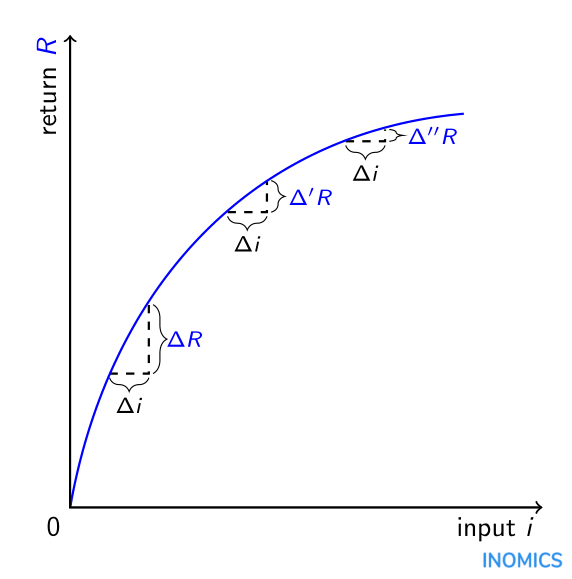
Law of Diminishing Marginal Returns INOMICS
Key Differences. Diminishing marginal returns primarily looks at changes in variable inputs and is a short-term metric. Variable inputs are easier to change in a short time horizon when compared.
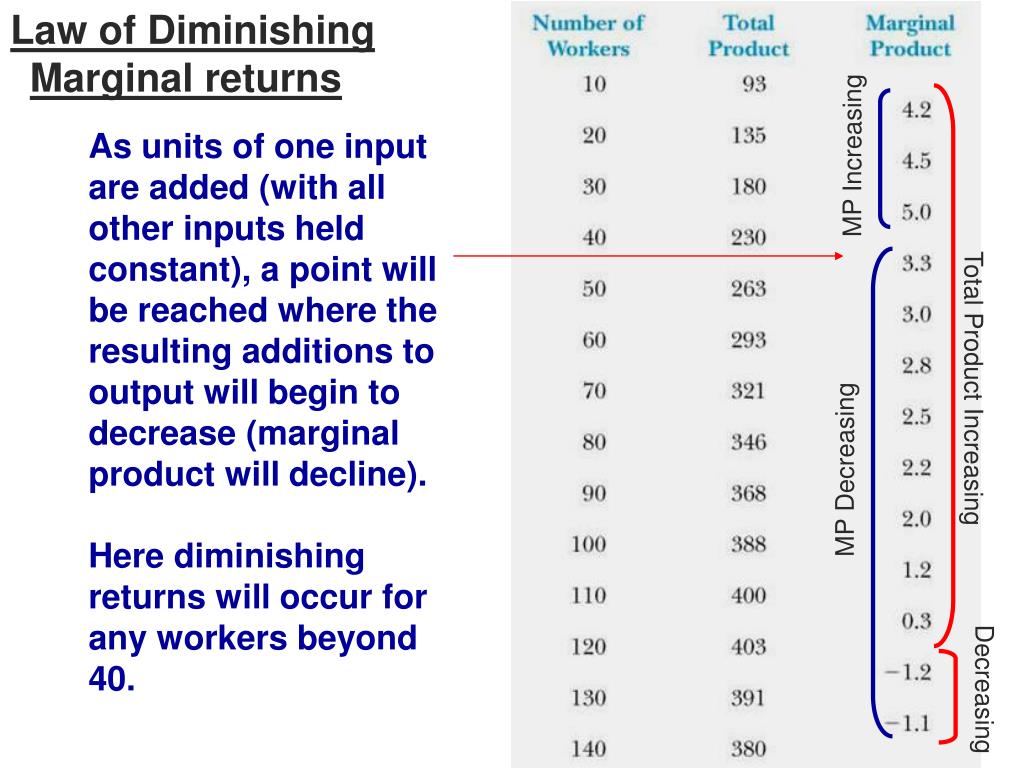
PPT Law of Diminishing Marginal returns PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6716631
The law of diminishing marginal returns is a short-run concept, and it explains the logic of the fall in marginal returns when a variable factor of production is applied to some fixed factors of production. Understanding the concept of diminishing returns allows firms to optimise resource allocation, improve productivity, and avoid inefficiencies.

Law of Diminishing Marginal Returns PPT and Google Slides
The law of diminishing marginal returns is a universal law that forms the basis of several other economic laws and concepts. For instance, the law of diminishing marginal returns is the basis on which the law of demand is formed. The law of demand states that consumers will purchase larger quantities of commodities at a lower price.
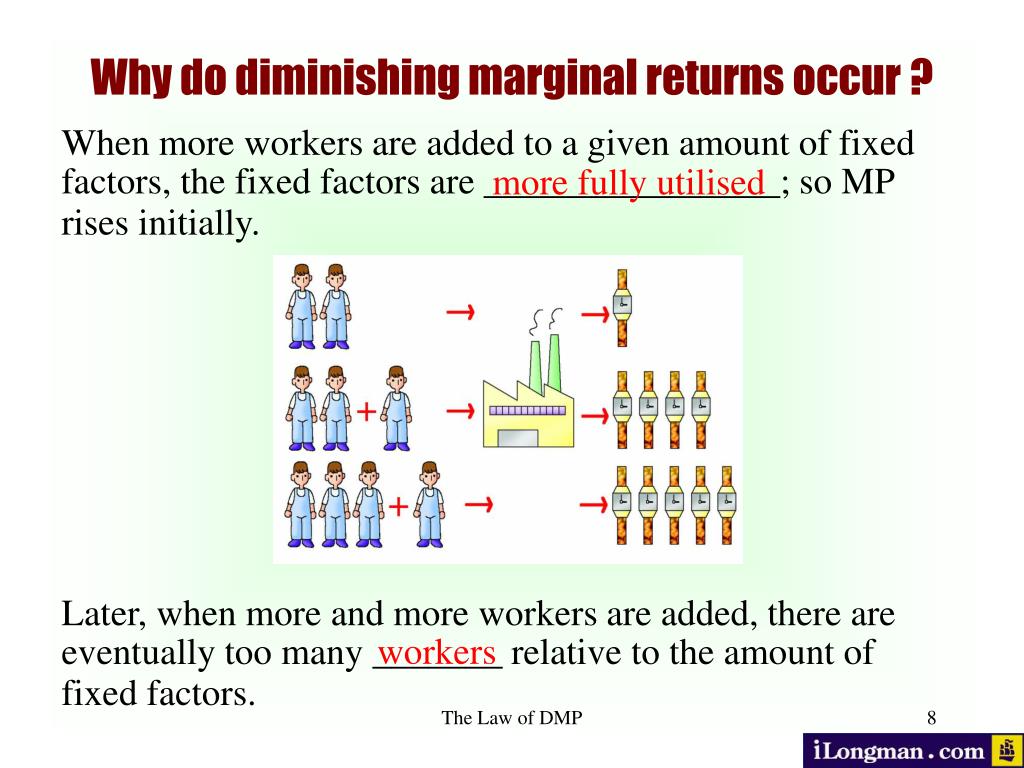
PPT The Law of Diminishing Marginal Returns PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID259342
The law of Diminishing Marginal Returns can only occur in the short-run. This is because all factors are variable in the long-run. For example, having an additional worker in the cafe may create for a chaotic environment. However, the employees may learn to work more efficiently together and therefore produce better returns in the long-term.
What Is The Law Of Diminishing Marginal Returns? (With Examples) Zippia
The law of diminishing marginal return membahas tentang keterbatasan peningkatan faktor input untuk meningkatkan suatu produksi. Dilansir dari Encyclopedia Britannica, the Law of Diminishing Margnal Return adalah hukum ekonomi yang menyatakan jika satu input dalam produksi ditingkatkan semantara input lainnya dipertahankan, pada akhirnya akan.
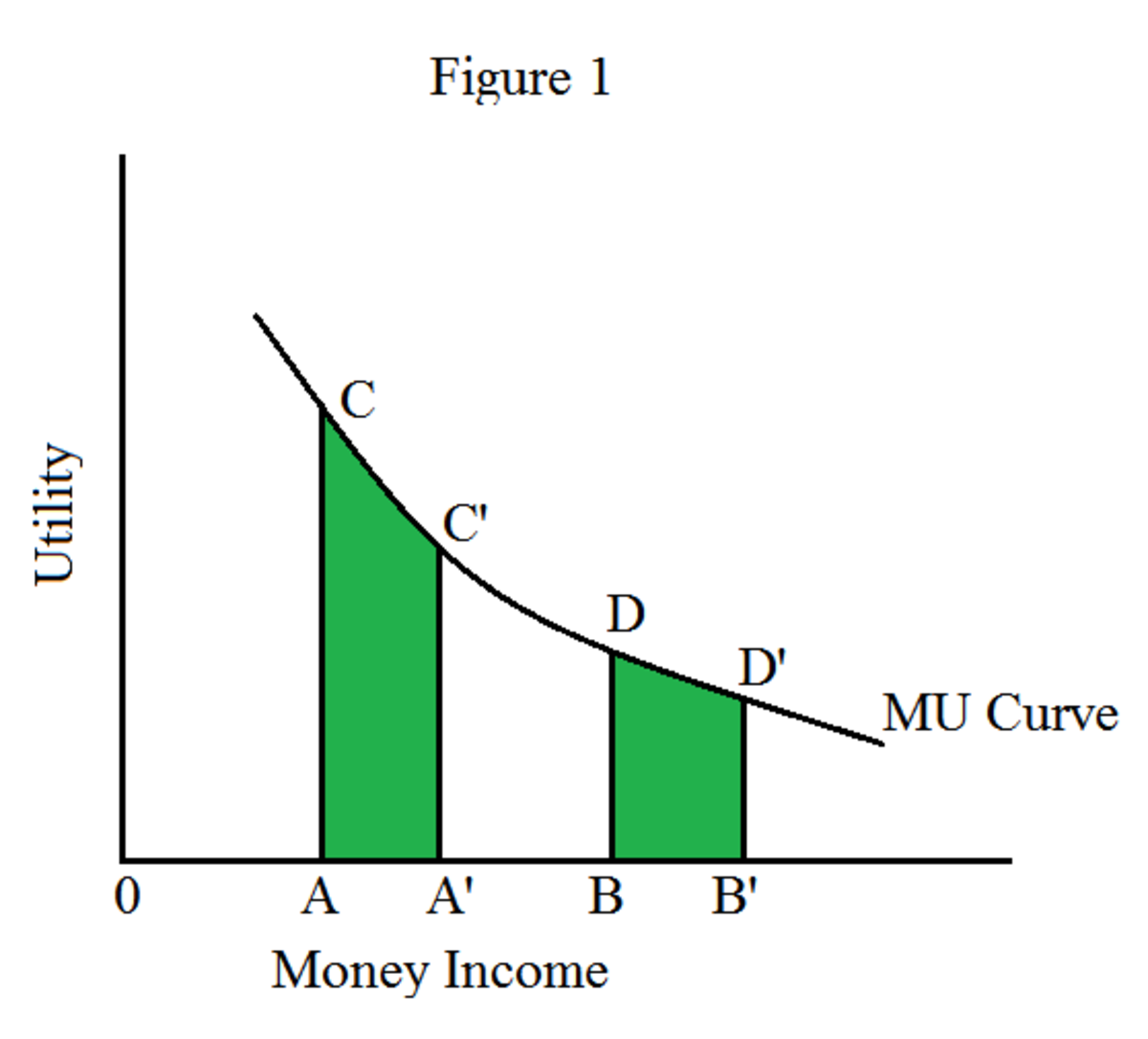
Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility Detailed Explanation Owlcation
The law of diminishing returns does not cause a decrease in overall production capabilities, rather it defines a point on a production curve whereby producing an additional unit of output will result in a loss and is known as negative returns. Under diminishing returns, output remains positive, but productivity and efficiency decrease.
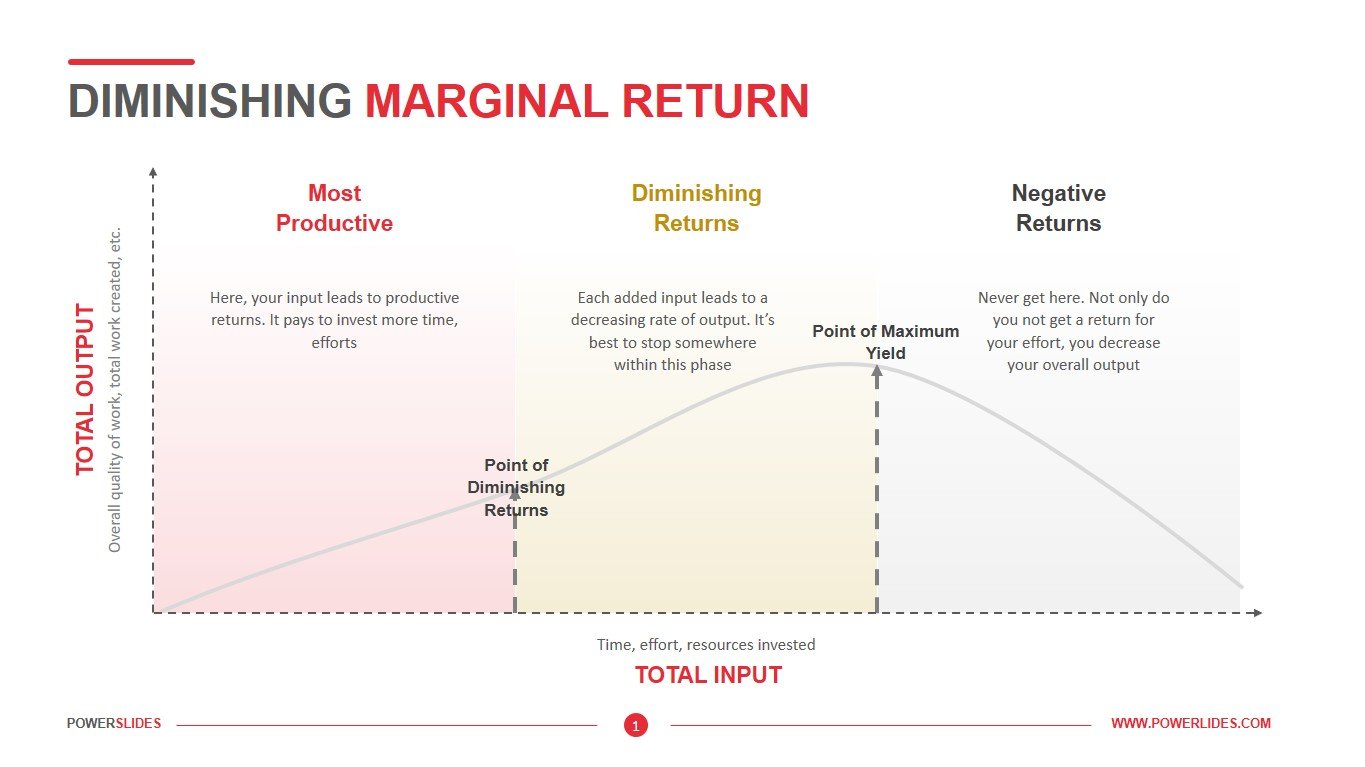
Diminishing Marginal Return Data Charts & Finance Templates
Learn about the law of diminishing returns, or diminishing marginal returns. See the point of diminishing returns graphed and how to calculate it with examples. Updated: 11/21/2023

Law of Diminishing Marginal Returns (Definition and 3 Examples) BoyceWire
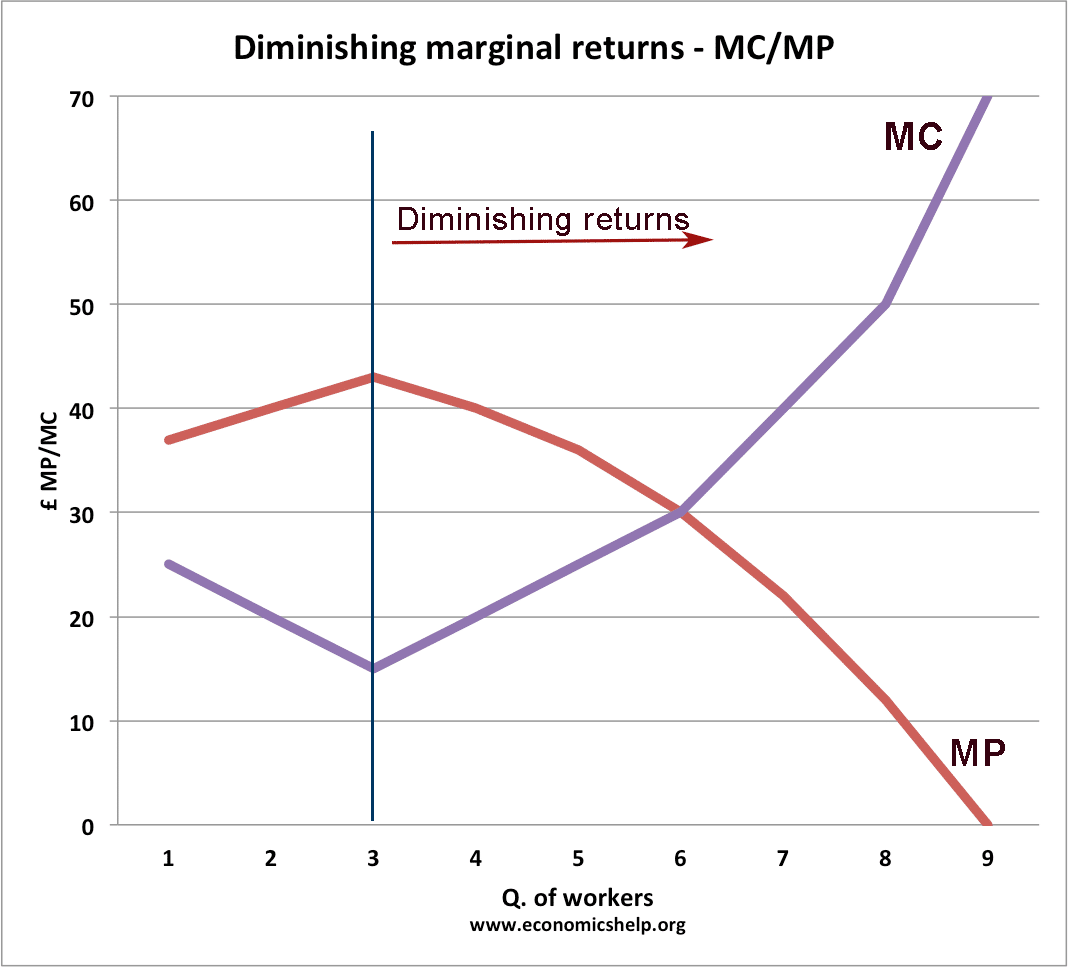
The Law of diminishing marginal returns explained. Assume the wage rate is £20, then an extra worker costs £20. The Marginal Cost (MC) of a sandwich will be the cost of the worker divided by the number of extra sandwiches that are produced. Therefore as MP increases MC declines and vice versa. Total Product (TP) This is the total output.

Law of Diminishing Marginal Return Defination and Example YouTube
What is Diminishing Marginal Returns. Diminishing marginal returns is a theory in economics that states if more and more units of a variable input are applied when other inputs are held constant, the returns from the variable input may decrease eventually even though there is an initial increase. This is also known as principle of diminishing.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/lawofdiminishingmarginalreturn-540a7d27fe254f1f85ec09bfa1fd2482.jpg)
Law of Diminishing Marginal Returns Definition, Example, Use in Economics
The law of diminishing returns describes a declining marginal product, but not necessarily a negative one. The law of diminishing returns applies to a given production technology. Over time, however, inventions and other improvements in technology may allow the entire total product curve in Figure 6.2a to shift upward, so that more output can.

The Law of Diminishing Marginal Returns Labour Economics Long Run And Short Run
The law of diminishing returns, which you'll also see called the law of diminishing marginal returns, says that - holding everything else constant - as a firm adds more factors of production, eventually each unit added won't add as much to the production process as the unit before it did. Let's break this definition down.
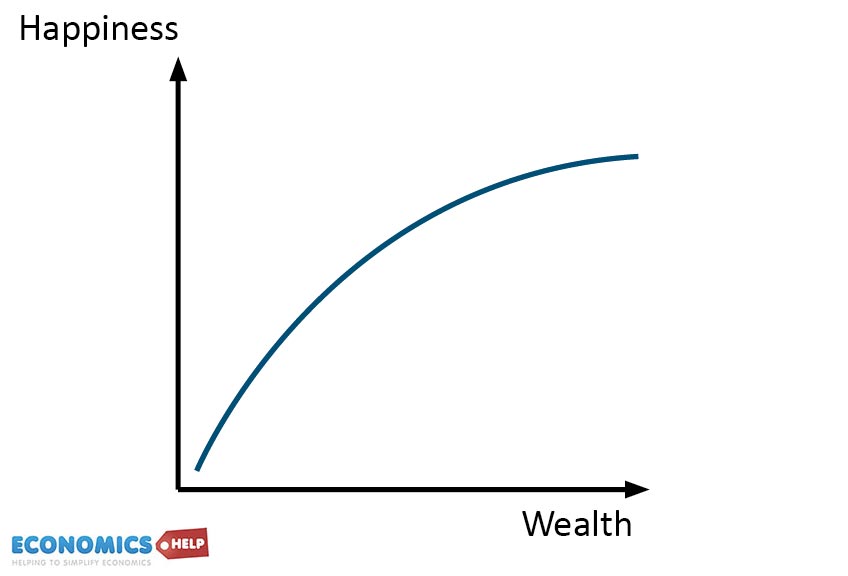
The Law of Diminishing Marginal Returns Economics Help
Illustration of the Law of Diminishing Marginal Returns. Lets look at the principle of diminishing returns with an example: Suppose a woodworks shop has 10 Lathe machines, 10 Hand Planes, and 20 workers. Increasing the number of Lathe machines to 15 might increase production by a small margin as the number of workers and Hand Planes remains the.

The Law Of Diminishing Marginal Return Membahas Tentang
Economists have long defined the law of diminishing returns imprecisely. and inconsistently. To modern economists, diminishing returns in the most. basic sense occurs when marginal product falls as a rising amount of a variable homogeneous input is applied to a fixed input. But past economists have often.
In The Diagram The Range Of Diminishing Marginal Returns Is Drivenheisenberg
The law of diminishing marginal returns is an economic theory that states that once an optimal level of production is reached, increasing one variable of that production will lead to a smaller and smaller output. To give a simple definition of the law of diminishing returns, adding more of something to a production process doesn't always.
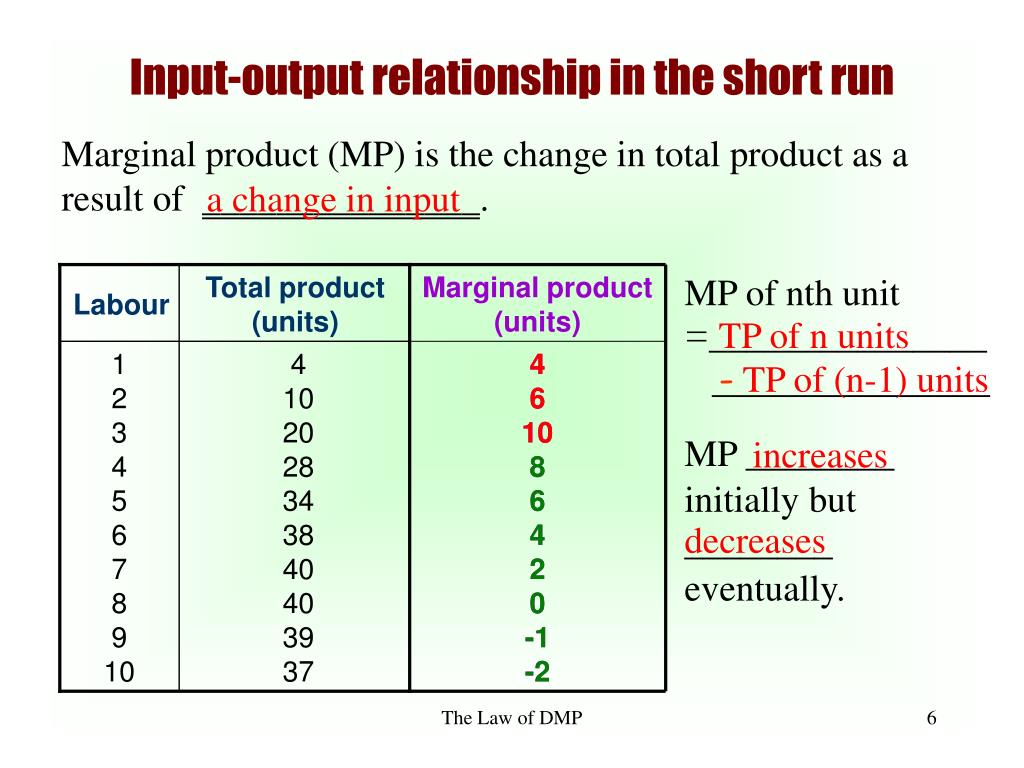
PPT The Law of Diminishing Marginal Returns PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6675650
The law of diminishing returns states that an additional amount of a single factor of production will result in a decreasing marginal output of production. The law assumes other factors to be constant. It means that if X produces Y, there will be a point when adding more quantities of X will not help in a marginal increase in quantities of Y.
The Law of Diminishing Marginal Returns Economics Help
Law of Diminishing Marginal Returns: The law of diminishing marginal returns is a law of economics that states an increasing number of new employees causes the marginal product of another employee.