
Stratified Sampling Definition, Formula, Examples, Types
Proportionate Stratified Random Sampling, teknik ini digunakan karena populasinya tidak homogen, mengacu pada pendapat Sugiyono (2011: 82) bahwa, "Proportionate Stratified Random Sampling digunakan bila populasi mempunyai anggota atau unsur yang tidak homogen dan berstrata secara proporsional". Strata

What is stratified random sampling methods & examples forms.app
Enhance evaluation precision through Stratified Random Sampling—a method that partitions populations into subgroups for nuanced insights. Whether adopting proportionate or disproportionate approaches, this strategy fosters inclusivity and robust representation, enriching the evaluative process, learn about it in this article.

Rumus Proportional Random Sampling Brain
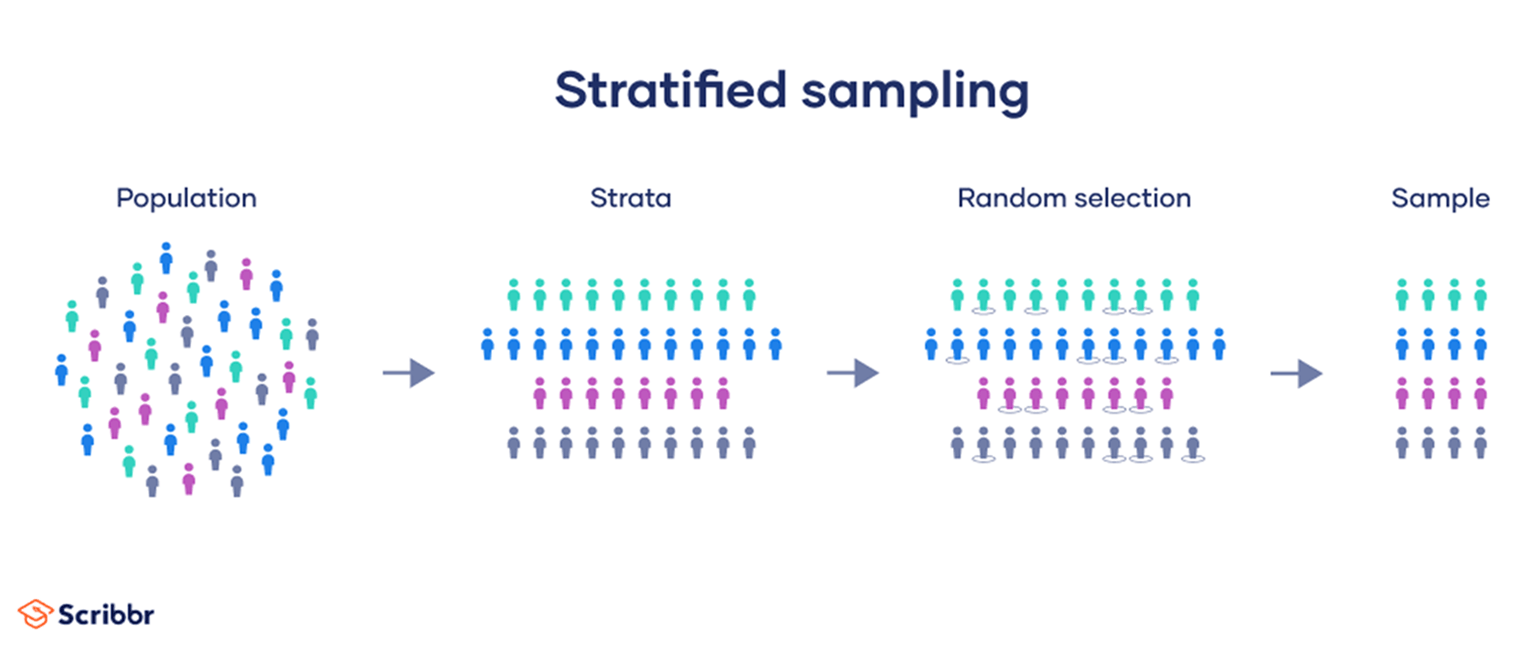
Table of contents. When to use stratified sampling. Step 1: Define your population and subgroups. Step 2: Separate the population into strata. Step 3: Decide on the sample size for each stratum. Step 4: Randomly sample from each stratum. Other interesting articles.
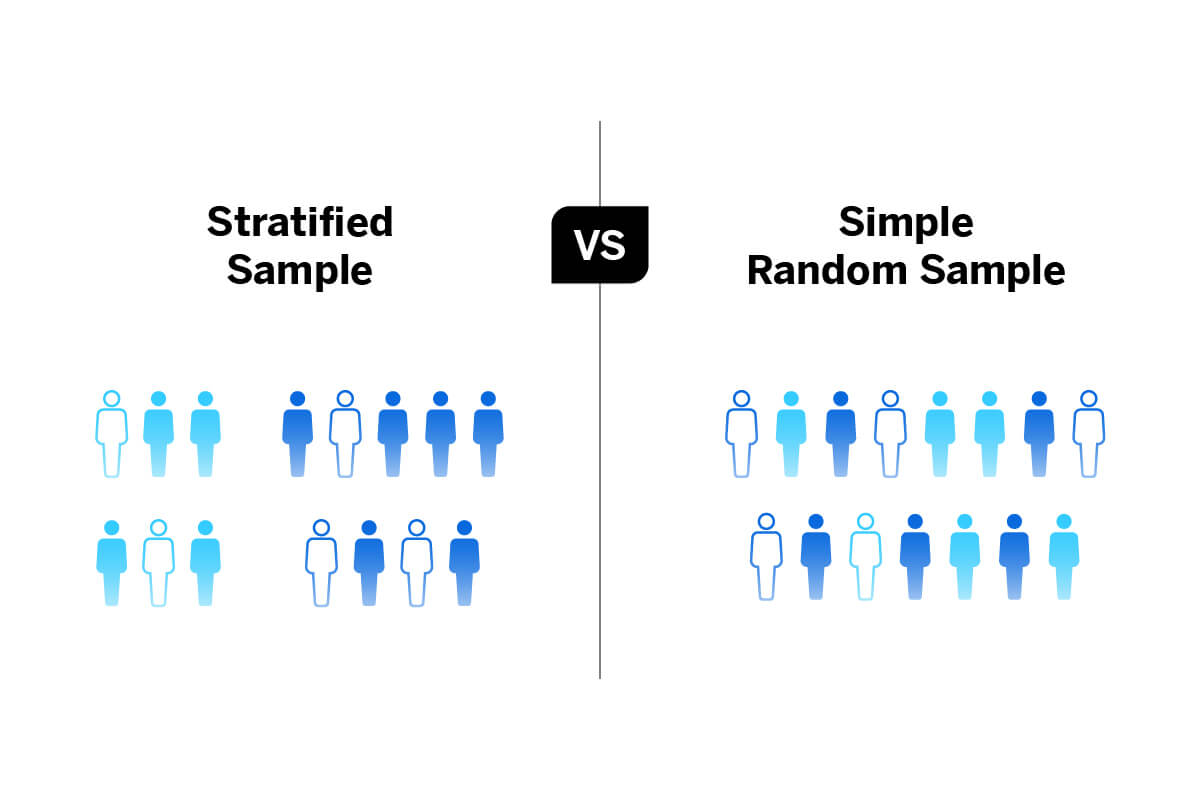
Stratified Random Sampling and How to Use It Qualtrics
If researchers want to preserve the ratio of each stratum in the sample, they use proportionate stratified random sampling. If the population has 47% females, 45% males, and 8% non-binary, the.

Rumus Proportional Random Sampling Brain
There are four major types of probability sample designs: simple random sampling, stratified sampling, systematic sampling, and cluster sampling (see Figure 5.1). Simple random sampling is the most recognized probability sam-pling procedure. Stratified sampling offers significant improvement to simple random sampling.
Chapter 5 Stratified Random Sampling
sugiarto, dkk. 2001, hlm. 76-77 rumus proportionate stratified random sampling: Rumus Proportionate Statified Random Sampling: ℎ= 𝑁ℎ 𝑁 Keterangan: nh = Jumlah sampel yang terpilih dengan proportionate stratified random sampling Nh = Jumlah populasi strata N = Jumlah total populasi n = Jumlah sampel (rumus slovin)

Proportionate Stratified Random Sampling / Stratified Sampling Stratified sampling explained
Disproportional Sampling. Disproportional sampling is a probability sampling technique used to address the difficulty researchers encounter with stratified samples of unequal sizes. This sampling method divides the population into subgroups or strata but employs a sampling fraction that is not similar for all strata; some strata are oversampled.

Stratified random sampling with proportional allocation Download Scientific Diagram
Cara Menghitung Rumus Proportionate Stratified Random Sampling. Setelah memahami konsep dasar dari proportionate stratified random sampling, kini saatnya kita masuk ke dalam rumusnya. Rumus proportionate stratified random sampling adalah sebagai berikut:n_h = (N_h / N) x nDi mana:- n_h: Jumlah sampel yang diambil dari strata ke-h.-. N_h: Jumlah.
Lesson Stratified Random Sampling Nagwa
Stratified Sampling Definition. Stratified sampling is a random sampling method of dividing the population into various subgroups or strata and drawing a random sample from each. Each subgroup or stratum consists of items that have common characteristics. This sampling method is widely used in human research or political surveys.
Stratified Sampling A StepbyStep Guide with Examples
Stratified random sampling is a widely used statistical technique in which a population is divided into different subgroups, or strata, based on some shared characteristics. The purpose of stratification is to ensure that each stratum in the sample and to make inferences about specific population subgroups.

Proportionate Stratified Random Sampling / Stratified Sampling Stratified sampling explained
In multistage sampling, you divide the population into clusters and select some clusters at the first stage. At each subsequent stage, you further divide up those selected clusters into smaller clusters, and repeat the process until you get to the last step. At the last step, you only select some members of each cluster for your sample.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Stratified-Random-Sampling-bfdd236e0ecf4a4c97aeec4c2a189740.png)
How Stratified Random Sampling Works, With Examples
A stratified random sample is one obtained by dividing the population elements into mutually exclusive, non-overlapping groups of sample units called strata, then selecting a simple random sample from within each stratum (stratum is singular for strata). Every potential sample unit must be assigned to only one stratum and no units can be excluded.

Stratified Random Sampling
Stratified Random Sampling Methods. There are two Stratified Random Sampling Methods: Proportional Stratified Random Sampling: In this method, the sample size for each stratum is proportional to the size of that stratum in the population. For example, if a population has three strata with sizes of 1000, 2000, and 3000, and a total sample size.
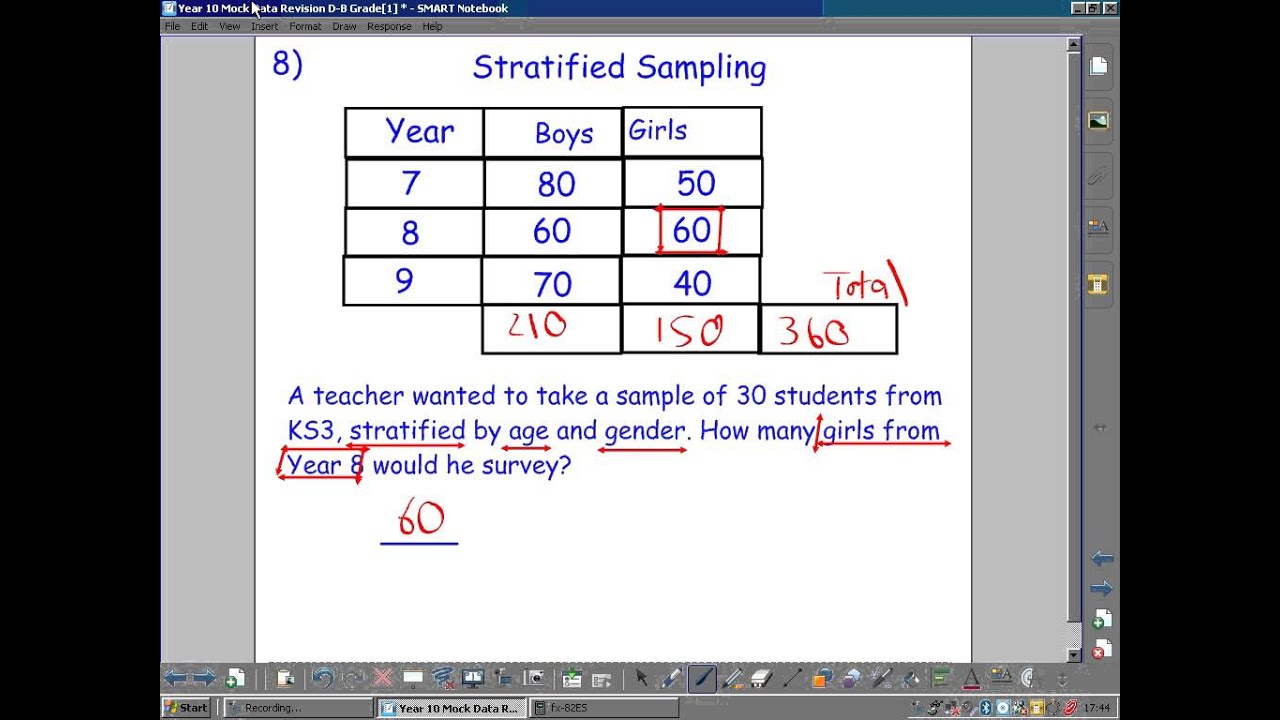
Proportionate Stratified Random Sampling / Stratified Sampling Stratified sampling explained
Stratified Sampling: Definition. Stratified sampling (SRS), also known as quota random sampling, is a probability sampling technique where the total population is divided into homogenous groups. We call these groups 'strata' and they complete the sampling process. Each of these stratum is based on similar attributes or characteristics.

Stratified Random Sampling Definition, Method and Examples
Stratified random sampling is a method of selecting a sample in which researchers first divide a population into smaller subgroups, or strata, based on shared characteristics of the members and then randomly select among each stratum to form the final sample. These shared characteristics can include gender, age, sex, race, education level, or.
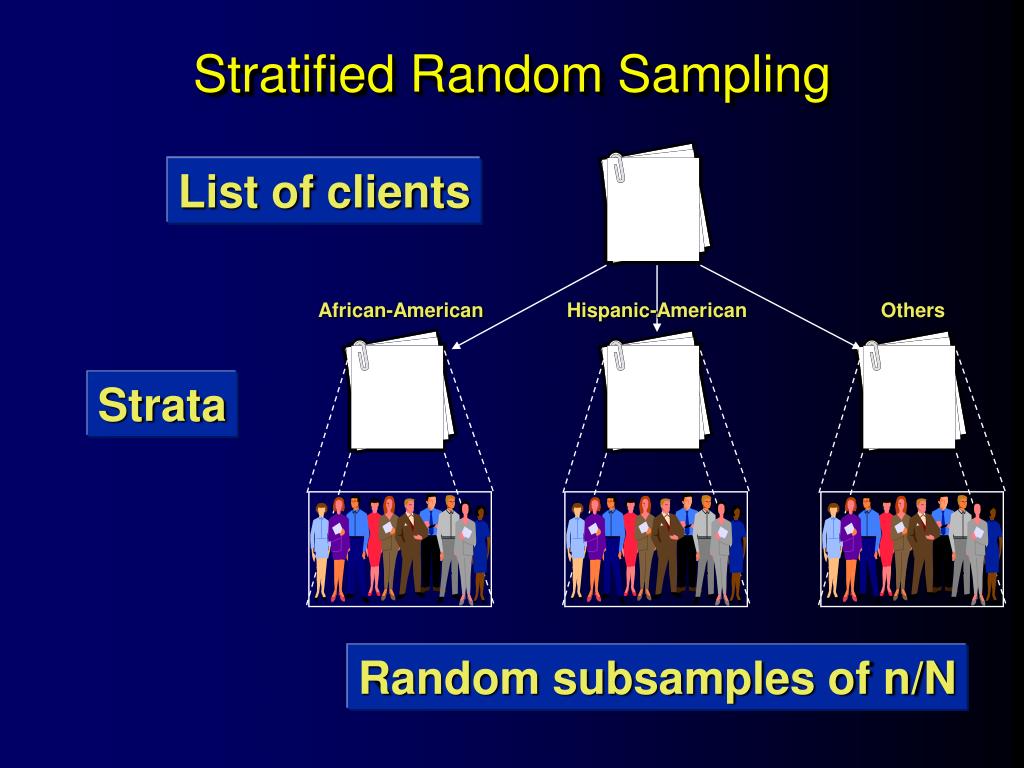
Stratified random sampling holodiki
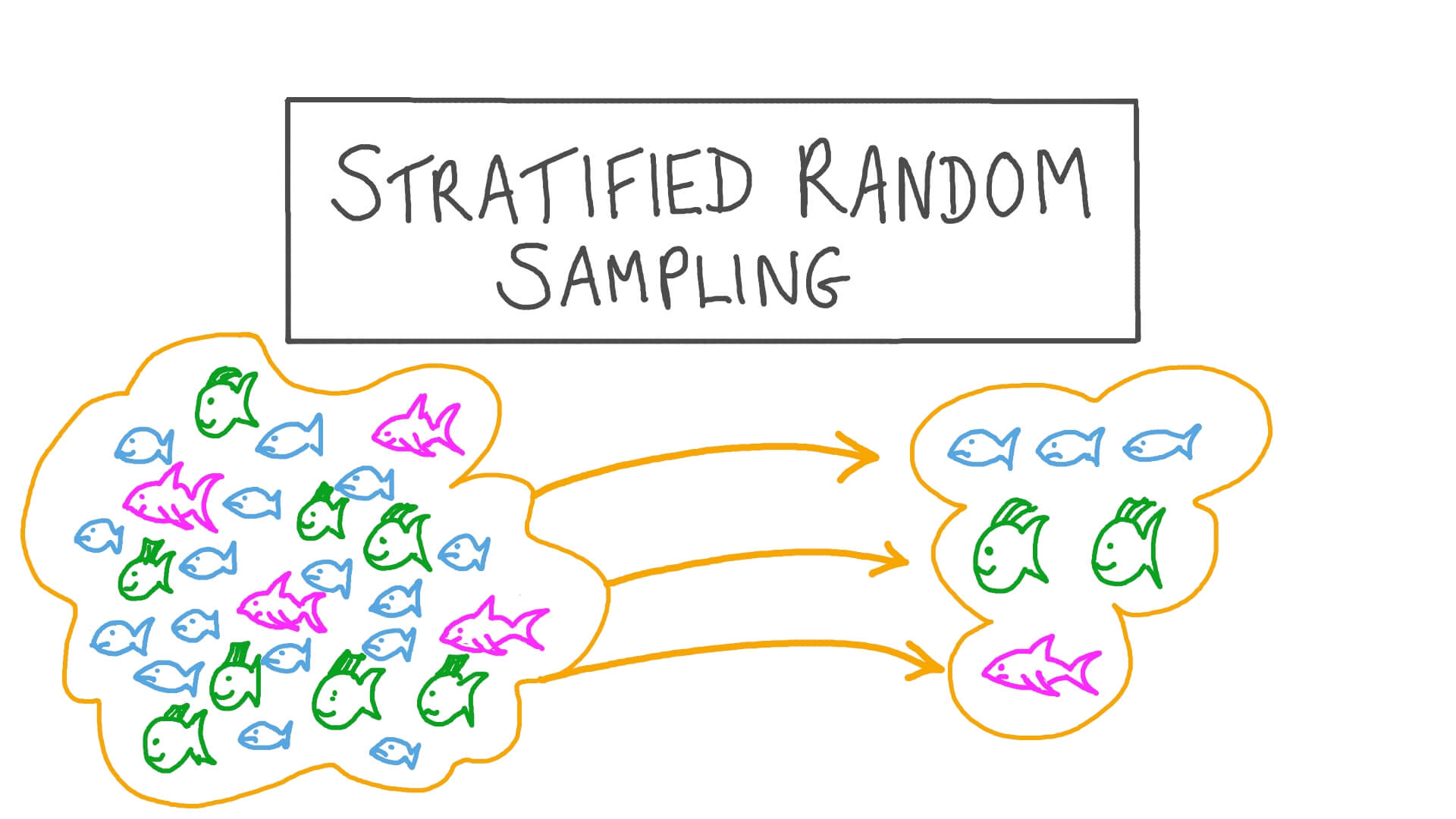
Stratified sampling is a method of obtaining a representative sample from a population that researchers have divided into relatively similar subpopulations (strata). Researchers use stratified sampling to ensure specific subgroups are present in their sample. It also helps them obtain precise estimates of each group's characteristics.