
Varicella The Lancet
Chickenpox or varicella is a contagious disease caused by the varicella-zoster virus (VZV). The virus is responsible for chickenpox (usually primary infection in non-immune hosts) and herpes zoster or shingles (following reactivation of latent infection). Chickenpox results in a skin rash that forms small, itchy blisters, which scabs over. It typically starts on the chest, back, and face then.

Varicella Chickenpox Nursing Diagnosis and Nursing Care Plan
Laboratory Testing. Laboratory testing is recommended to: Confirm suspected cases of varicella. Confirm varicella as the cause of outbreaks. Confirm varicella in severe cases (hospitalizations or deaths) or unusual cases. Determine susceptibility to varicella. Determine if suspected vaccine-related adverse events were caused by vaccine-strain VZV.
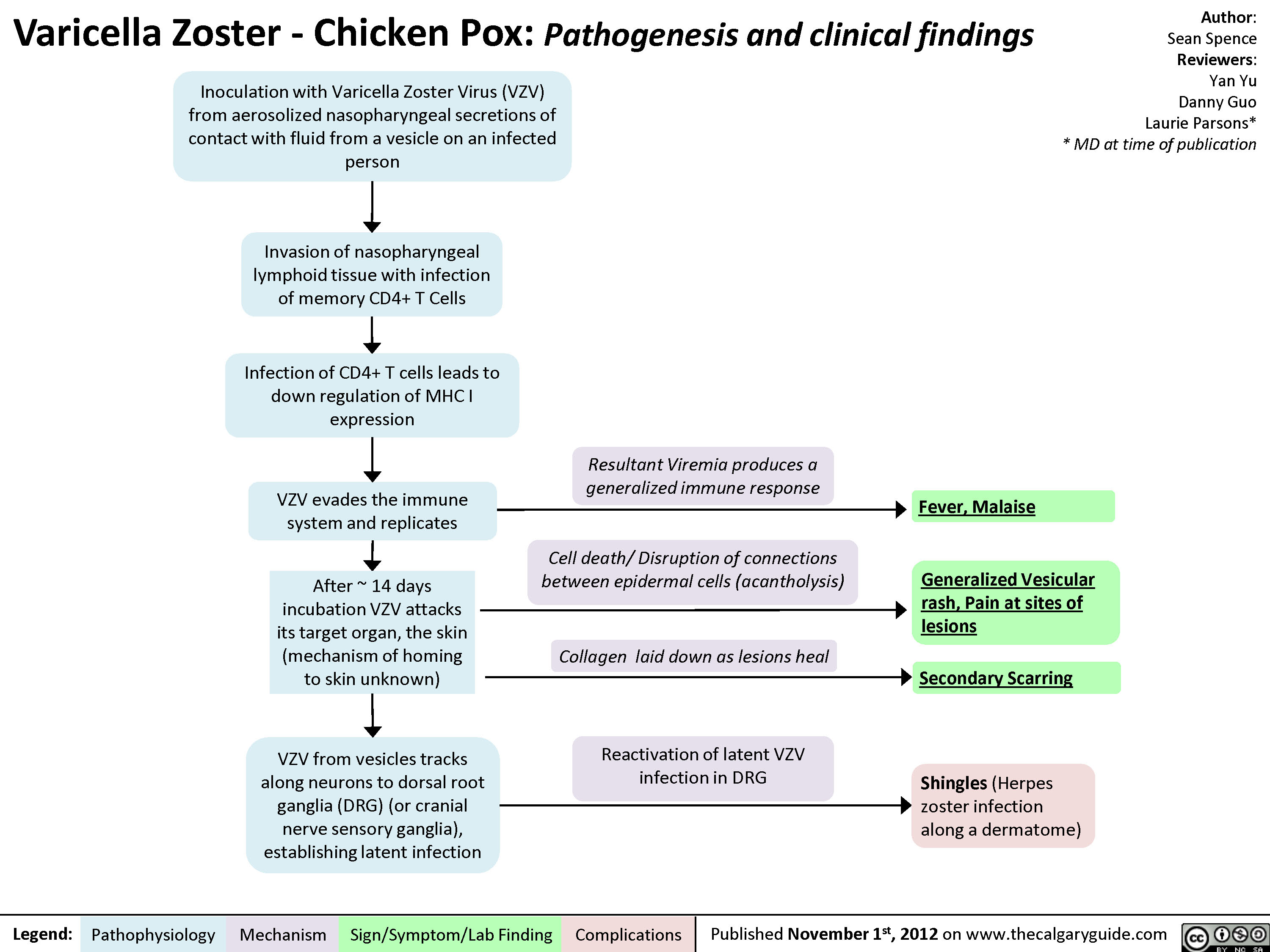
Varicella Zoster (Chicken Pox) Calgary Guide
Varicella (chickenpox) is an acute infectious disease. It is caused by varicella-zoster virus (VZV), which is a DNA virus that is a member of the herpesvirus group. After the primary infection, VZV stays in the body (in the sensory nerve ganglia) as a latent infection. Primary infection with VZV causes varicella.

Varicella (chickenpox) Immunisation Advisory Centre
Varicella [chickenpox] B01 Varicella [chickenpox] B01-Clinical Information. A contagious childhood disorder caused by the varicella zoster virus. It is transmitted via respiratory secretions and contact with chickenpox blister contents. It presents with a vesicular skin rush, usually associated with fever, headache, and myalgias.
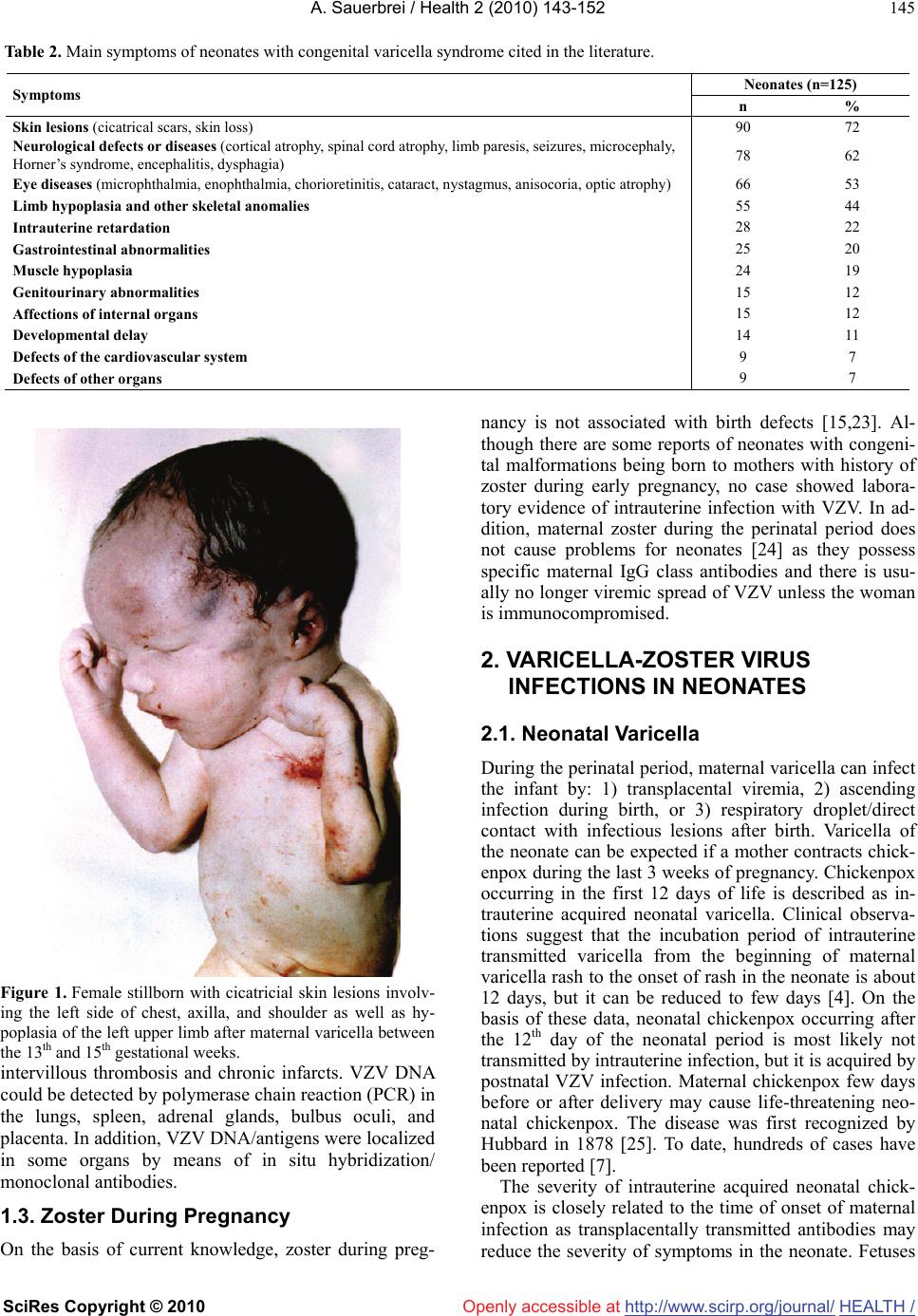
Review of varicellazoster virus infections in pregnant women and neonates
Varicella, also known as chickenpox, is a self-limited viral infection caused by varicella-zoster virus (VZV), a member of the Herpesviridae family. Prior to the clinical implementation of the varicella vaccine, more than 99% of adults aged 40 and older had evidence of previous infection. Transmission occurs via airborne respiratory droplets or.

Chickenpox (varicella zoster) Clinical Review
The diagnosis of VZV infection is usually a clinical diagnosis based on the characteristic vesicular lesions, which are seen widespread in chickenpox (varicella) or in a restricted dermatomal pattern with associated neuritis in shingles (herpes zoster). However, additional diagnostic information may be useful in the following situations:

Disseminated Varicella Infection NEJM
Although most cases of varicella or zoster are clinically unambiguous, serology may be occasionally useful in the differential diagnosis of other blistering illnesses or when infection shows an unusual complication, such as hepatitis. It may also be important to establish whether an individual is susceptible when clinical history is unclear, or.

Diagnosis Varicella Alomedika
In the differential diagnosis, providers should consider possible varicella-related complications when biologically plausible, even when varicella vaccine was received. It is also possible to distinguish vaccine-type VZV from wild type by examination of the viral deoxyribonucleic acid through specialized PCR testing [ 29 , 31 ].
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/chickenpox-symptoms1-5ae1f76a30371300367d3032.png)
Chickenpox Signs, Symptoms, and Complications
Diagnosis varicella atau cacar air (chickenpox) umumnya ditegakkan secara klinis berdasarkan karakteristik lesi kulit. Akan tetapi, pemeriksaan penunjang seperti tes Tzanck, pemeriksaan serologis, dan isolasi virus dengan polymerase chain reaction atau kultur dapat dilakukan jika perlu, terutama pada kasus-kasus yang atipikal. [3] Anamnesis.

Varicella sintomi, cause e cure Ohga!
VZG. Varicella-Zoster Ab, IgG, S. 15410-4. DEXG4. Varicella IgG Antibody Index. 5403-1. Laboratory diagnosis of acute and recent infection with varicella-zoster virus (VZV) Determination of immune status of individuals to the VZV Documentation of previous infection with VZV in an individual without a previous record of immunization to VZV.
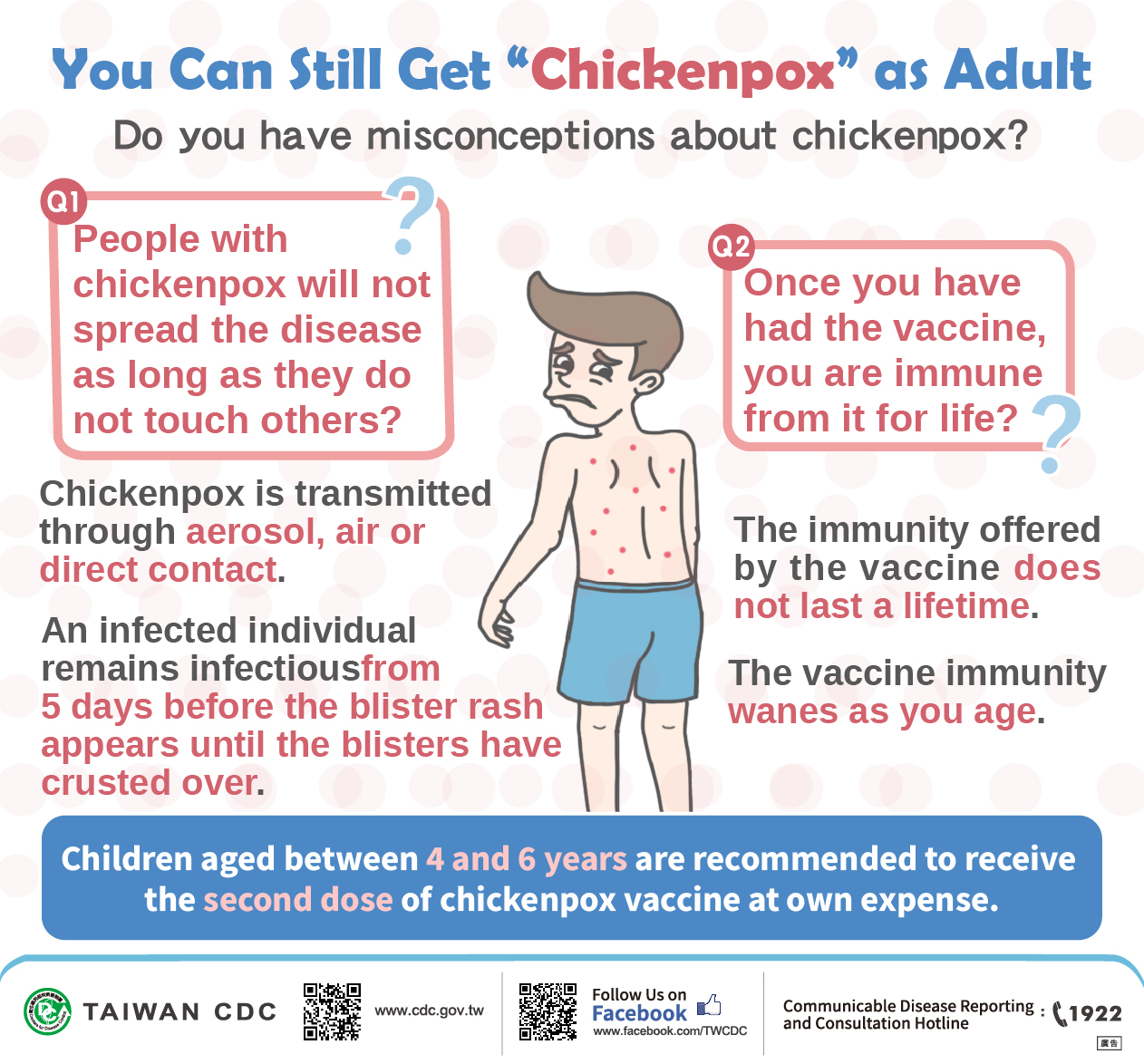
Complicated Varicella Taiwan Centers for Disease Control
A contagious childhood disorder caused by the varicella zoster virus. It is transmitted via respiratory secretions and contact with chickenpox blister contents. It presents with a vesicular skin rush, usually associated with fever, headache, and myalgias. The pruritic fluid-filled vesicles occur 10-21 days after exposure and last for 3-4 days.

VaricellaZoster Virus/Chickenpox Concise Medical Knowledge
Varicella (chickenpox) is an acute, highly contagious disease caused by varicella-zoster virus (VZV), a member of the herpesvirus family. Only one serotype of VZV is known, and humans are the only reservoir. Following infection, the virus remains latent in neural ganglia and in about 10-20% of cases it is reactivated it is reactivated to cause herpes zoster, or shingles, generally in persons.

Disseminated varicella zoster virus encephalitis The Lancet
Varicella is a highly contagious disease caused by the varicella-zoster virus (VZV). It usually presents as a generalized pruritic maculopapulovesicular rash. The incubation period is typically 14-16 days after exposure to the virus (range 10-21 days). Patients are contagious 1-2 days before rash onset until all lesions have crusted or.
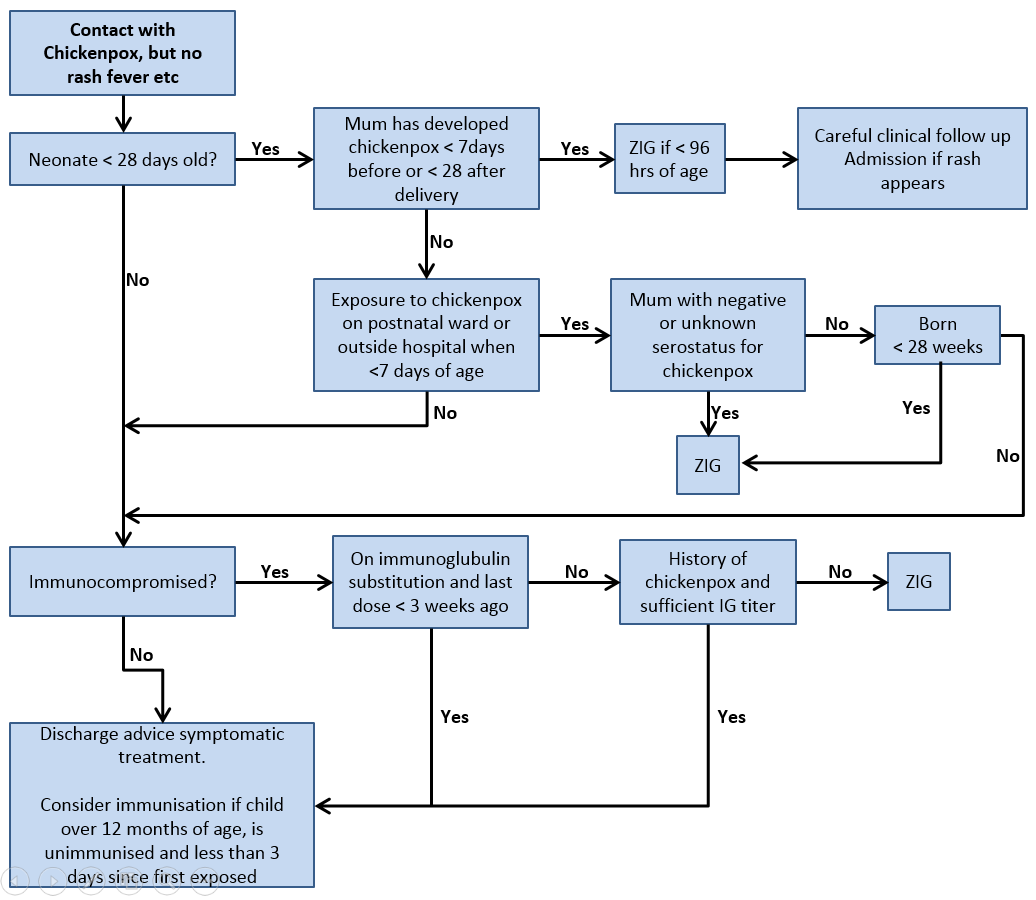
Clinical Practice Guidelines Chickenpox (varicella)
Clinical Focus: This value set contains concepts that represent varicella zoster (i.e., chickenpox and shingles) infections. Data Element Scope: This value set may use the Quality Data Model (QDM) category related to Diagnosis. Inclusion Criteria: Includes only relevant concepts associated with all varicella zoster infections. This is a grouping of ICD-10-CM and SNOMED CT codes.

Varicella Pneumonia in an Adult NEJM
Varicella was a common viral disease of children until childhood vaccination in the United States became routine during the 1990s. The disease remains common in nondeveloped countries and is seen more frequently in older children and adults. In vaccinated individuals, "breakthrough varicella" can occur. Illness is usually mild (low fever or no.
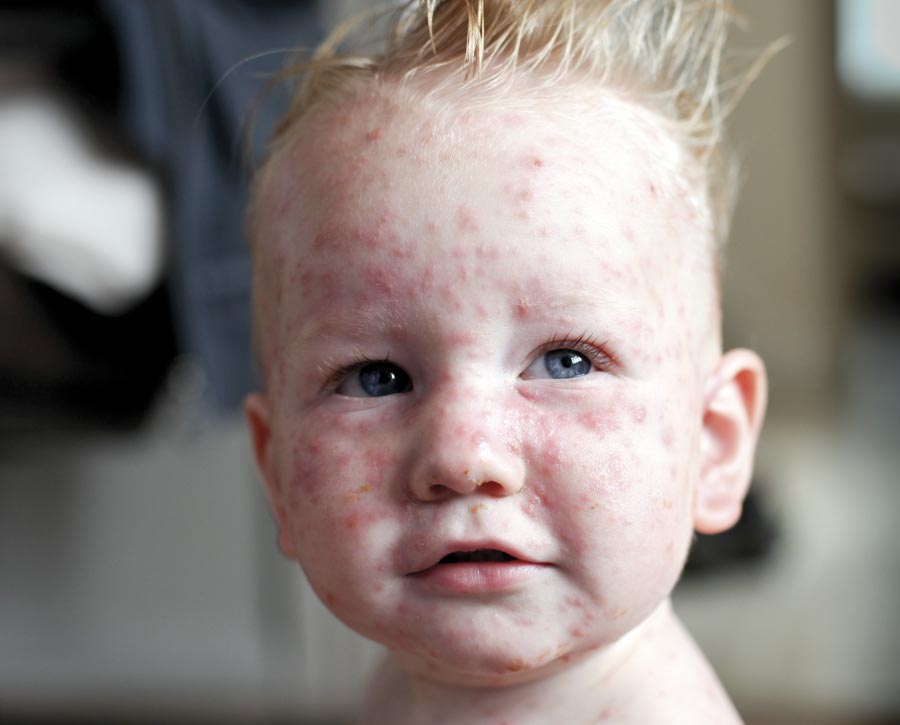
Chickenpox No Adults Allowed Medical Forum
The varicella-zoster virus (VZV) is a highly contagious virus of the herpes family. Chickenpox (or primary VZV infection) is a common childhood disease. With universal childhood varicella vaccination, which was introduced in 1995, most adults in the United States (US) and Europe are immune.[1] It is estimated that >90% of the antenatal population is seropositive for VZV IgG antibody and.