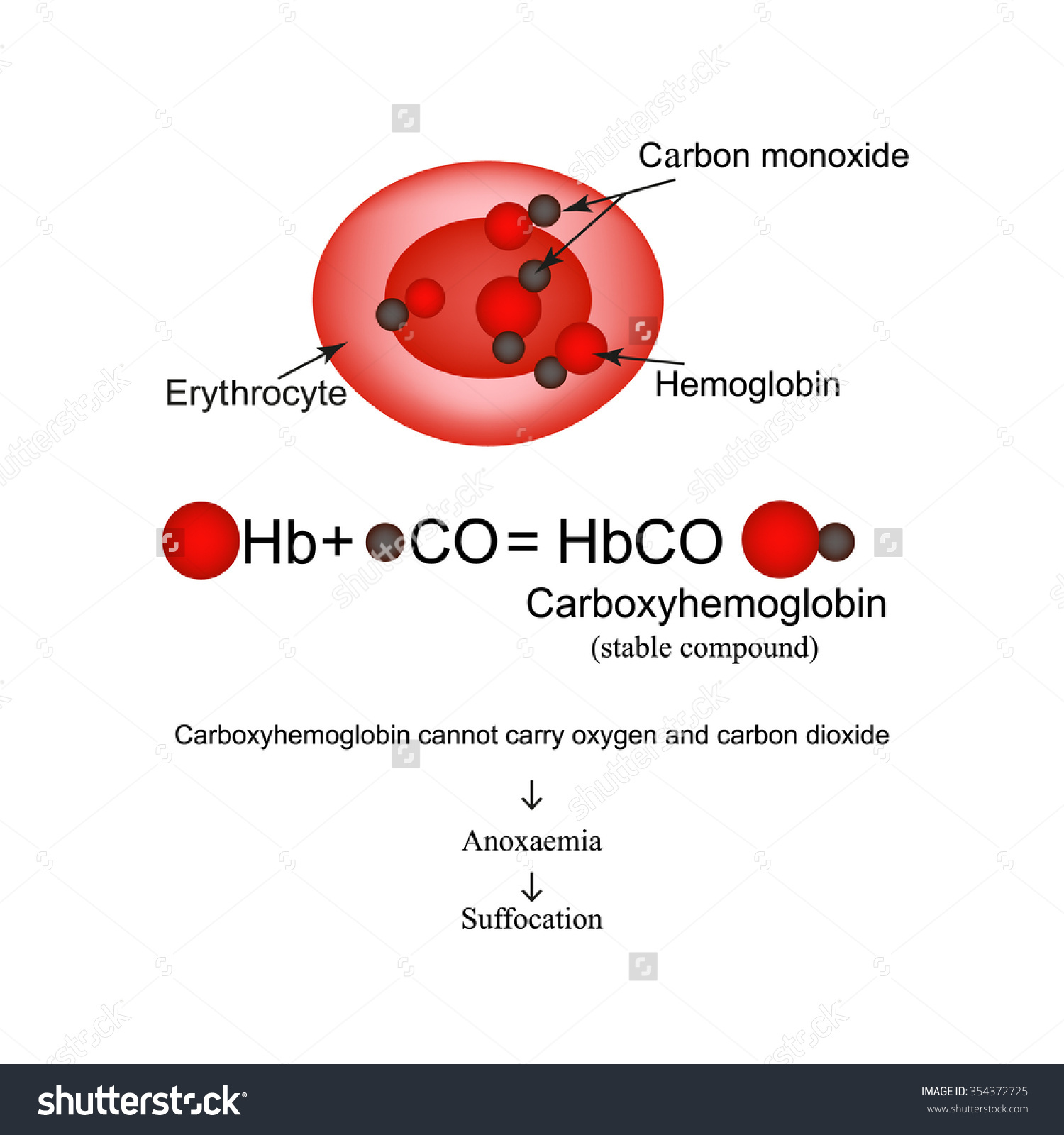
What is mostly present in our blood carbaminohaemoglobin or carboxyhaemoglobin? Socratic
Reference Range. Carboxyhemoglobin (COHb) is a stable complex of carbon monoxide that forms in red blood cells when carbon monoxide is inhaled. COHb should be measured if carbon monoxide or methylene chloride poisoning is suspected. COHb is also useful in monitoring the treatment of carbon monoxide poisoning.

Hemoglobin levels in blood Hemoglobin Test MedlinePlus Medical Test
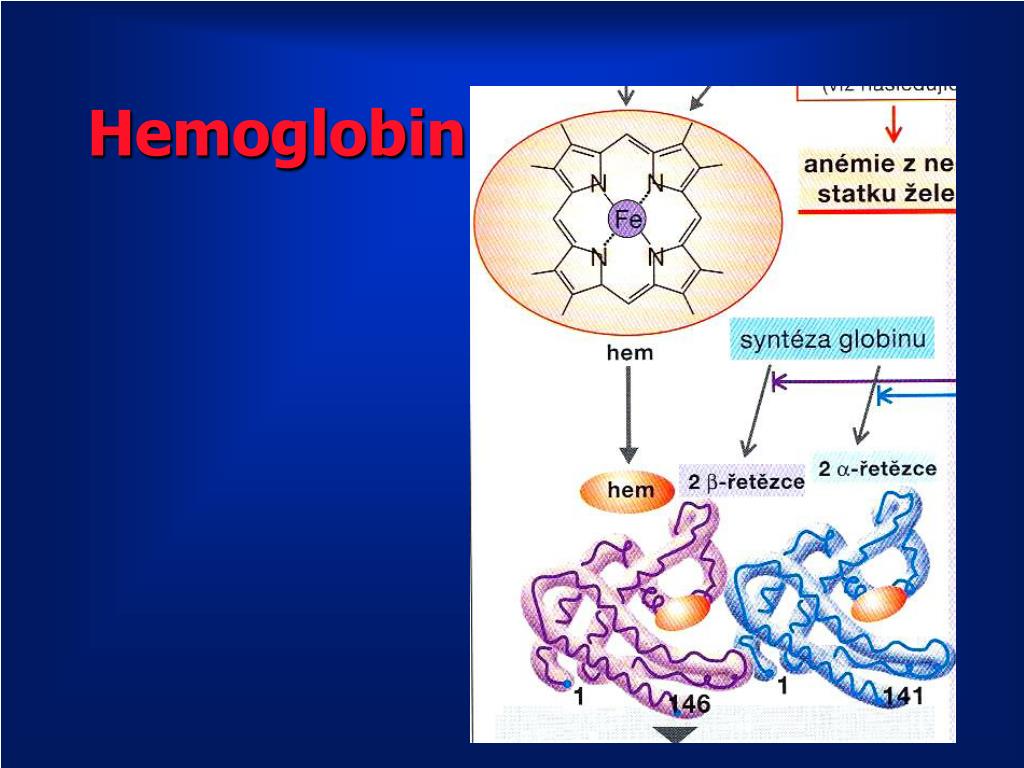
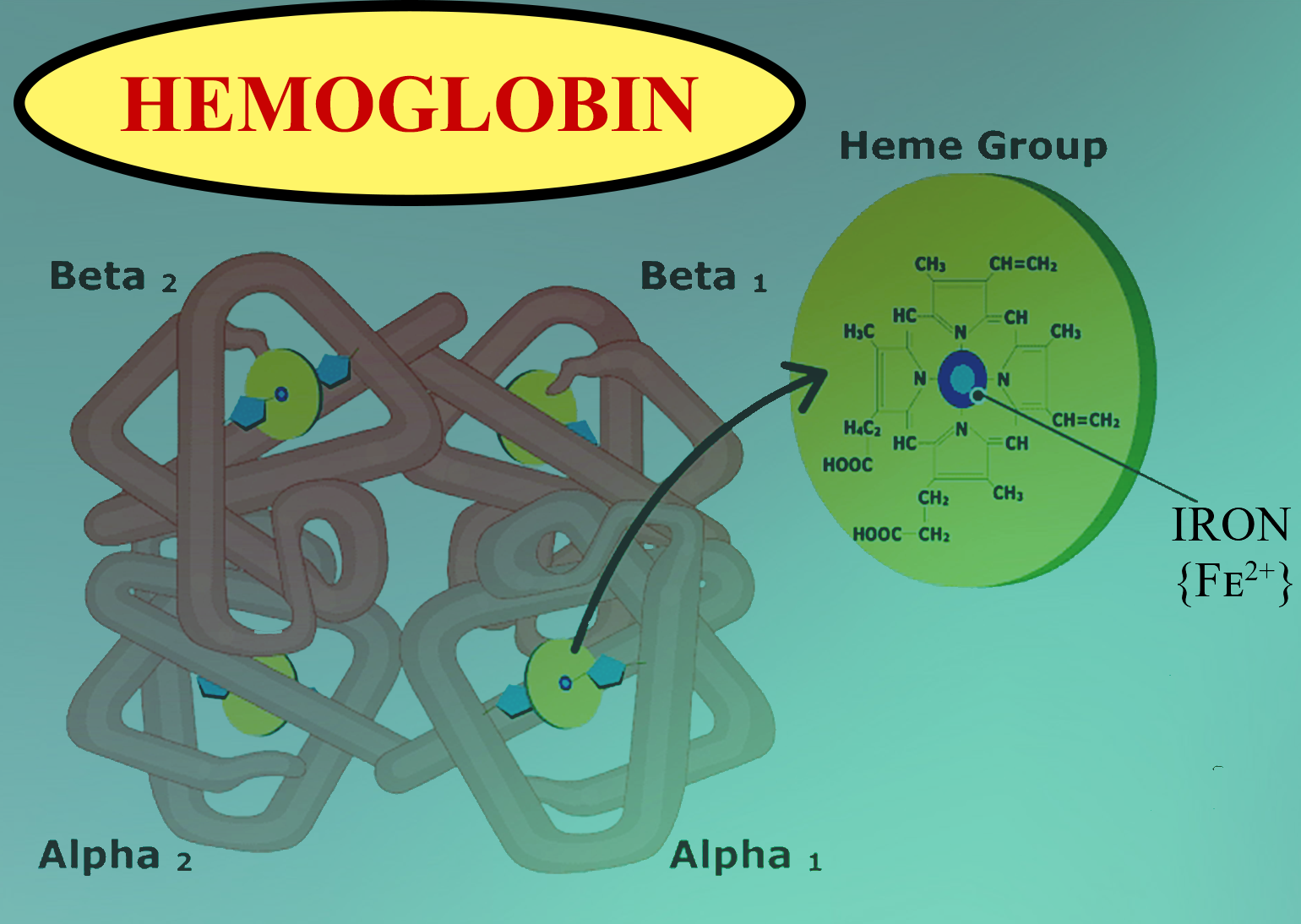
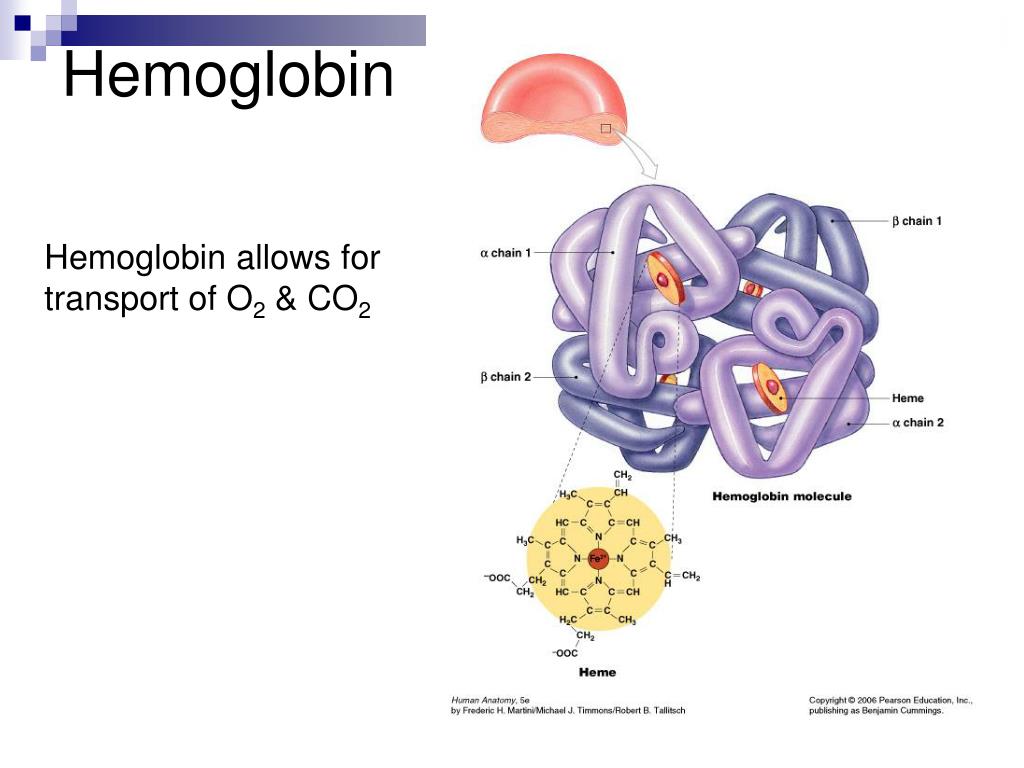
CO 2 reacts with free NH 2 terminal groups on both the α and β chains of hemoglobin to form a new compound, carbaminohemoglobin (see Figure 6.4.9).This reaction can also occur with plasma proteins. The combination of CO 2 with NH 2 groups is called a carbamate.Carbamate formation is reversible and influenced by P O 2, pH, and [2,3-DPG].When P O 2 increases, as it does when the blood enters.
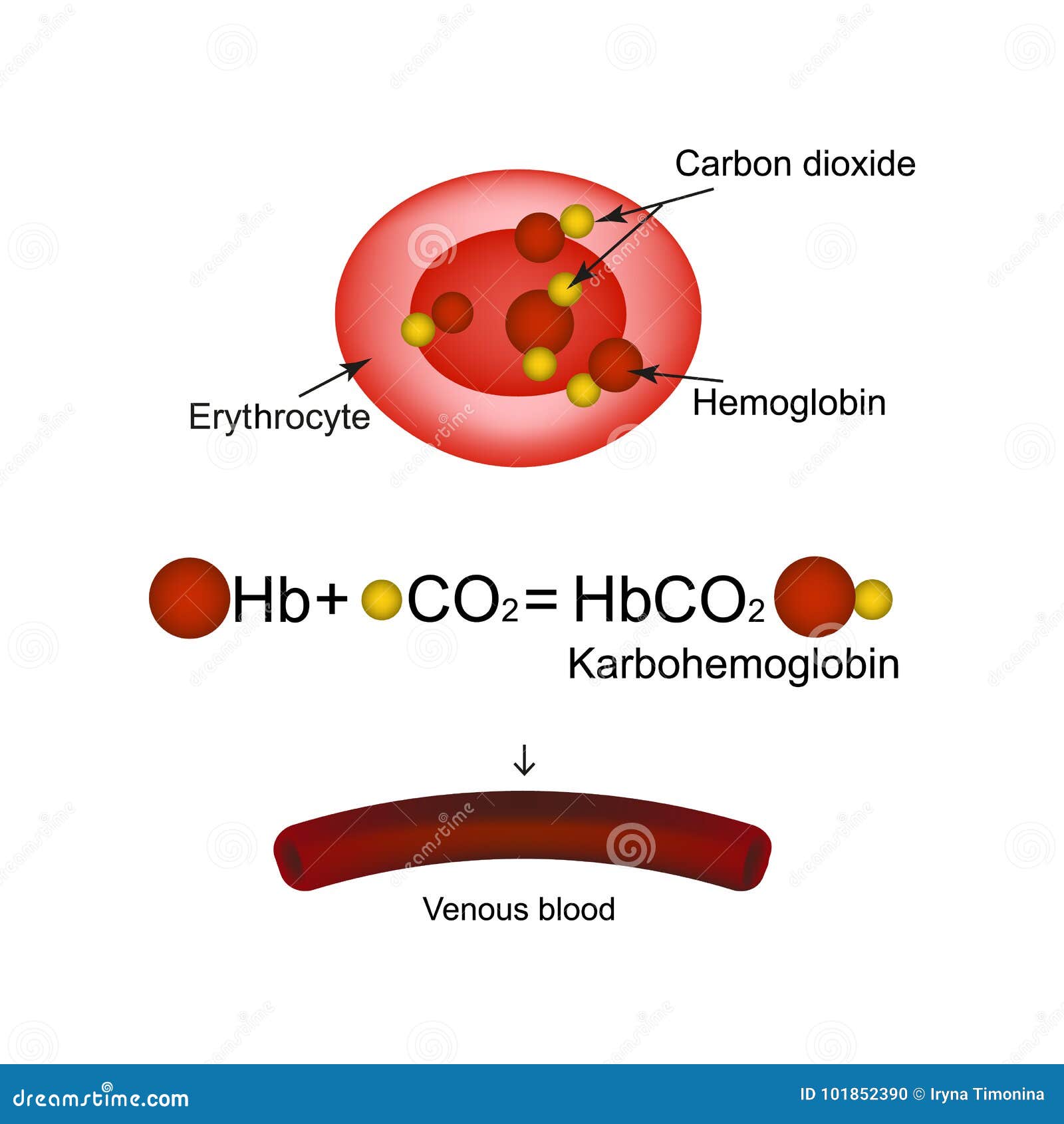
Karbogemoglobin. Hemoglobin Carries Carbon Dioxide. Infographics. Vector Illustration
Carbon monoxide is a tasteless, odorless, colorless, and non-irritating gas formed with the combustion of hydrocarbons (fossil fuels). It binds to hemoglobin with a much greater affinity than oxygen to form carboxyhemoglobin, subsequently reducing oxygen-carrying capacity and oxygen utilization. Hypoxia ensues, and toxicity can lead to cerebrovascular ischemia and myocardial infarction. By.

Carboxyhemoglobin joining the hemoglobin carbon Vector Image
8.6: Transport of Gases. The other major activity in the lungs is the process of respiration, the process of gas exchange. The function of respiration is to provide oxygen for use by body cells during cellular respiration and to eliminate carbon dioxide, a waste product of cellular respiration, from the body.