PPT The Energy Equation PowerPoint Presentation ID3821957
This paper contains a revision of the Harris-Benedict equations through the development and validation of new equations for the estimation of resting metabolic rate (RMR) in normal, overweight, and obese adult subjects, taking into account the same anthropometric parameters. A total of 722 adult Caucasian subjects were enrolled in this analysis.

CARA MUDAH MENGHITUNG KEBUTUHAN KALORI DENGAN RUMUS HARRIS BENEDICT YouTube
Contoh menghitung kebutuhan gizi pasien dengan menggunkan Rumus Harris Benedict yang di sesuaikan dengan kondisi pasien baik aktivitas dan faktor stress. Kasus: Ibu X usia 33 tahun dengan usia kehamilan hampir menginjak 6 bulan (22 minggu). Aktivitas ibu X hanya seorang ibu rumah tangga dan pekerjaan rumah dikerjakan bersama suami.

PPT Nutrition Chapter 18 PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5653871
Rumus yang paling banyak digunakan oleh ahli gizi untuk menghitung BMR adalah Rumus Harris-Benedict. Caranya bisa kamu hitung berdasarkan usia, jenis kelamin, berat badan, dan tinggi badan. Berikut cara menghitung kebutuhan kalori: Untuk laki-laki: 66,5 + (13,75 x berat badan dalam kilogram) + (5,003 x tinggi badan dalam cm) - (6,75 x usia)

The Harris Benedict Equation Understanding Your Basal Metabolic Rate
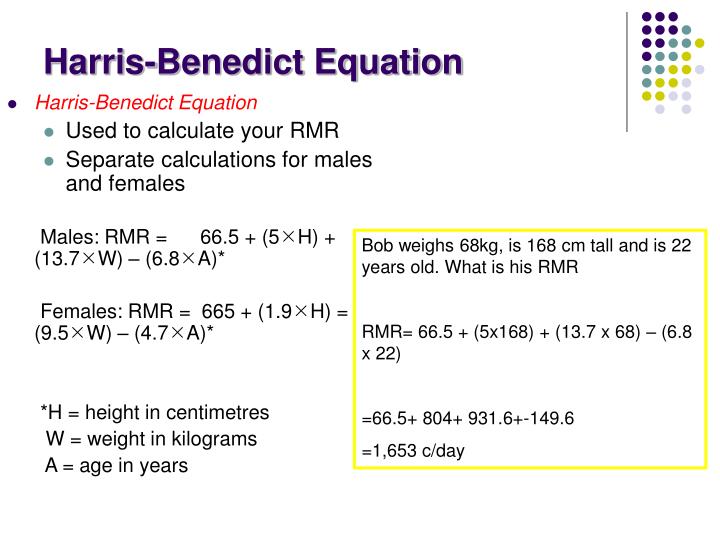
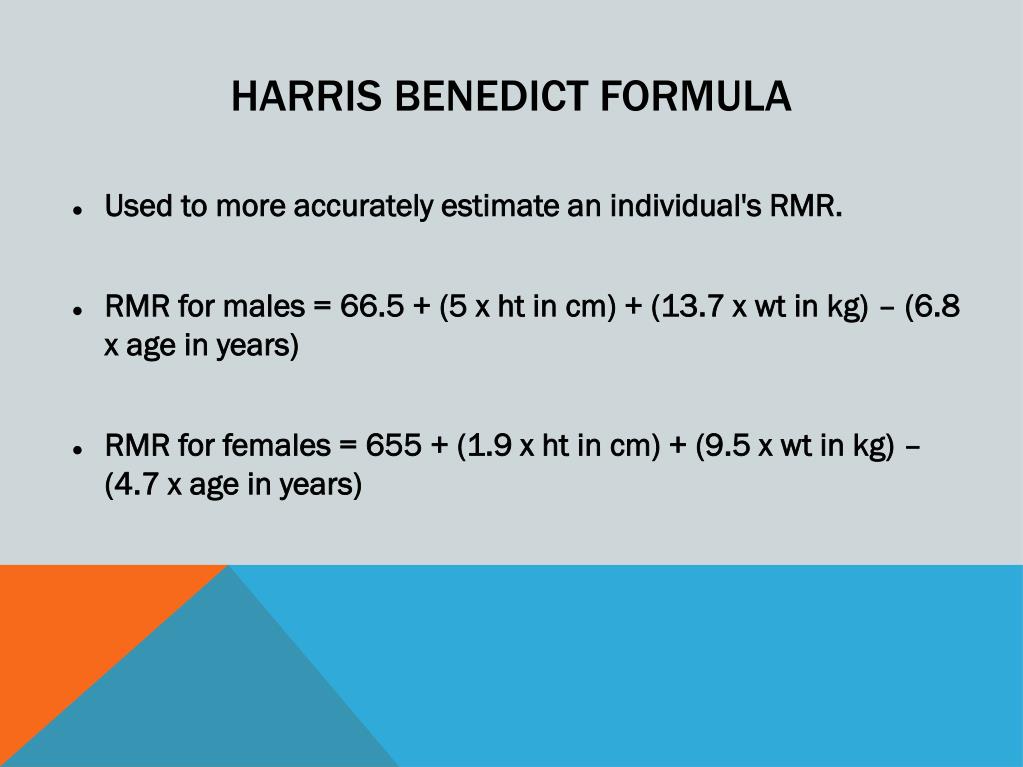
Cara paling mudah untuk mengetahui BMR Anda yaitu dengan menggunakan rumus Harris-Benedict. Rumus BMR ini dibedakan antara pria dan wanita. Cara menghitung BMR pada pria dan wanita dapat diketahui dengan rumus di bawah ini. BMR Pria = 66,5 + (13,7 × berat badan) + (5 × tinggi badan) - (6,8 × usia)

Harris Benedict Formula Example
Harris-Benedict Equation was proposed by J. A. Harris and F. G. Benedict in the book "A Biometric Study of Basal Metabolism in Man" published in 1919. To determine daily calorie requirements, the value of Basal Metabolic Rate is multiplied by a factor that reflects the activity level of an individual. The result is the recommended daily calorie.
Use Harris Benedict Formula Calculator for BMR
Rumus Harris-Benedict merupakan salah satu rumus yang sering digunakan oleh ahli gizi. Rumus ini memperhitungkan usia, jenis kelamin, berat badan, tinggi badan, dan tingkat aktivitas Anda. Pertama-tama, Anda perlu menghitung basal metabolism rate (BMR) terlebih dahulu. BMR atau laju metabolisme basal adalah perkiraan jumlah energi yang.

Estimating Daily Caloric Intake using Harris Benedict Equation YouTube
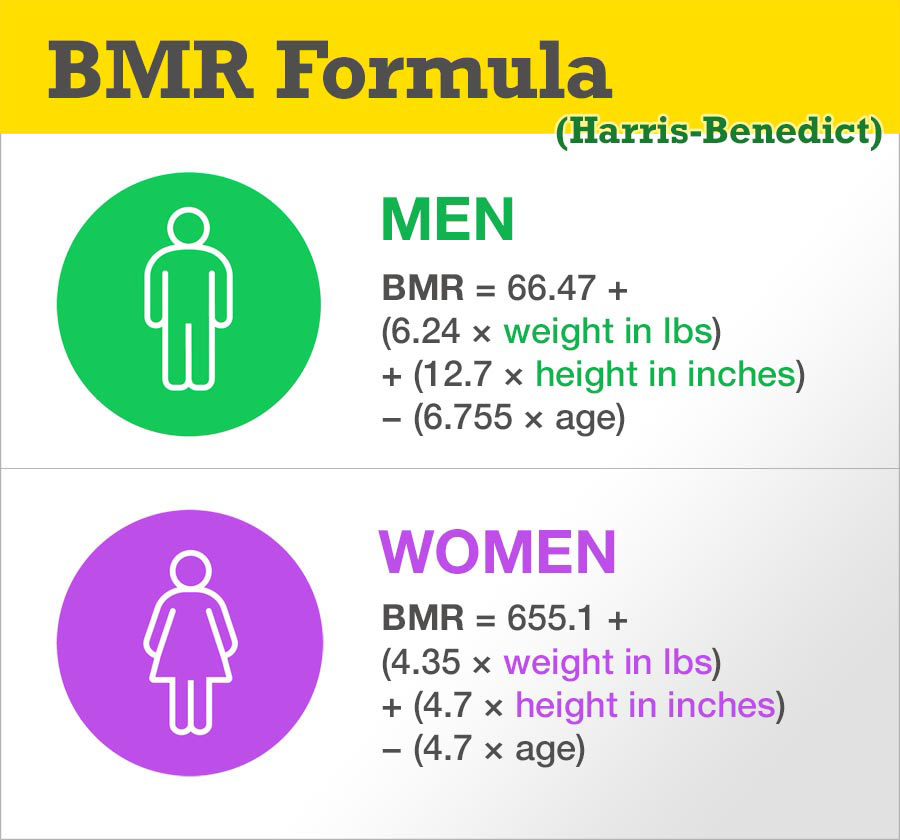
Rumus Harris-Benedict untuk wanita: BMR = 655,1 + (9.563 * berat dalam kg) + (1.850 * tinggi dalam cm) - (4.676 * usia) Tingkat metabolisme basal Anda (BMR) adalah hasilnya. Kalikan ini dengan tingkat aktivitas Anda - Sobat - untuk menghitung pengeluaran energi harian Anda - TDEE. Jika Anda mengkhawatirkan kesehatan dan tubuh Anda.

Rumus Bmr Harris Benedict Brain
The Harris-Benedict equation (also called the Harris-Benedict principle) is a method used to estimate an individual's basal metabolic rate (BMR). The estimated BMR value may be multiplied by a number that corresponds to the individual's activity level; the resulting number is the approximate daily kilocalorie intake to maintain current body.
Harris Benedict Formula / Formula Harris Benedict En Excel Calcular Geb Y Get Excel Nutriologos
Harris-Benedict Equation. The first formula created to calculate BMR was the Harris-Benedict formula. The equation was derived in 1919 and is still one of the most widely used BMR formulas. There are two separate equations for men and women. Men: BMR = 66.5 + (13.75 × weight [kg]) + (5.003 × height [cm]) - (6.775 × age [years])
PPT Nutrition Chapter 18 PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5653871
Rumus yang paling banyak digunakan oleh ahli gizi untuk menghitung BMR adalah Rumus Harris-Benedict. Rumus ini dihitung berdasarkan usia, jenis kelamin, berat badan, dan tinggi badan. Untuk laki-laki: (88,4 + 13,4 x berat dalam kilogram) + (4,8 x tinggi dalam sentimeter) - (5,68 x usia dalam tahun)

Rumus Harris Benedict PDF
The Harris-Benedict equations and other predictive equations are widely used in spite of low levels of accuracy ranging from 18% to 70%. Resting energy expenditure cannot be predicted accurately for each individual. Technology for indirect calorimetry continues to advance alongside growing recognition for the importance of assessment of body.

HarrisBenedict Calculator Calculate Your Daily Calorie Needs
Berdasarkan rumus Harris-Benedict yang telah direvisi oleh Roza dan Shizgal (1984) Rumus menghitung BMR berdasarkan Harris-Benedict dengan revisi dari Roza dan Shizgal adalah sebagai berikut: BMR laki-laki = 88.362 + (13.397 x BB kg) + (4.799 x TB cm) - (5.677 x umur tahun)

Menghitung Kebutuhan Gizi Ibu Hamil Rumus Harris Benedict Informasi Seputar Gizi
The original Harris-Benedict equation was created in 1919 following a study by James Arthur Harris and Francis Gano Benedict. The equations were revised in 1984 using new data, in order to improve accuracy. The Harris-Benedict equation was the primary, relied-upon formula for BMR calculations until 1990, when the Mifflin St Jeor equation was.

Menghitung Kebutuhan Gizi Ibu Hamil Rumus Harris Benedict Informasi Seputar Gizi
ini telah ber hasil mengimplementasikan rumus Harris Benedict pada aplikasi perhitungan kebutuhan gizi berbasis mobile Android yan g memberikan output kategori bera t badan, berat badan ideal, dan.

PPT Nutrition Chapter 18 PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5653871
The original Harris Benedict equation was revised in 1984. This newer equation may have greater accuracy in obese patients. BMR calculation for men (metric) BMR = 88.362 + ( 13.397 x weight in kg ) + ( 4.799 x height in cm ) - ( 5.677 x age in years )

Rumus Harris Benedict (1919) ♂ = 66,5 +(13,7xBB)+(5xTB)(6,8xU) ♀ = 655 +(9,5xBB)+(1)(4) Ket
Menggunakan Rumus Harris Benedict Laki-laki= 66 + (13,7 x BB) + (5 x TB) - (6,8 x U). Rumus cepat (a) = 0,95 kkal x kg BB x 24 jam = 0,95 kkal x 52 x 24 = 1185,8 kkal (dibulatkan 1186 kkal) 3. Rumus cepat (b) = 25 kkal x kg BB =25 x 52 =1300 kkal 4. Rumus FAO/WHO/UNU