
Molisch's Test Definition, Reaction, Reagent, and Procedure
Molisch's test is a sensitive chemical test, named after Austrian botanist Hans Molisch,. and polysaccharides (except trioses and tetroses)- should give a positive reaction, and nucleic acids and glycoproteins also give a positive reaction, as all these compounds are eventually hydrolyzed to monosaccharides by strong mineral acids.

Réaction de Molisch
Molisch's test is a qualitative test used to detect the presence of aldehydes and ketones in a sample. The test uses a reagent made up of Schiff's reagent and concentrated sulfuric acid. When the reagent is added to a sample containing aldehydes or ketones, the aldehydes or ketones will react with the Schiff's reagent to form a colored.

PPT Lecture 1. WET METHODS OF CARBOHYDRATE ANALYSES PowerPoint Presentation ID323603
Quick Reference. A biochemical test to detect the presence of carbohydrates in solution, also known as Molisch's test (after the Austrian chemist H. Molisch (1856-1937), who devised it). A small amount of alcoholic alpha-naphthol is mixed with the test solution and concentrated sulphuric acid is poured slowly down the side of the test tube.

Molisch’s Test Objectives, Principle, Reagents, Procedure and Result Online Biology Notes
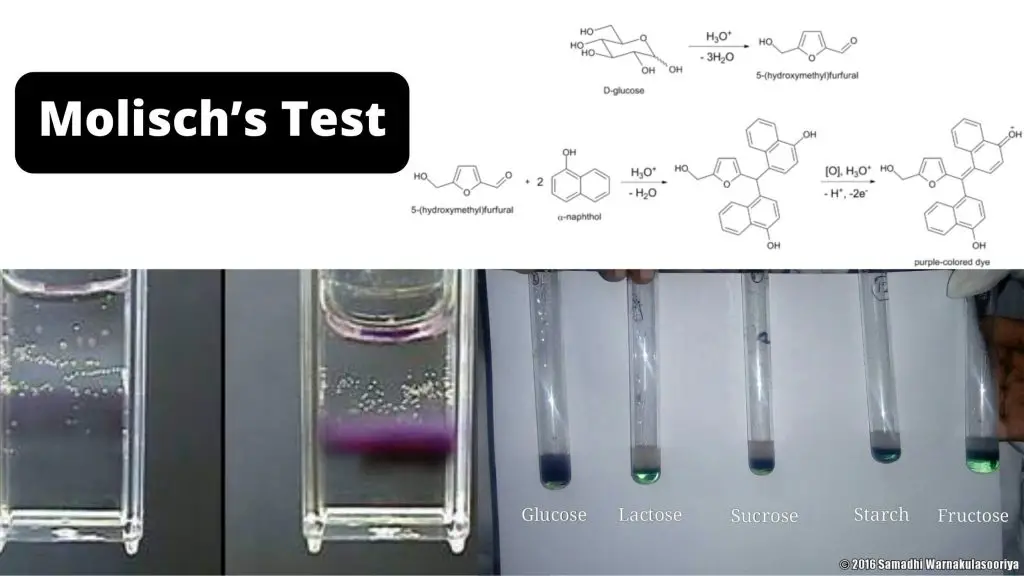
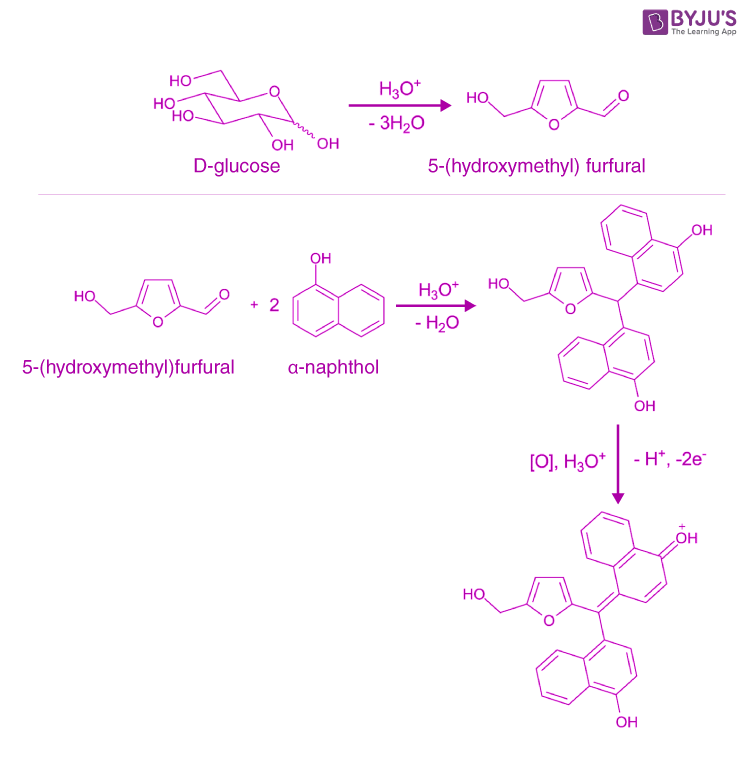
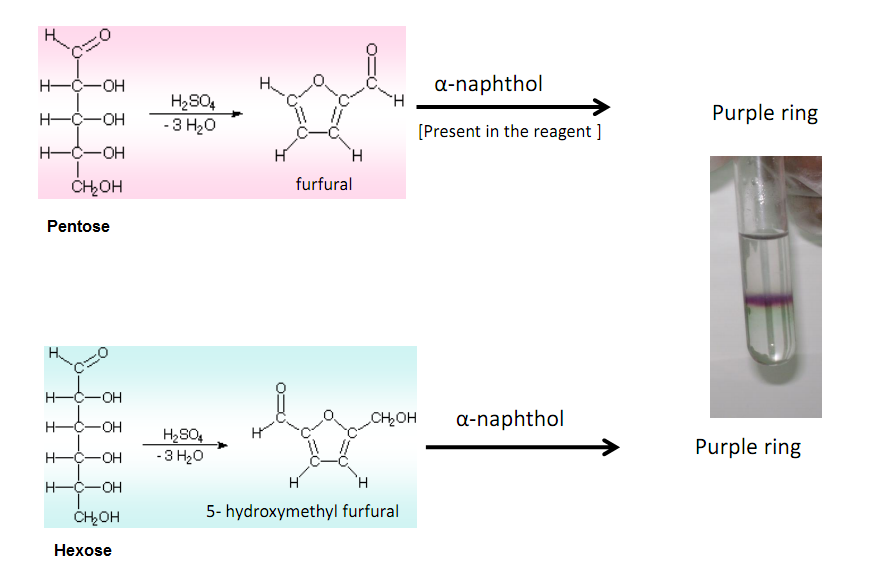
Molisch Test Principle. During the reaction, applying sulphuric acid can remove the water molecules from the given carbohydrate; hence aldehyde is generated. The α-naphthol in molischs reagent undergoes condensation with the aldehyde, forming a reddish-purple-coloured complex. A detailed feature of the Molisch Test on D-glucose is provided.

Reacción de Molish Mecanismo Completo Identificación de carbohidratos YouTube
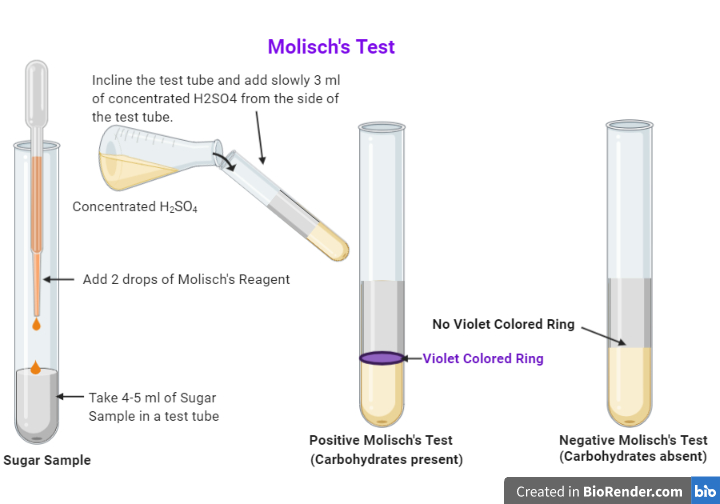
Molisch's Test Procedure. 2-3 drops of Molisch's reagent must be added to a small amount of the analyte in a test tube and mixed well. Now, a few drops of concentrated sulphuric acid must be added drop-wise along the walls of the test tube to facilitate the formation of a layer and avoid mixing. The development of a purple ring at the layer.

A, B and C are three biomolecules. the results of teh tests performed on them are given below
Request PDF | On Jan 1, 2021, Zhiyou Hao and others published Molisch's Reaction: Discovery, Mechanism and Application | Find, read and cite all the research you need on ResearchGate

Reactie van Molisch
Molisch's reaction. Molisch's test: reactives, sulphuric acid and 2% -naphtol in ethanol (a) and steps of procedure of application (b and c).

Figure 1. Molisch test for Carbohydrates Laboratory Activities to Introduce Carbohydrates
Molisch test is a group test for all carbohydrates, either free or bound to proteins or lipids.. so they do not give a positive result for this reaction. Molisch test is not a specific test for carbohydrates. Furfurals as such or furfural yielding substance, some organic acids like citric acids, lactic acid, oxalic acid, formic acid, etc.
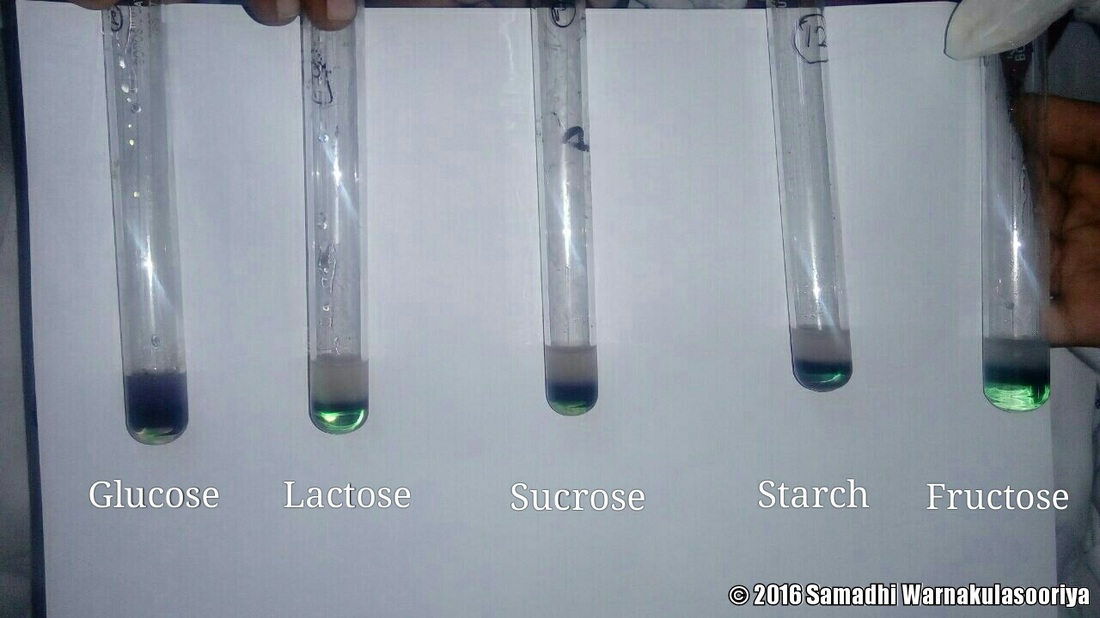

Molisch’s Test Objectives, Principle, Reagents, Procedure and Result
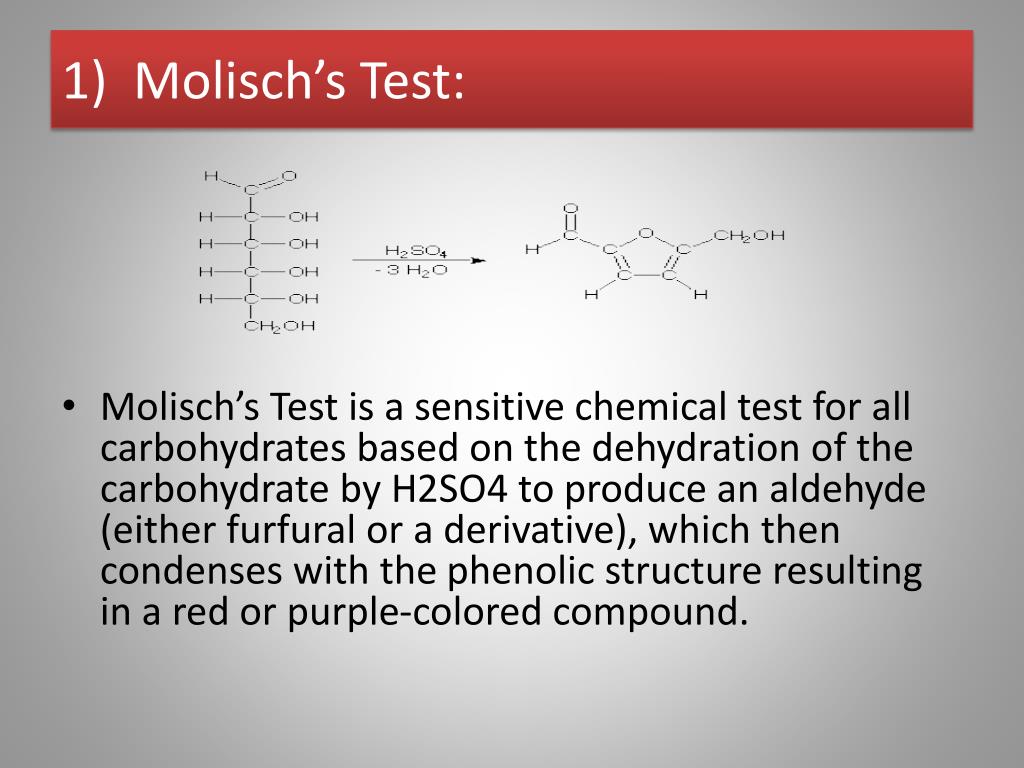
Therefore, Molisch's test is very important for the detection of the presence of carbohydrates in a substance. Principle of Molisch Test. The reaction is generally based on the fact that the concentrated acid helps in catalysing the dehydration of sugars to form furfural (via pentoses) or hydroxymethylfurfural (via hexoses).
PPT Lab Activity1 Carbohydrates PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1998637
Reactions: The test reagent dehydrates pentoses to form furfural (top reaction) and dehydrates hexoses to form 5-hydroxymethyl furfural (bottom reaction).. Two drops of the Molisch reagent (a solution of -napthol in 95% ethanol) is added. The solution is then poured slowly into a tube containing two ml of concentrated sulfuric acid so that.
Molisch’s Test Objective, Principle, Procedure, Result
Molisch's test is a general test for all carbohydrates. In this test, carbohydrates when reacted with conc. H2SO4 get dehydrated to form furfural and its derivatives. When monosaccharide are treated with conc H2SO4 or conc HCl, -OH group of sugar are removed in the form of water and furfural is formed from pentose sugar and hydroxymethyl furfural is formed from hexose sugar.

01 Réaction de MOLISCH YouTube
: After the discovery in the year 1886, Molisch's reaction used to be applied as a powerful tool to differentiate carbohydrates and glycosides qualitatively from other materials. A brief review is given herein on the discovery, reaction mechanism and application of Molisch's reaction. Perspectives are also given on the potential applications of Molisch's reaction.

Practical Biochemistry
PROCEDURE: To 2ml of sugar solution (original solution) add 2 to 3 drops of Molisch's reagent. Mix thoroughly. Carefully pour 5 ml concentrated H2SO4 along the side of the test tube. Acid being heavier will form a layer beneath the sugar solution.
Molisch’s Test Principle, Procedure, Reaction, & Reagent Preparation
What is Molisch's Test? Molisch test is a colourimetric method for the analysis of the presence of carbohydrates in a given analyte. This test is named after Austrian botanist Hans Molisch. Molisch's test is done by using Molisch reagent. A solution of naphthol in ethanol (95%) is known as Molisch reagent. It's also known as the purple.
Molisch's Test Definition, Principle, Procedure, Result, Uses
Identification Tests for Carbohydrates (Playlist 👇🏻)https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TB7lbHTOoh0&list=PLEIbY8S8u_DJunHAPAJ8_GcQQ1Rbn1NMVBasics of Analytical.
Molisch’s Test Objectives, Principle, Reagents, Procedure and Result Online Biology Notes
Wikipedia says. Molisch's test is a sensitive chemical test, named after Austrian botanist Hans Molisch, for the presence of carbohydrates, based on the dehydration of the carbohydrate by sulfuric acid or hydrochloric acid to produce an aldehyde, which condenses with two molecules of a phenol (usually α-naphthol, though other phenols such as resorcinol and thymol) also give colored products.