
What is Plasmodium Vivax? Life Cycle & Morphology Video & Lesson Transcript
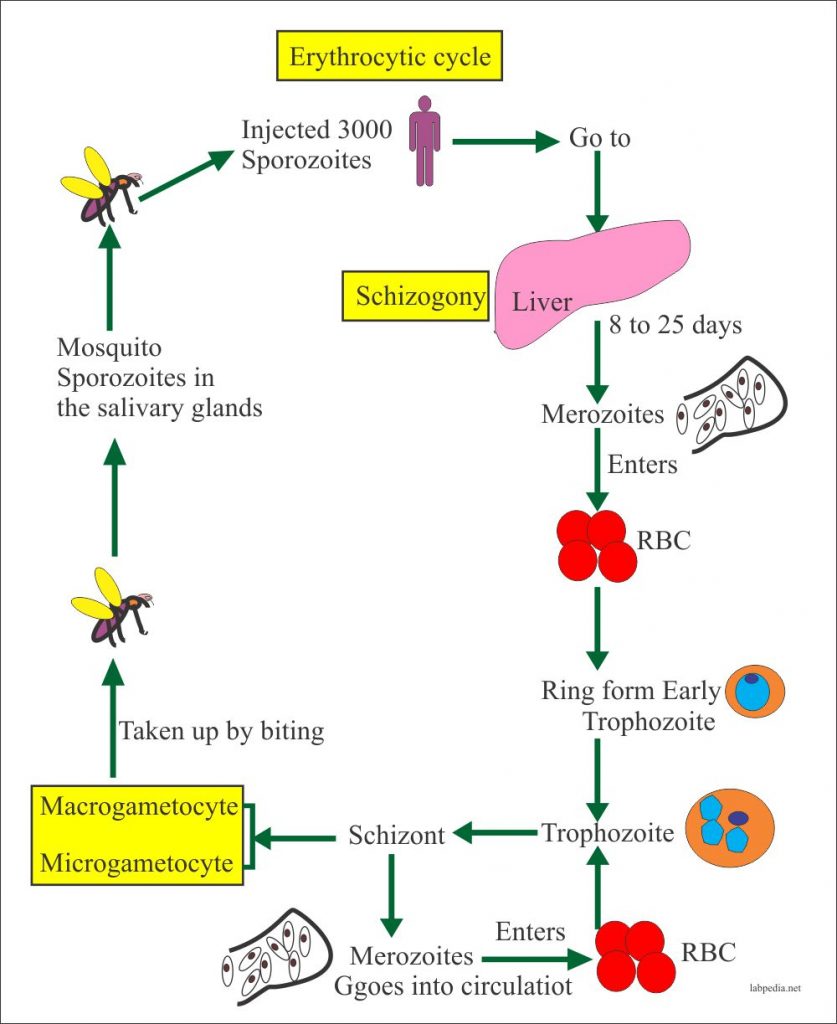
Plasmodium vivax is a protozoal parasite and a human pathogen.This parasite is the most frequent and widely distributed cause of recurring malaria. Although it is less virulent than Plasmodium falciparum, the deadliest of the five human malaria parasites, P. vivax malaria infections can lead to severe disease and death, often due to splenomegaly (a pathologically enlarged spleen).

Severity in Plasmodium vivax malaria claiming global vigilance and exploration a tertiary care
View ICD-10 Tree. Chapter 1 - Certain infectious and parasitic diseases (A00-B99) » Protozoal diseases (B50-B64) » Plasmodium vivax malaria (B51) ICD-10 Subcodes (3) B51.0 - Plasmodium vivax malaria with rupture of spleen.
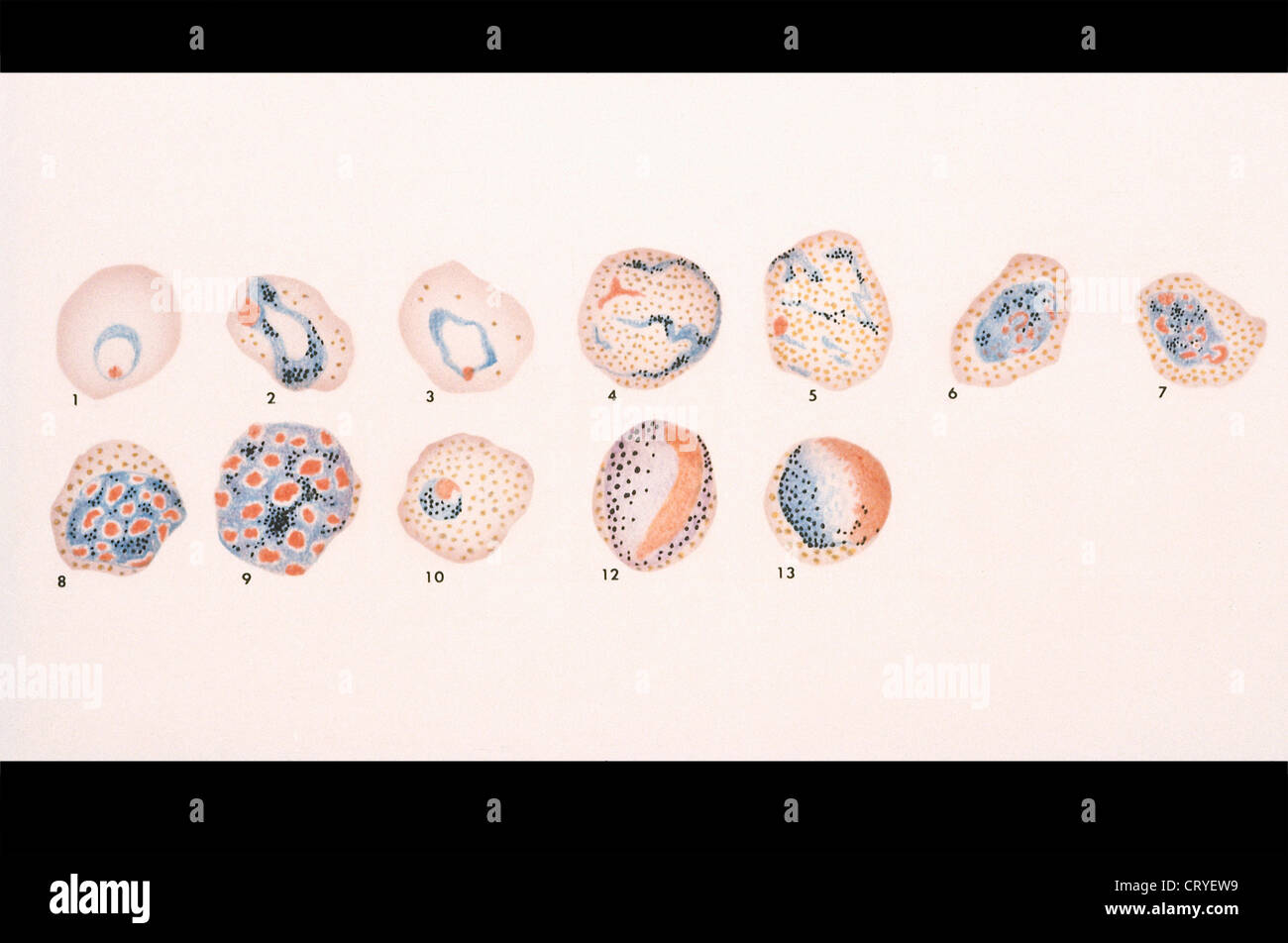
Malarial parasite Part 3 Plasmodium vivax, MP
The worldwide burden of Plasmodium vivax malaria has more than halved from an estimated 17.3 to 6.5 million cases between 2010 and 2019. This resulted from increased deployment of conventional malaria control measures (rapid diagnostic tests, effective antimalarial treatment, vector control) and significant global investment in malaria elimination.
Plasmodium vivax malaria Fotos und Bildmaterial in hoher Auflösung Seite 2 Alamy
Infection by Plasmodium vivax poses unique challenges for diagnosis and treatment. Relatively low numbers of parasites in peripheral circulation may be difficult to confirm, and patients infected by dormant liver stages cannot be diagnosed before activation and the ensuing relapse. Radical cure thus requires therapy aimed at both the blood.
Prevention of Malaria in Travelers AAFP
2024 ICD-10-CM Range B50-B64. Protozoal diseases. Type 1 Excludes. amebiasis ( A06.-) other protozoal intestinal diseases ( A07.-) Protozoal diseases. Clinical Information. Malaria caused by plasmodium vivax. This form of malaria is less severe than malaria, falciparum, but there is a higher probability for relapses to occur.

The anaemia of Plasmodium vivax malaria Malaria Journal Full Text
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code B50. B50 Plasmodium falciparum malaria. B50.0 Plasmodium falciparum malaria with cerebral c. B50.8 Other severe and complicated Plasmodium falci. B50.9 Plasmodium falciparum malaria, unspecified. B50.-) Includes. mixed infections of Plasmodium vivax with other Plasmodium species, except Plasmodium falciparum.

Plasmodium vivax Scientists Against Malaria
Includes. mixed infections of Plasmodium malariae with other Plasmodium species, except Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium vivax. The following code (s) above B52 contain annotation back-references that may be applicable to B52 : A00-B99. 2024 ICD-10-CM Range A00-B99. Certain infectious and parasitic diseases.
Free picture micrograph, cells, malaria, vivax, trophozoites
Plasmodium vivax malaria without complication. B51.9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2024 edition of ICD-10-CM B51.9 became effective on October 1, 2023. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of B51.9 - other international versions of ICD-10 B51.9 may differ.

Protection against malaria The BMJ
Malaria is a significant global health problem with a substantial disease burden worldwide. In 2019 there were approximately 229 million cases of malaria responsible for about 409000 deaths, the majority on the African continent (WHO World Malaria Report 2020). Malaria results from infection with single-celled parasites belonging to the Plasmodium genus. Five species of Plasmodium are known to.

Key gaps in the knowledge of Plasmodium vivax, a neglected human malaria parasite The Lancet
Summary points. The worldwide burden of Plasmodium vivax malaria has more than halved from an estimated 17.3 to 6.5 million cases between 2010 and 2019. This resulted from increased deployment of conventional malaria control measures (rapid diagnostic tests, effective antimalarial treatment, vector control) and significant global investment in malaria elimination.
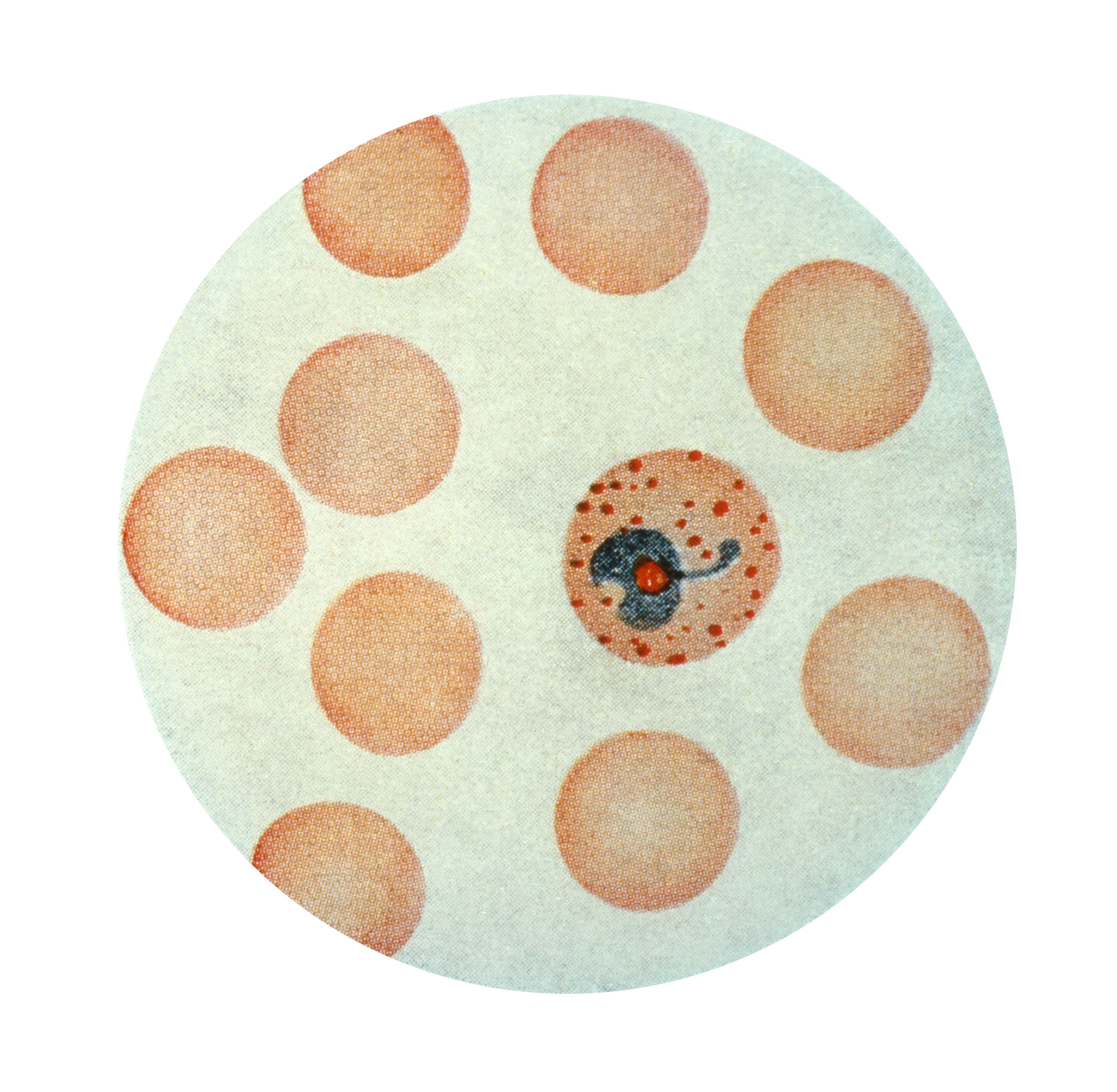
Free picture plasmodium vivax, erythrocytic, trophozoite, stage
View ICD-10 Tree Chapter 1 - Certain infectious and parasitic diseases (A00-B99) » Protozoal diseases (B50-B64) » Plasmodium vivax malaria without complication (B51.9) Related MeSH Terms Malaria, Vivax D016780. 1 indication for 38 drugs (16 approved, 22 experimental).
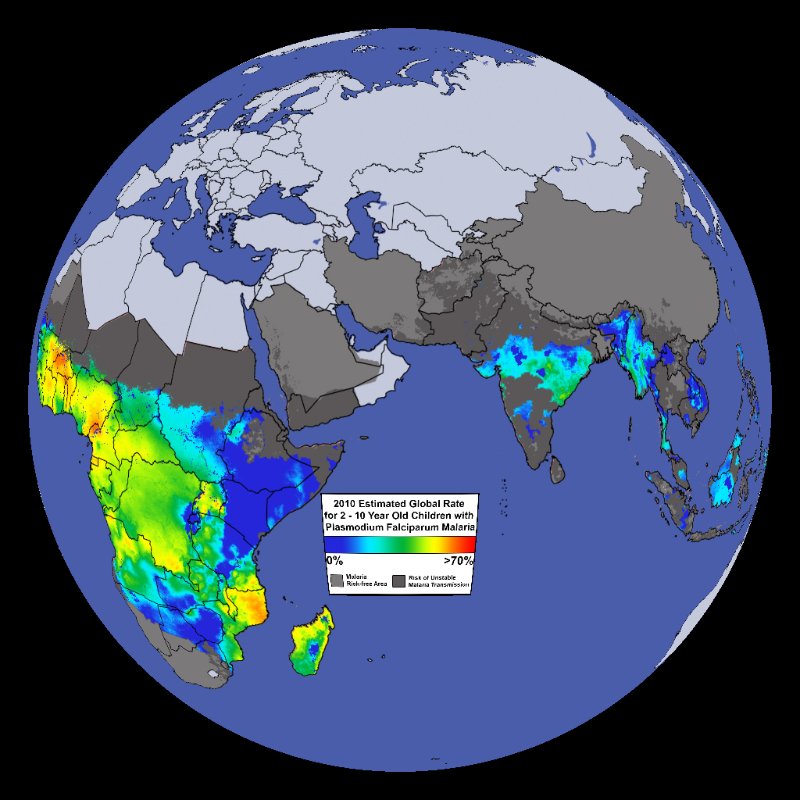
Malaria Plasmodium Vivax with Duffynegative layer Science On a Sphere
ICD-10. ICD-10-CM Codes. Certain infectious and parasitic diseases. Protozoal diseases. Plasmodium vivax malaria (B51) B50.9. B51. B51.0.

Plasmodium vivax MSP1 The Native Antigen Company
2 Strategies for the control and elimination of P. vivax malaria 22 2.1 Vector control 22 2.2 Chemoprevention 25 2.3 Diagnosis of P. vivax infections 26 2.4 Diagnosis of G6PD deficiency 28 2.5 Treatment of uncomplicated P. vivax malaria 30 2.6 Treatment of severe P. vivax malaria 34 2.7 Drug resistance 36 2.8 Surveillance 38 3 Innovations needed 42
PLASMODIUM VIVAX MALARIA Stockfotografie Alamy
Plasmodium vivax malaria with rupture of spleen. B51.0 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2024 edition of ICD-10-CM B51.0 became effective on October 1, 2023. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of B51.0 - other international versions of ICD-10 B51.0 may differ.
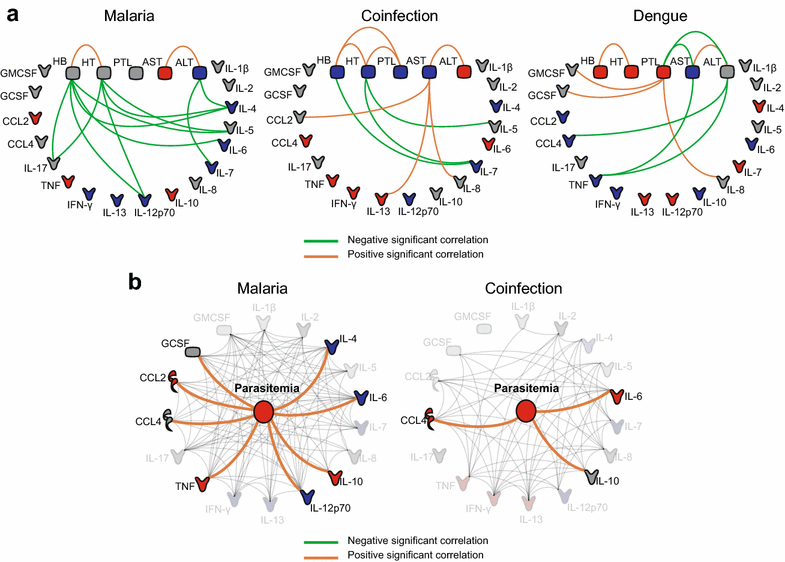
Unravelling the patterns of host immune responses in Plasmodium vivax malaria and dengue co
Non-falciparum malaria refers to malaria infection due to Plasmodium species other than P. falciparum; these include P. vivax, P. ovale, P. malariae, and P. knowlesi ( table 1 ). Worldwide, the greatest mortality due to malaria is associated with P. falciparum infection. However, the non-falciparum malarias can also cause significant morbidity.
Frontiers Plasmodium vivax Biology Insights Provided by Genomics, Transcriptomics and Proteomics
Microscopy. Standards for malaria microscopy training, certification, and practice are available from World Health Organization (WHO). 3, 4 Examination of at least 200 fields of a thick blood film under oil immersion magnification (×1,000) should be undertaken before a negative diagnosis is made. The limit of detection for expert microscopists is considered to be about 10-20 parasites/μL.