
STEMI EKG Map
ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) is a clinical syndrome defined by the presence of myocardial ischemic symptoms, electrocardiographic (ECG) findings of new ST-segment elevations in two continuous leads or new left bundle branch block, and subsequent detection of biomarkers indicative of myocardial injury. 1 It is estimated.

STEMI case examples wikidoc
A total of 110 (4.4%) patients met diagnostic criteria for MINOCA. All-cause mortality at 30-days and 1-year were 3.6% and 4.5%, respectively. In our cohort, 1 in 20 patients presenting with STEMI had MINOCA. This is the first description of the relatively high incidence of MINOCA in a STEMI cohort using current ESC definition and diagnostic.

STElevation Myocardial Infarction (STEMI) Guidelines Pocket Guide Guideline Central
I. Introduction. Although considerable improvement has occurred in the process of care for patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI), room for improvement exists. 1-3 The purpose of the present guideline is to focus on the numerous advances in the diagnosis and management of patients with STEMI since 1999. This is reflected in the changed name of the guideline: "ACC/AHA.
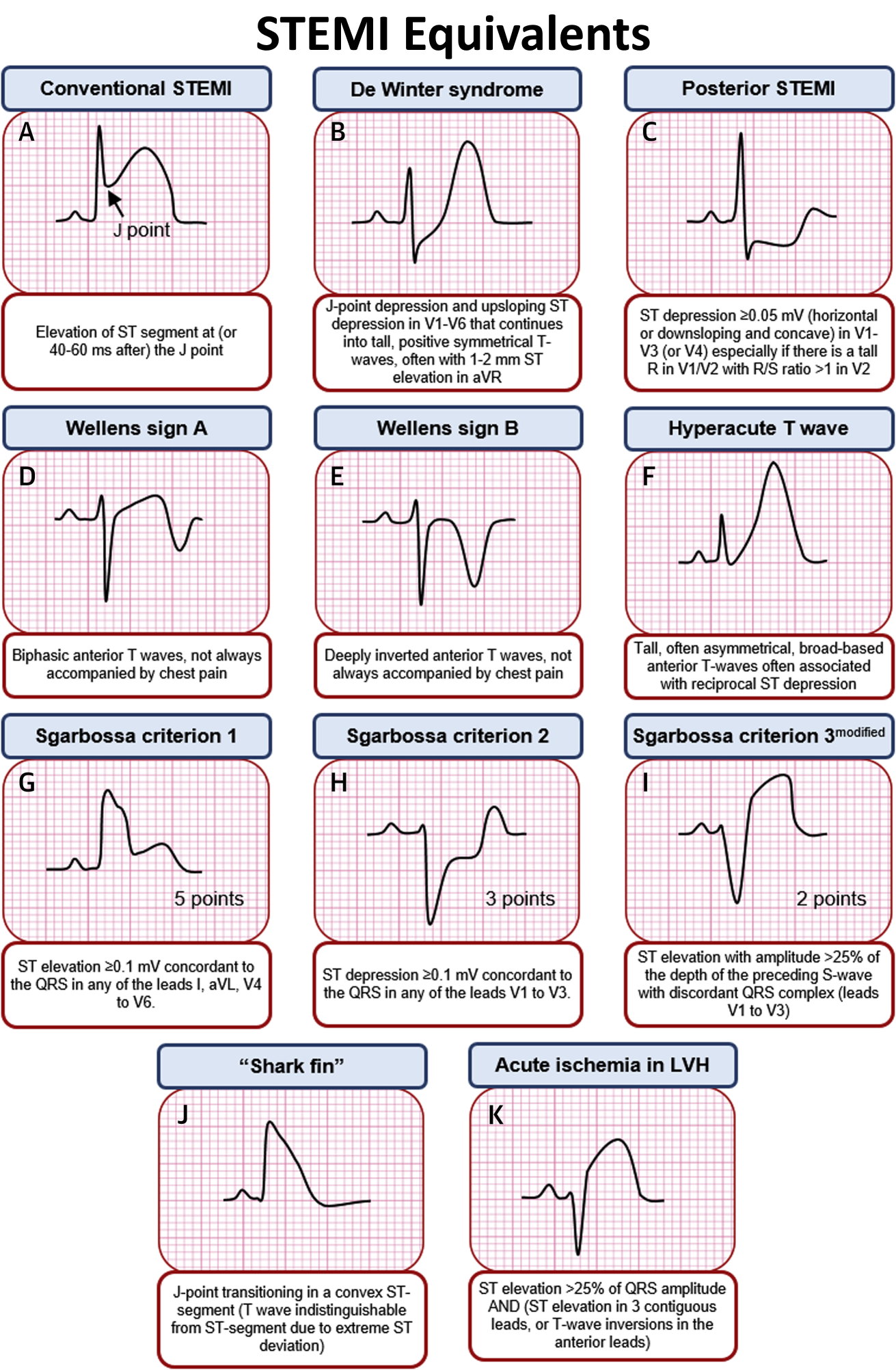
STEMI Equivalents on ECG • Conventional STEMI Elevation GrepMed
Introduction. Antithrombotic therapy is an essential part of the management of the full spectrum of acute coronary syndromes (ACS). 1 Both antiplatelets and anticoagulants seem to be necessary in the management of ACS (Figures 1 and 2), although the exact proportion of antithrombotic effect that each drug and class should ideally provide remains a matter of ongoing study.
Acute Stemi Ekg
An ST elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) most commonly occurs when plaque rupture and thrombus formation results in complete occlusion of a major epicardial coronary vessel. STEMI is a life-threatening, time-sensitive emergency that must be diagnosed and treated promptly. This is because heart muscle starts to be lost once a coronary.

Mastering STEMI ECG
Approximately 90% of patients with myocardial infarction have angiographic evidence of obstructive coronary artery disease (CAD) based on registry studies published more than 30 years ago [1, 2].The realisation that obstructive CAD was causative in the majority of patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI), led to the development of current management strategies including.
Diagnosis dan Tatalaksana ACS STEMI Dengan Kasus Kedokteran Caiherang
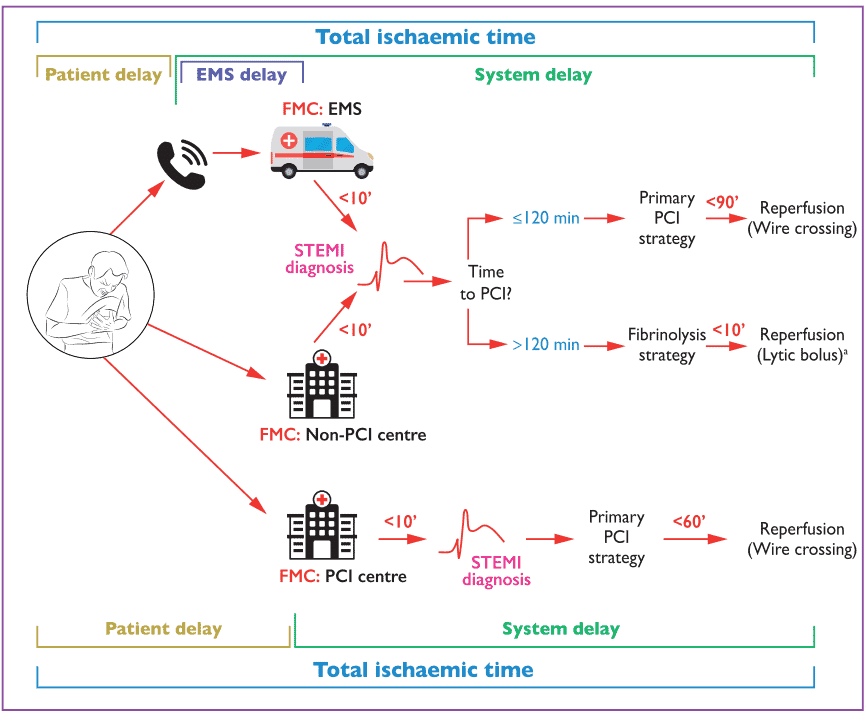
In 2007, the American Heart Association (AHA) introduced Mission: Lifeline, a national initiative to coordinate and improve the quality of care delivered to patients with ST-segment-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) and to decrease related mortality and morbidity. 1 The initial focus of Mission: Lifeline was to increase the number of patients with STEMI with timely access to primary.

Šlep služba Stemi RV monaco izgoreo unutra YouTube
Introduction. Acute ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) is a major cause of mortality worldwide. The rapid restoration of blood flow in the occluded culprit coronary artery with primary percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) will prevent heart failure, preserves ventricular function and reduces mortality [1-4].The cause of STEMI is erosion or rupture of an atherosclerotic plaque.

Diagnostic−therapeutic pathway of STEMI in patients undergoing 5FU... Download Scientific Diagram
In an analysis published online last week in JAMA Network Open, the 5-year mortality risk was nearly twofold higher in true MINOCA patients than in those with obstructive CAD (HR 1.93; 95% CI 1.06-3.53), investigators report. "Traditionally, MINOCA and mimickers are thought to be less-lethal diseases," lead author Odayme Quesada, MD (The.
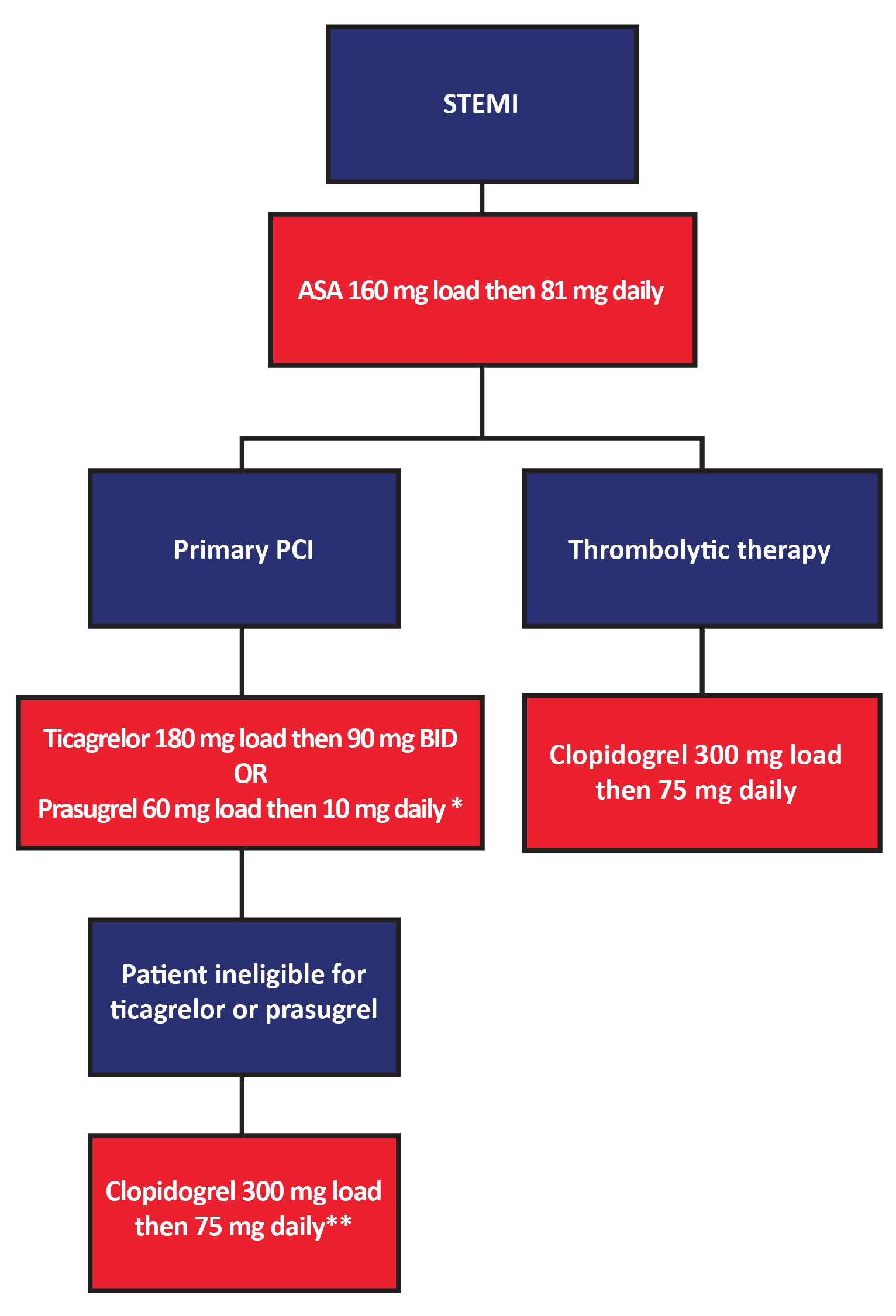
antiplatelet management of STEMI01 Thrombosis Canada Thrombose Canada
Cardiovascular disease and its sequalae remain one of the largest health care problems in the United States. Each year there are approximately 620,000 new cases of acute coronary syndrome (ACS) and 295,000 recurrent ACS events. 7 ACS can be subdivided into three different categories: unstable angina (UA), non ST-elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI), and ST-elevation myocardial infarction.
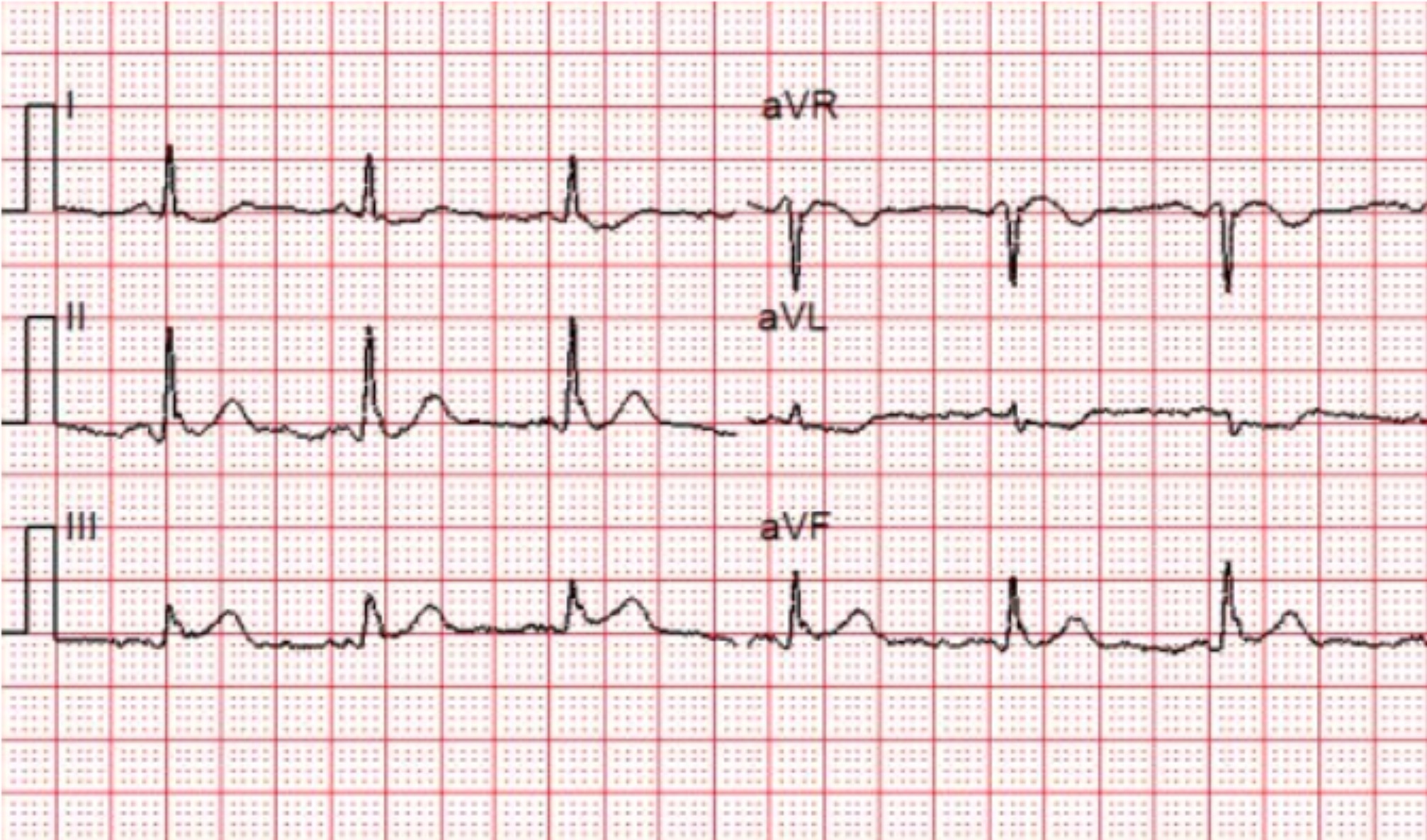
Sgarbossa STEMI 25 File
By L.A. McKeown. ATLANTA, GA—Patients who present with STEMI and a current or recent COVID-19 infection often have no culprit lesion, with a greater likelihood of this being the case in women than men, a prespecified analysis of the North American COVID-19 Myocardial Infarction (NACMI) registry shows. One-third of women and 18% of men had no.
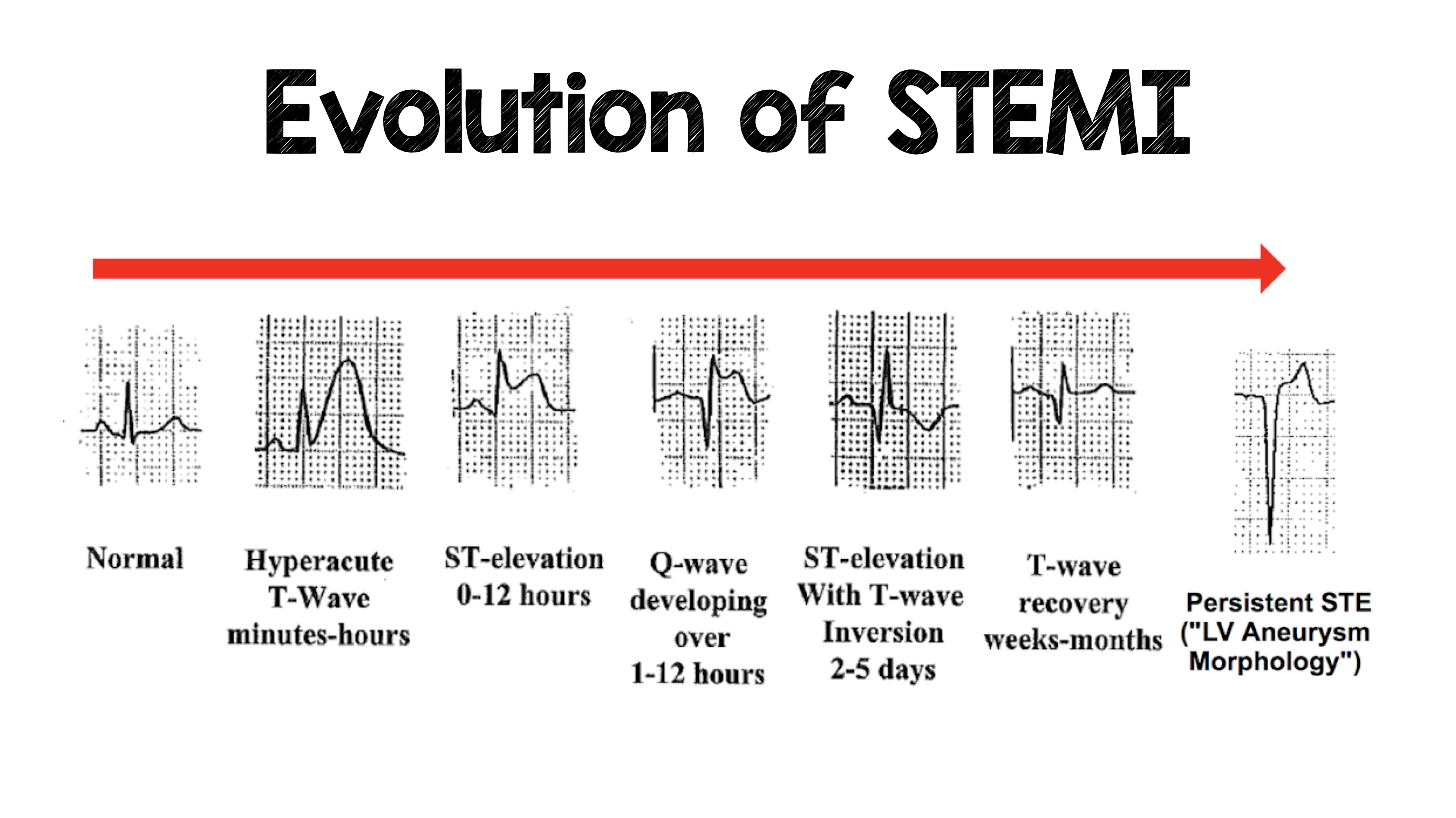
The Evolution of STEMI ECG Changes STEMI Evolution GrepMed
STEMI Heart Attack. An ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) is a type of heart attack that mainly affects your heart's lower chambers. They are named for how they change the appearance of your heart's electrical activity on a certain type of diagnostic test. STEMIs tend to be more severe and dangerous compared to other types of heart.
Dr. Smith's ECG Blog Anterorlateral STEMI? Old Anterior MI? But cath shows RCA thrombotic stenosis.
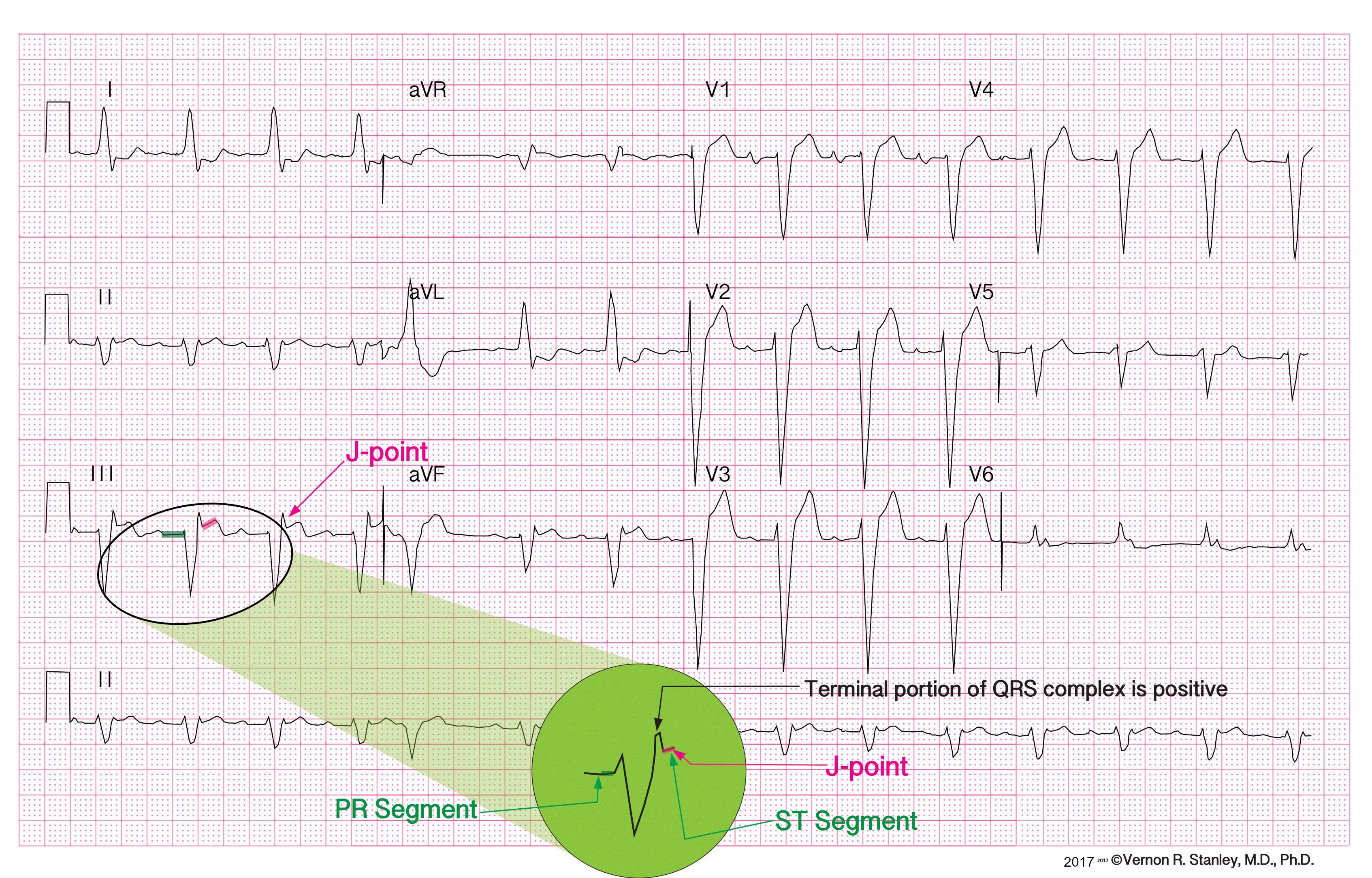
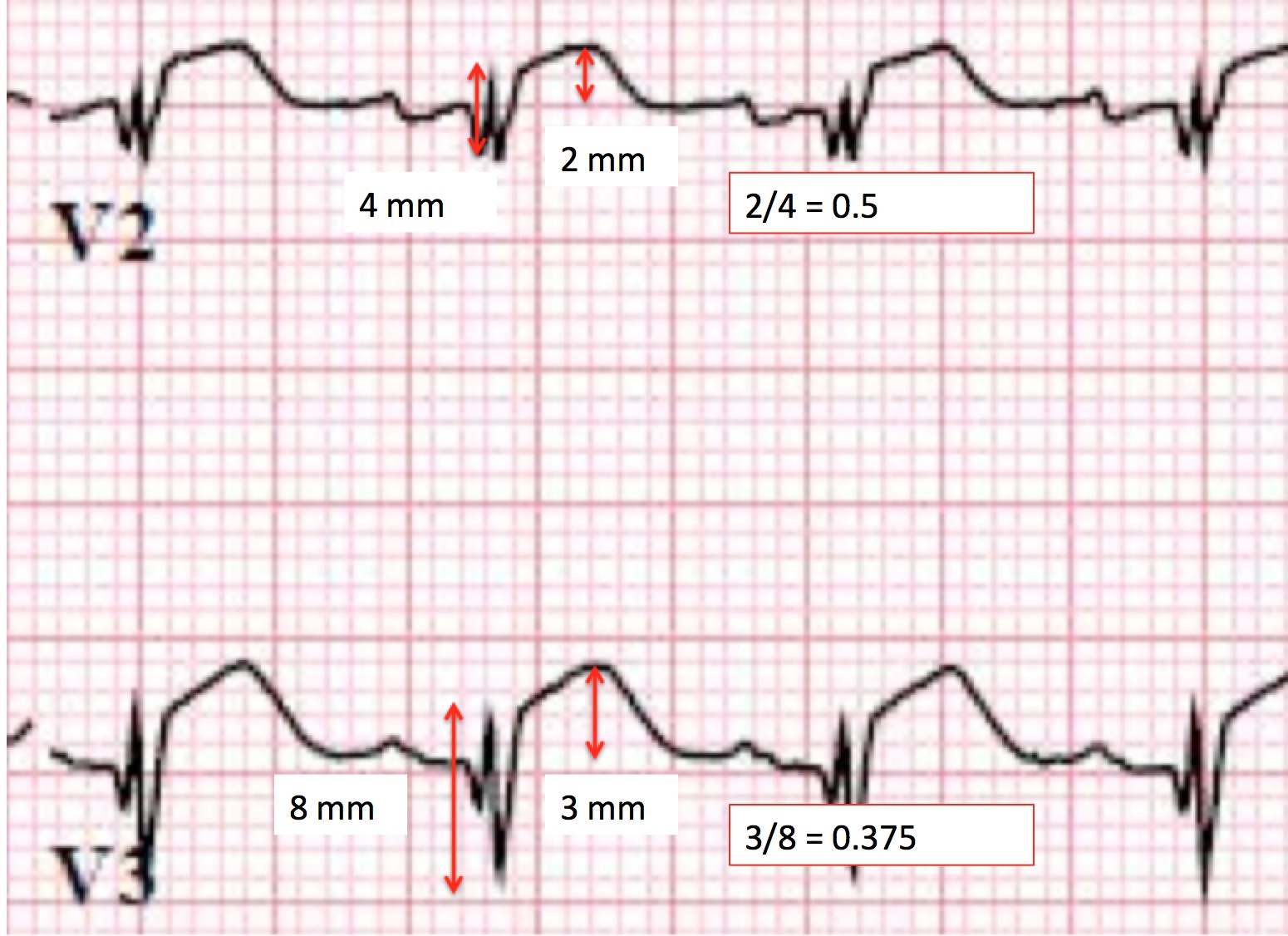
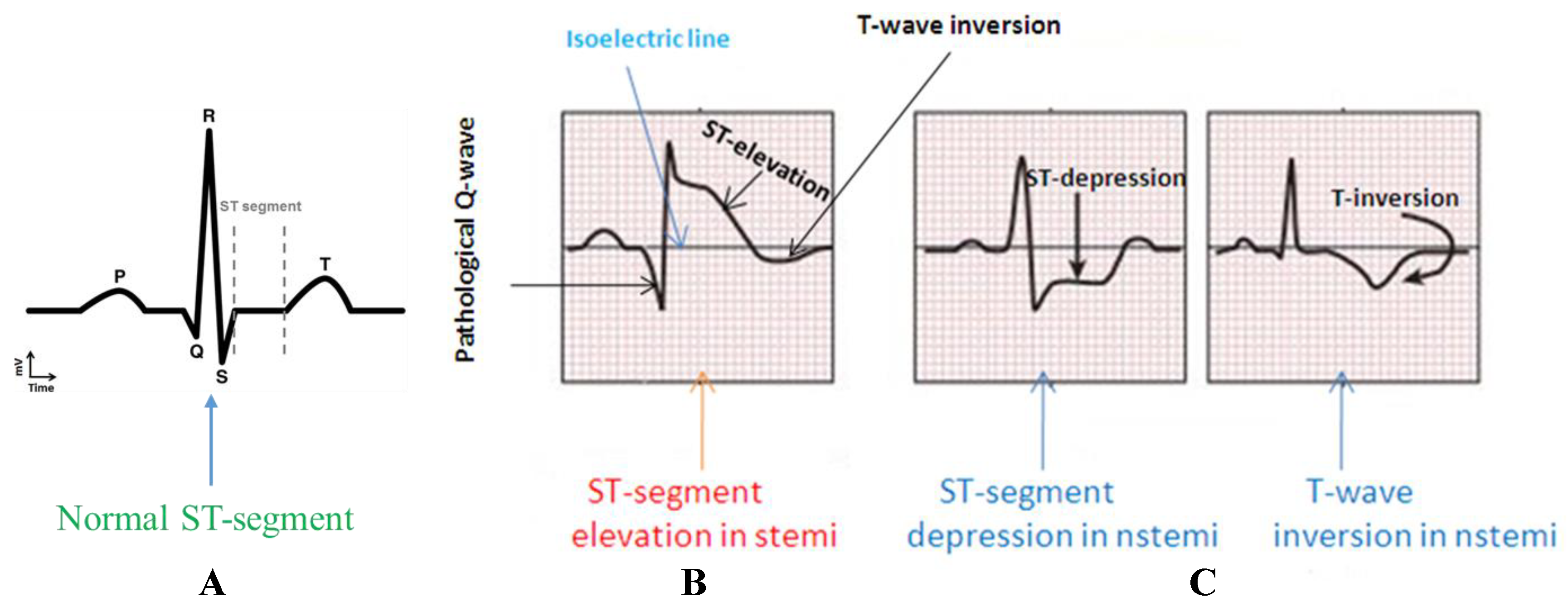
ECG (EKG) in acute STEMI (ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction) The ECG is the key to diagnosing STEMI. ECG criteria for STEMI are not used in the presence of left bundle branch block or left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) because these conditions cause secondary ST-T changes which may mask or simulate ischemic ST-T changes. ST segment elevation is measured in the J-point and the elevation must.
Eck Ecg Made Easy Ischemia Nstemi Stemi Myocardial Infarction Lead Sexiz Pix
The 'Enoxaparin and Thrombolysis Reperfusion for Acute Myocardial Infarction Treatment Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction' (ExTRACT-TIMI 25) trial performed in 2006 was a randomized controlled trial that involved 20,506 patients who received intravenous unfractionated heparin with maintenance of an activated partial-thromboplastin time at 1..

Introduction to ACS Thrombosis Adviser
MONABASH - Management of ACS. MNEMONICS, Pharmacy and Therapeutics. UA/NSTEMI (NSTE ACS) Anti-Ischemic and other Treatment. - M orphine sulfate 2 to 4 mg IV PRN for severe pain. May repeat dose of 2 to 8 mg at 5 to 15-minute intervals. - O xygen via nasal cannula to keep SaO2 > 92%. - N itroglycerin (NTG) 0.3-0.6 mg SL q5min PRN chest pain.

STEMI Old Dominion EMS Alliance, Inc.
Importance Recognizing the association between timely treatment and less myocardial injury for patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI), US national guidelines recommend specific treatment-time goals.. Objective To describe these process measures and outcomes for a recent cohort of patients.. Design, Setting, and Participants Cross-sectional study of a diagnosis-based.