Typhoid Fever Get Facts Health Tips from Kokilaben Hospital
Typhoid fever. A01.0 should not be used for reimbursement purposes as there are multiple codes below it that contain a greater level of detail. The 2024 edition of ICD-10-CM A01.0 became effective on October 1, 2023. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of A01.0 - other international versions of ICD-10 A01.0 may differ.
Typhoid Fever, Enteric Fever (Salmonella typhi)
Serious complications of typhoid fever occur in 10%-15% of hospitalized patients, generally after 2-3 weeks of illness, and include life-threatening gastrointestinal hemorrhage, intestinal perforation, and encephalopathy. Paratyphoid fever appears to have a lower case-fatality ratio than typhoid fever; however, severe cases do occur. Diagnosis
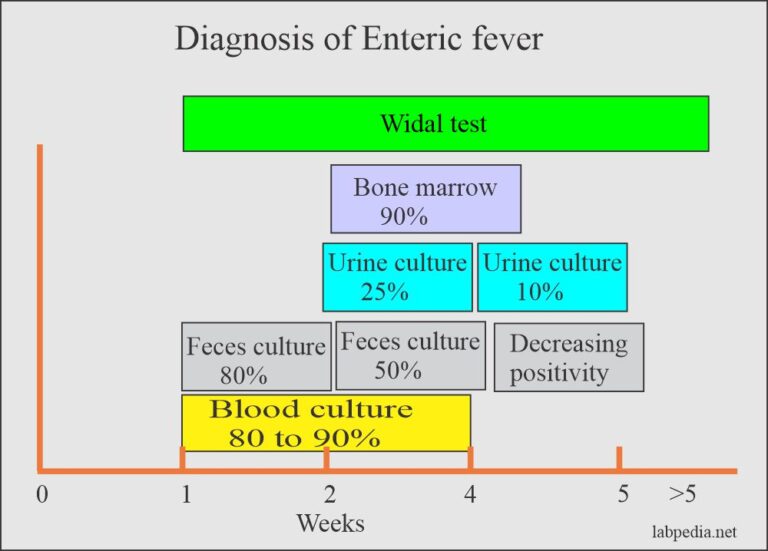
Enteric fever Part 2 Typhoid / Enteric fever Diagnosis, Widal test, Its Procedure and
Persons with typhoid fever carry the bacteria in their bloodstream and intestinal tract. Symptoms include prolonged high fever, fatigue, headache, nausea, abdominal pain, and constipation or diarrhoea. Some patients may have a rash. Severe cases may lead to serious complications or even death. Typhoid fever can be confirmed through blood testing.

Typhoid fever Definition, Symptoms, & Treatment Britannica
Symptoms include: High fever. Headache. Stomach pain. Constipation or diarrhea. Most people who have typhoid fever feel better about a week after they start treatment to kill bacteria, called antibiotics. But without treatment, there is a small chance of death from typhoid fever complications.

Typhoid Symptoms, treatment, causes, prevention and Diagnosis
These medicines may be used alone or together. Antibiotics that may be given for typhoid fever are: Fluoroquinolones. These antibiotics, including ciprofloxacin (Cipro), may be a first choice. They stop bacteria from copying themselves. But some strains of bacteria can live through treatment. These bacteria are called antibiotic resistant.
Enteric fever Part 3 Typhoid / Enteric fever Diagnosis, Widal test, Its Procedure and
In routine healthcare settings in low- and middle-income countries, typhoid fever is suspected and treated empirically. Though many diagnostic tests are available for typhoid diagnosis, there are currently no diagnostic tests that meet ideal requirements for sensitivity, specificity, speed, and cost-effectiveness.
Typhoid Fever Outbreaks in the United States GIDEON Global Infectious Diseases and
ICD-10-CM Codes › A00-B99 › A00-A09 › Typhoid and paratyphoid fevers A01 Typhoid and paratyphoid fevers A01-

Symptoms and Diagnosis of Typhoid
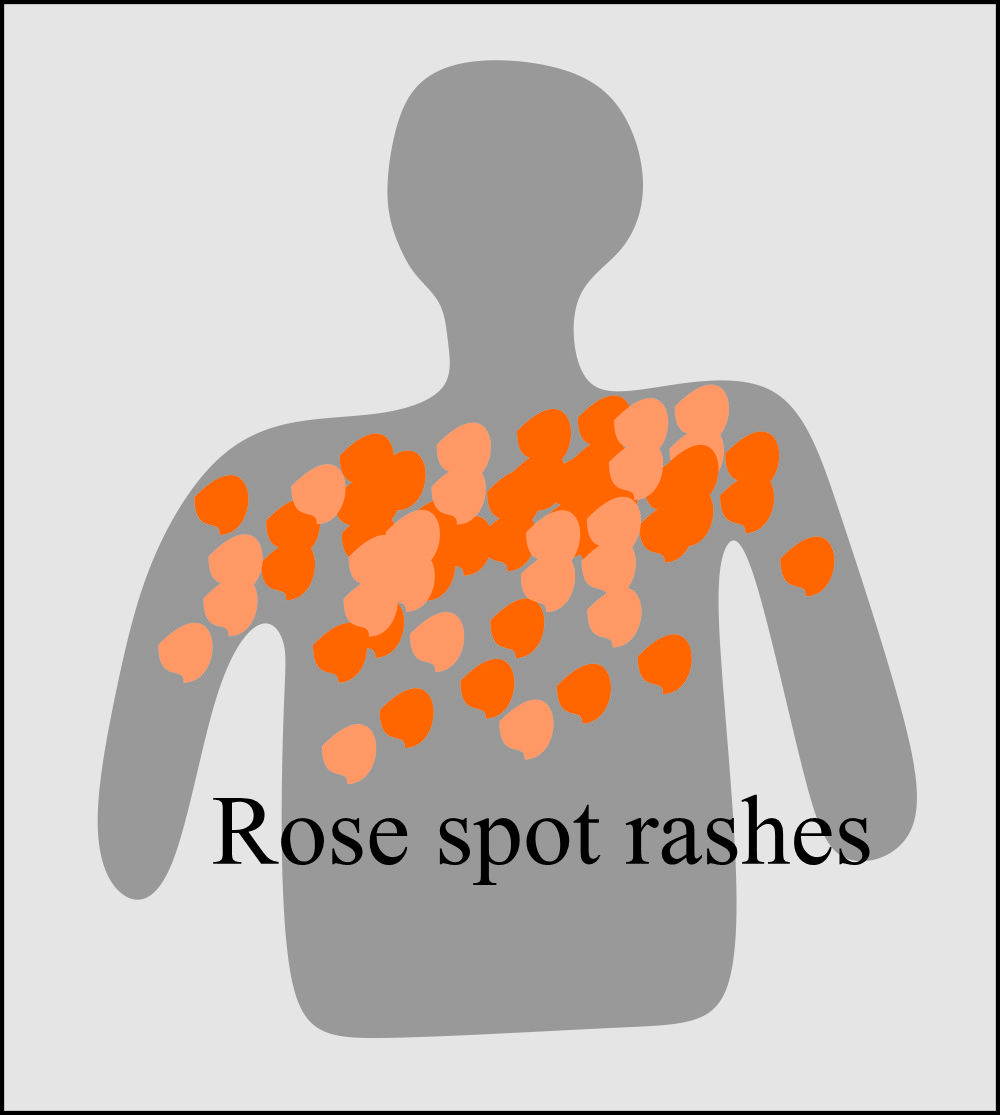
Typhoid fever is a serious infection caused by bacteria. In the U.S., most cases are in people who get the disease while traveling abroad. Symptoms include a high fever, weakness, stomach pains, headache, and loss of appetite. Sometimes, a rash of flat, rose-colored spots may appear. Antibiotics are often used to treat the disease.

Typhoid Fever Nursing Diagnosis and Nursing Care Plan
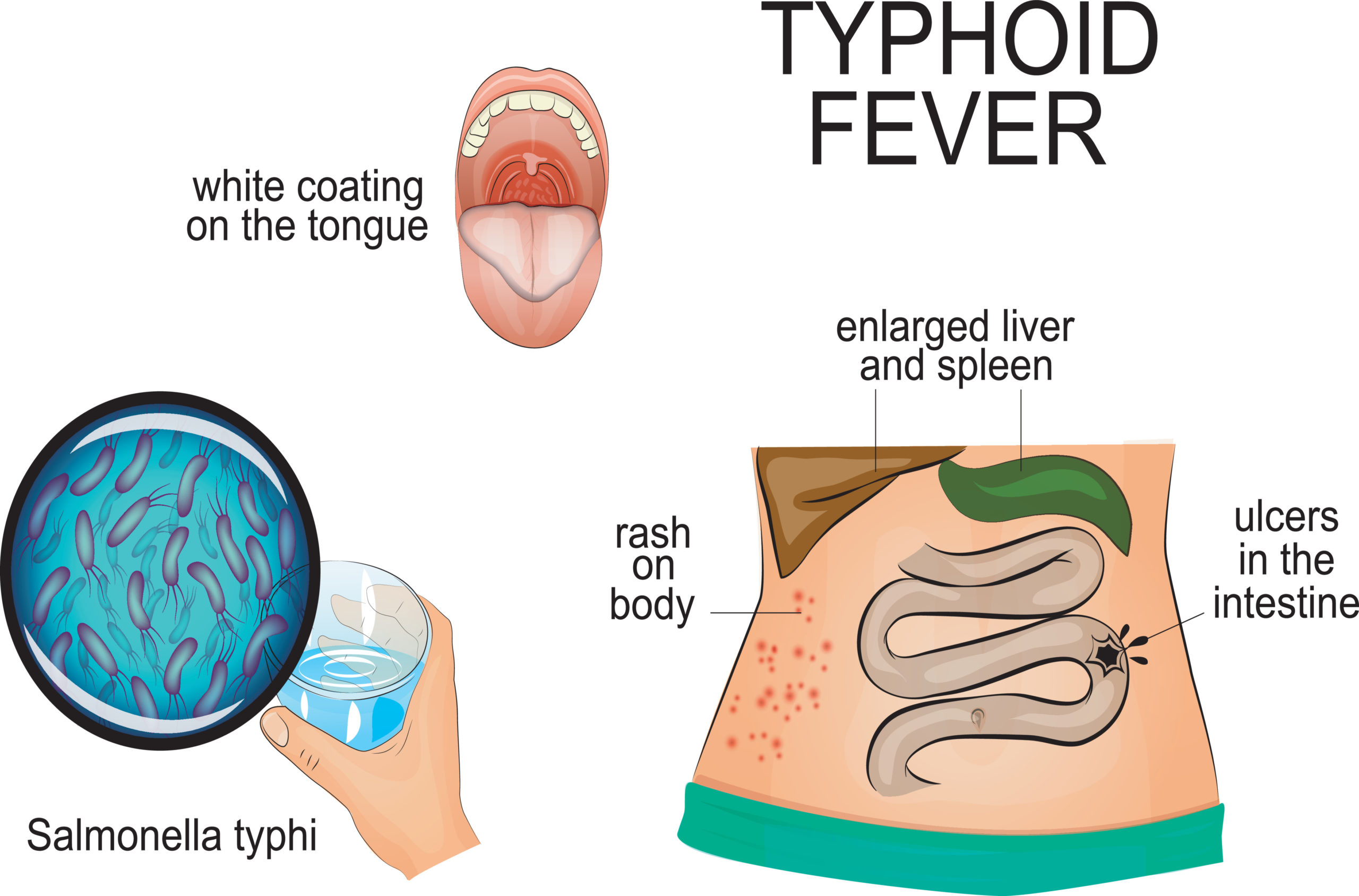
Typhoid fever, also known simply as typhoid, is a disease caused by Salmonella enterica serotype Typhi bacteria, also called Salmonella Typhi. Symptoms vary from mild to severe, and usually begin six to 30 days after exposure. Often there is a gradual onset of a high fever over several days. This is commonly accompanied by weakness, abdominal pain, constipation, headaches, and mild vomiting.
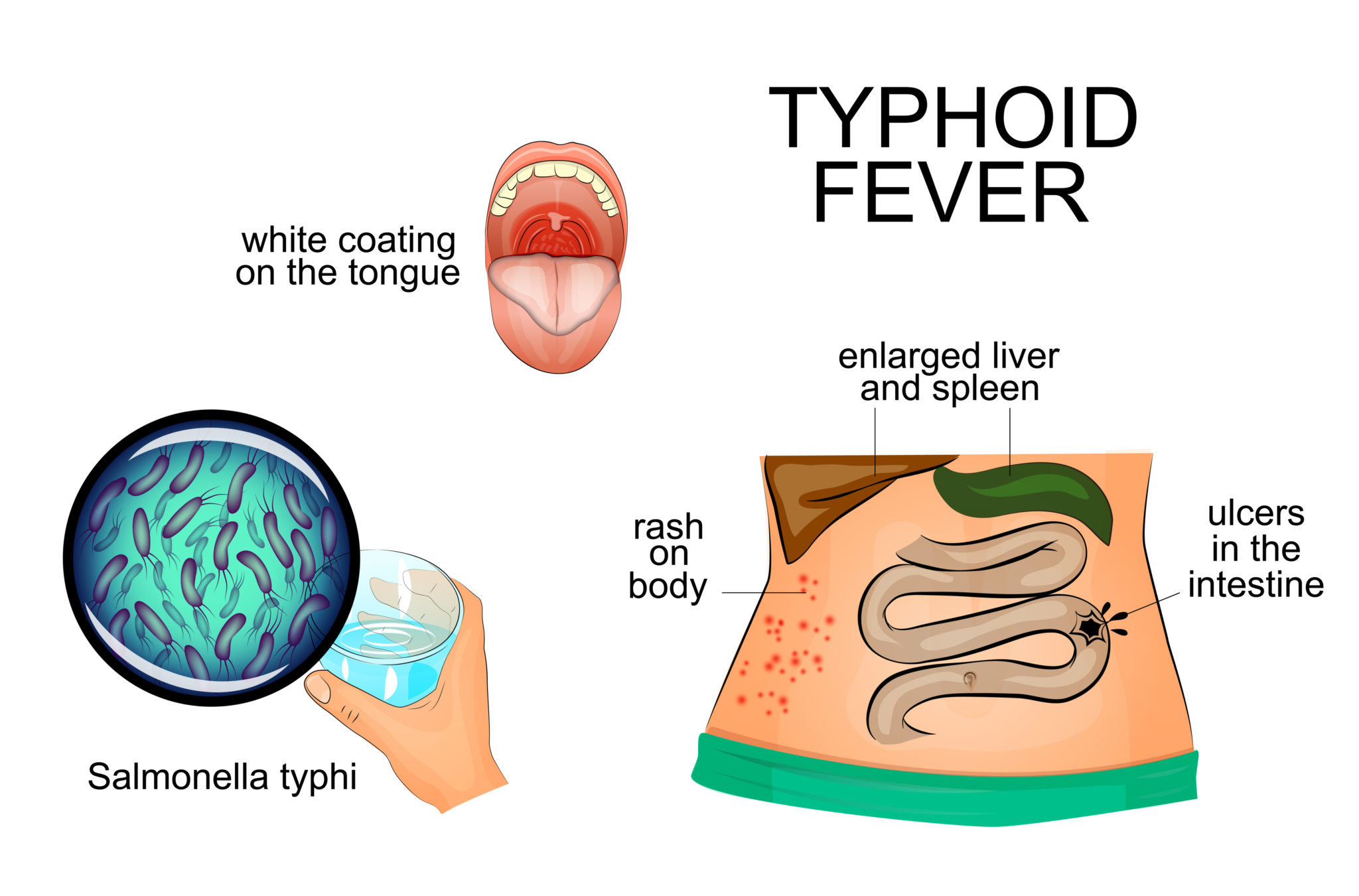
Examining Salmonella Typhi and Typhoid Fever GIDEON Global Infectious Diseases and
Typhoid fever is also called enteric fever. It is a prospectively, multisystemic illness that has been a public health problem, especially in the developing world. It is caused by Salmonella typhi and Salmonella paratyphi.[1] Enteric fever is a cumulative term that illustrates both typhoid and paratyphoid fever. Paratyphoid is clinically indistinct from typhoid fever; thus, enteric and typhoid.

Typhoid Symptoms 5 ways the infection can spread; telltale symptoms to note and how to prevent it
Symptoms include: High fever. Headache. Stomach pain. Constipation or diarrhea. Most people who have typhoid fever feel better about a week after they start treatment to kill bacteria, called antibiotics. But without treatment, there is a small chance of death from typhoid fever complications.

Typhoid Fever by kelsi_tucker321
Possibly a rash of flat, rose-colored spots. If the disease progresses, it can lead to more serious symptoms, including: Extreme fatigue. Breathlessness. Irregular heartbeat. Vomiting blood and bloody stools. Dark, tar-like stools. Severe abdominal pain and rigidity. Loss of consciousness and other neurological signs.
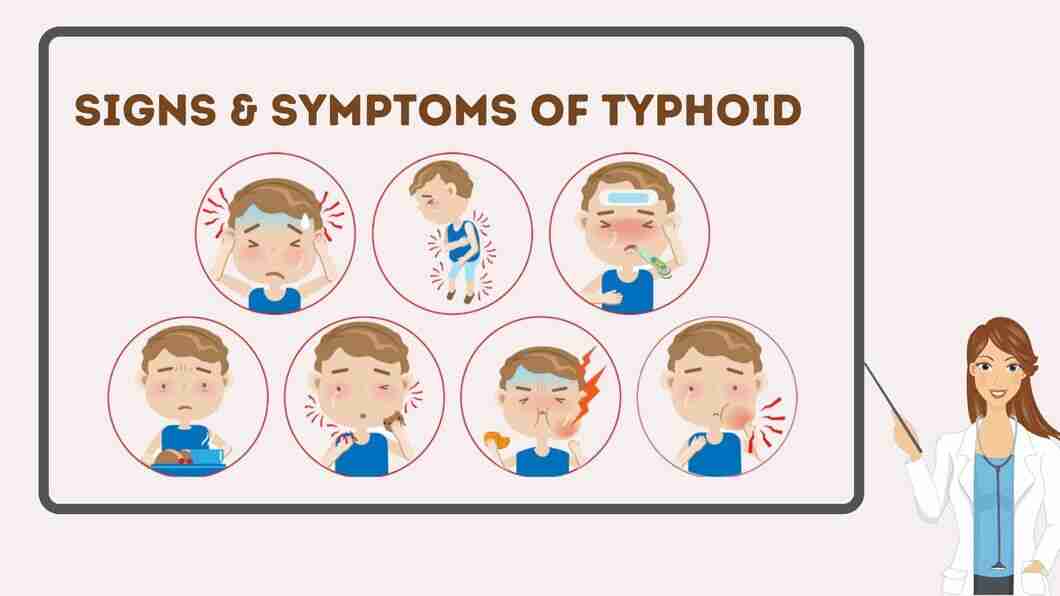
Typhoid Symptoms Causes & Treatment
A diagnosis of typhoid fever can usually be confirmed by analysing samples of blood, poo, or pee. These will be examined under a microscope for the Salmonella typhi bacteria that cause the condition. The bacteria aren't always detected the first time, so you may need to have a series of tests. Testing a sample of bone marrow is a more accurate.
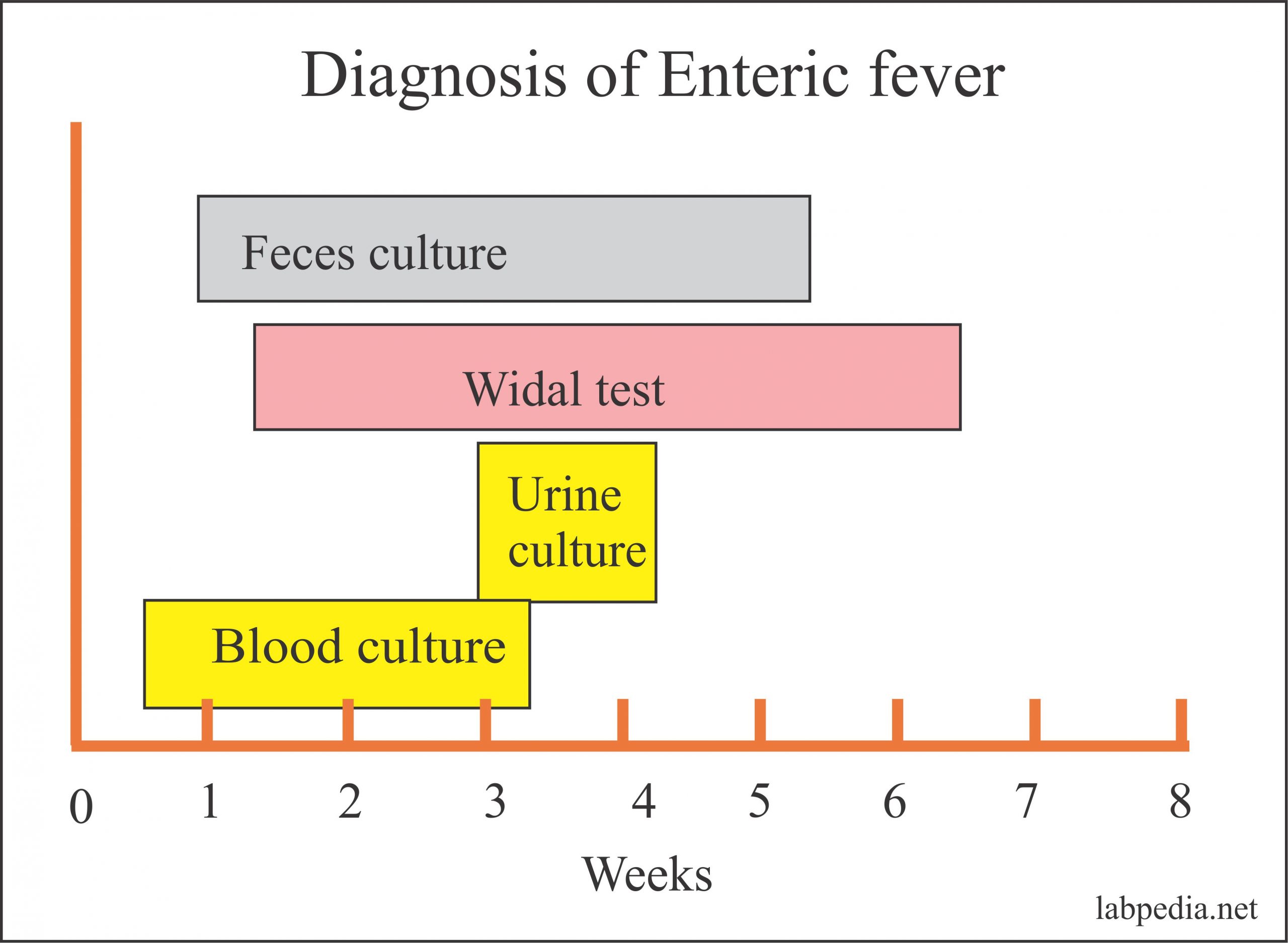
Enteric fever Part 3 Typhoid / Enteric fever Diagnosis, Widal test, Its Procedure and
Typhoid fever, unspecified. A01.00 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2024 edition of ICD-10-CM A01.00 became effective on October 1, 2023. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of A01.00 - other international versions of ICD-10 A01.00 may differ.
Typhoid Fever Facts Causes, Types, Possible Treatments Accuhealth Diagnostics
Background. Differentiating both typhoid (Salmonella Typhi) and paratyphoid (Salmonella Paratyphi A) infection from other causes of fever in endemic areas is a diagnostic challenge.Although commercial point‐of‐care rapid diagnostic tests (RDTs) for enteric fever are available as alternatives to the current reference standard test of blood or bone marrow culture, or to the widely used Widal.

Typhoid Fever Symptoms, Causes, Complications & Prevention
Typhoid fever is a systemic infection with the bacterium Salmonella enterica serotype typhi. This highly adapted, human-specific pathogen has evolved remarkable mechanisms for persistence in its.