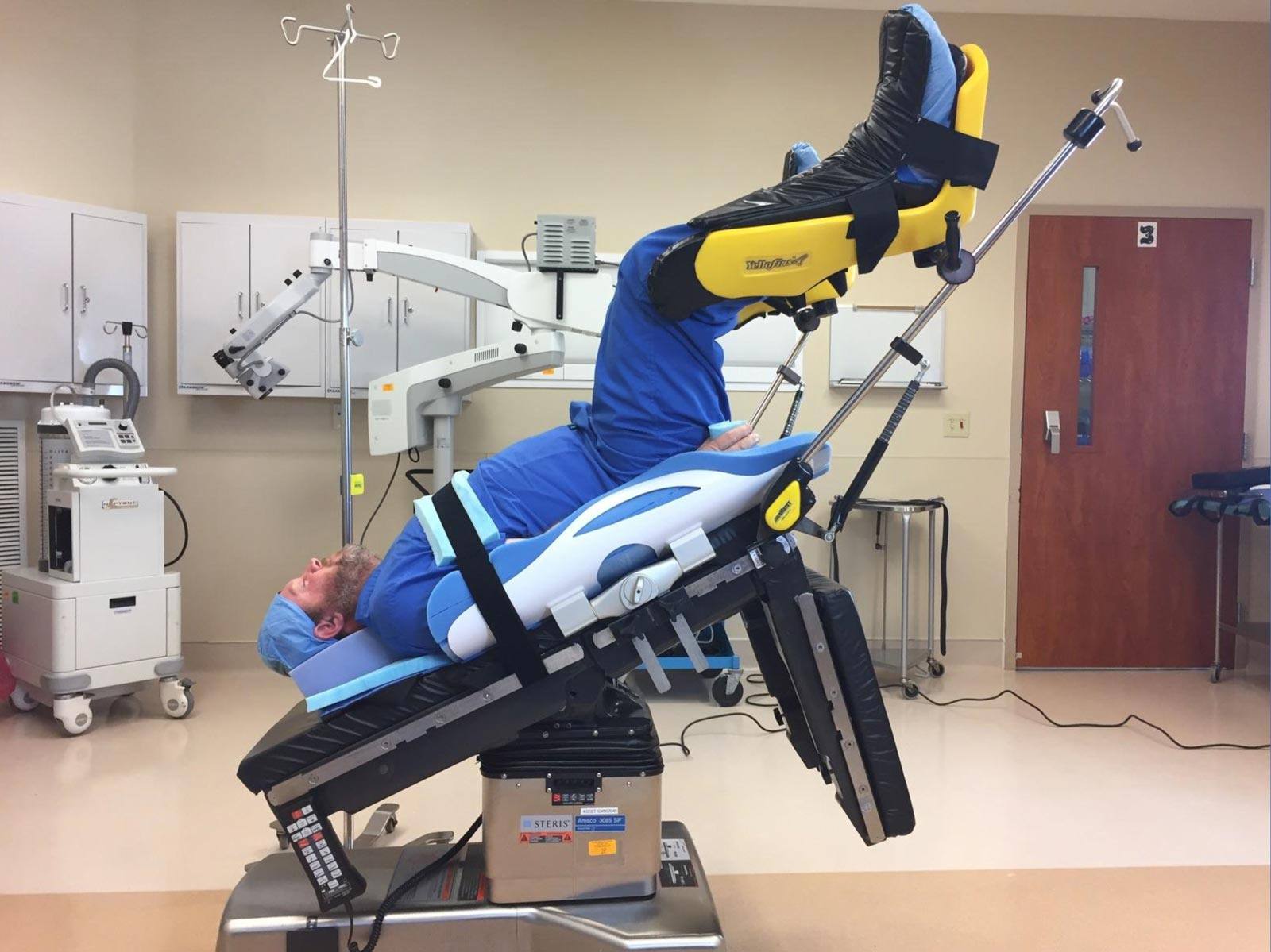
Trendelenburg Position Hysterectomy
The meaning of TRENDELENBURG POSITION is a position of the body for medical examination or operation in which the patient is placed head down on a table inclined at about 45 degrees from the floor with the knees uppermost and the legs hanging over the end of the table.

Storm Anesthesia Trendelenburg
The lithotomy-Trendelenburg position — supine with both legs separated, flexed and supported in stirrups — can compress the lateral side of the legs, which could ultimately result in peroneal neve injury. Other potential complications associated with this position: injury to the obturator nerve, which causes pain in the inner thigh; injury.

Trendelenburg Positioner Trendelenburg Stabilizer
Terrai, Anada, Masushima, Shimizu, and Okada (1995) evaluated the effects of a 10-degree head-down-tilt Trendelenburg position on central hemodynamics and flow through the internal jugular vein. Results showed an increase in left ventricular end-diastolic volume (LVEDP), stroke volume (SV), and CO (increased 16%) with a reduced heart rate after.
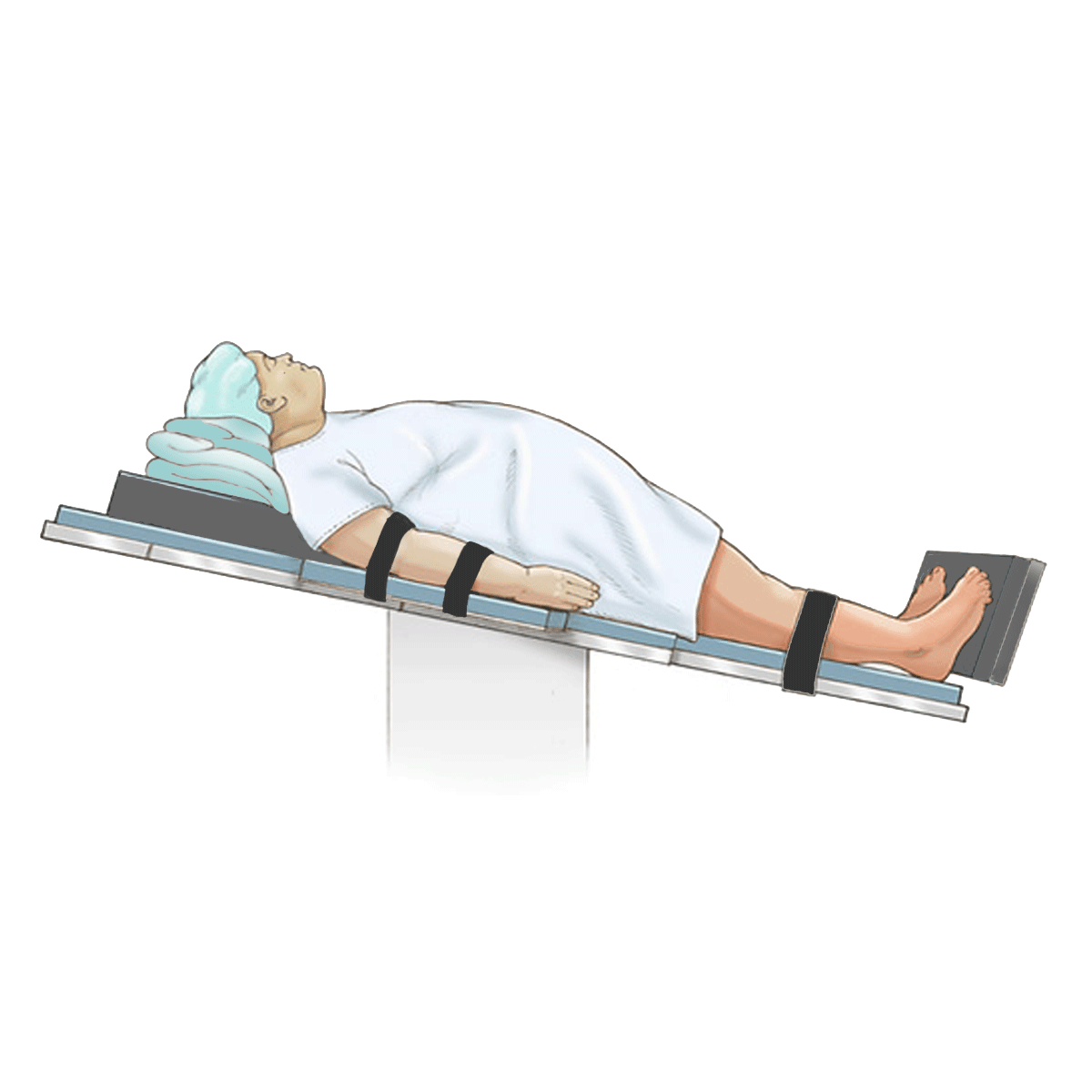
Trendelenburg position Wikipedia
The Trendelenburg position is used in surgery, especially of the abdomen and genitourinary system. It allows better access to the pelvic organs as gravity pulls the intra-abdominal organs away from the pelvis. Evidence does not support its use in hypovolaemic shock, with concerns for negative effects on the lungs and brain.
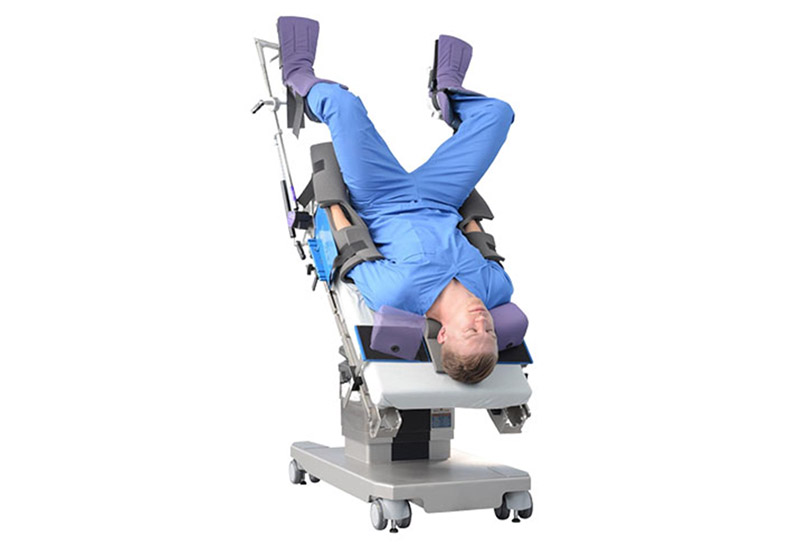
The Ultimate Guide to the Trendelenburg Position
The Trendelenburg Position is a position in which the patient is laid supine, with the head declined to an angle between 30-45 degrees. The Trendelenburg position is most often used in surgical procedures of the lower abdomen, pelvis and genitourinary system as it allows gravity to pull the abdominal contents away from the pelvis. The […]
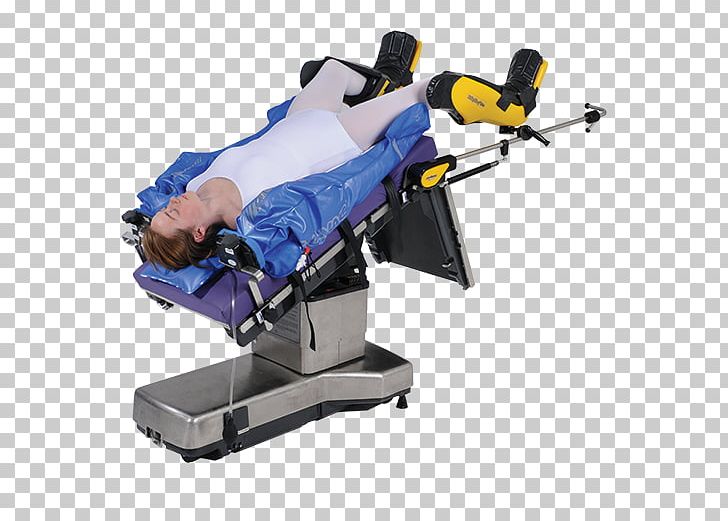
Trendelenburg Position Surgical Positions Gynaecology Patient Trendelenburg's Sign PNG, Clipart
Trendelenburg Position. The Trendelenburg position produces an increased venous return and central venous pressure which may produce deleterious effects in those with coronary artery disease or ventricular dysfunction. From: Surgery of the Anus, Rectum & Colon (Third Edition), 2008. Add to Mendeley.

PATIENT POSITIONING KNEECHEST/GENUPECTORAL & TRENDELENBURG’S POSITION Nurse Info
Currently, the Trendelenburg position is often used in lower abdominal surgeries, including colorectal, gynecological, and genitourinary procedures. In this position, gravity pulls the intra-abdominal organs away from the pelvis, allowing for better surgical access to the pelvic organs. In critical care settings, the Trendelenburg position is.
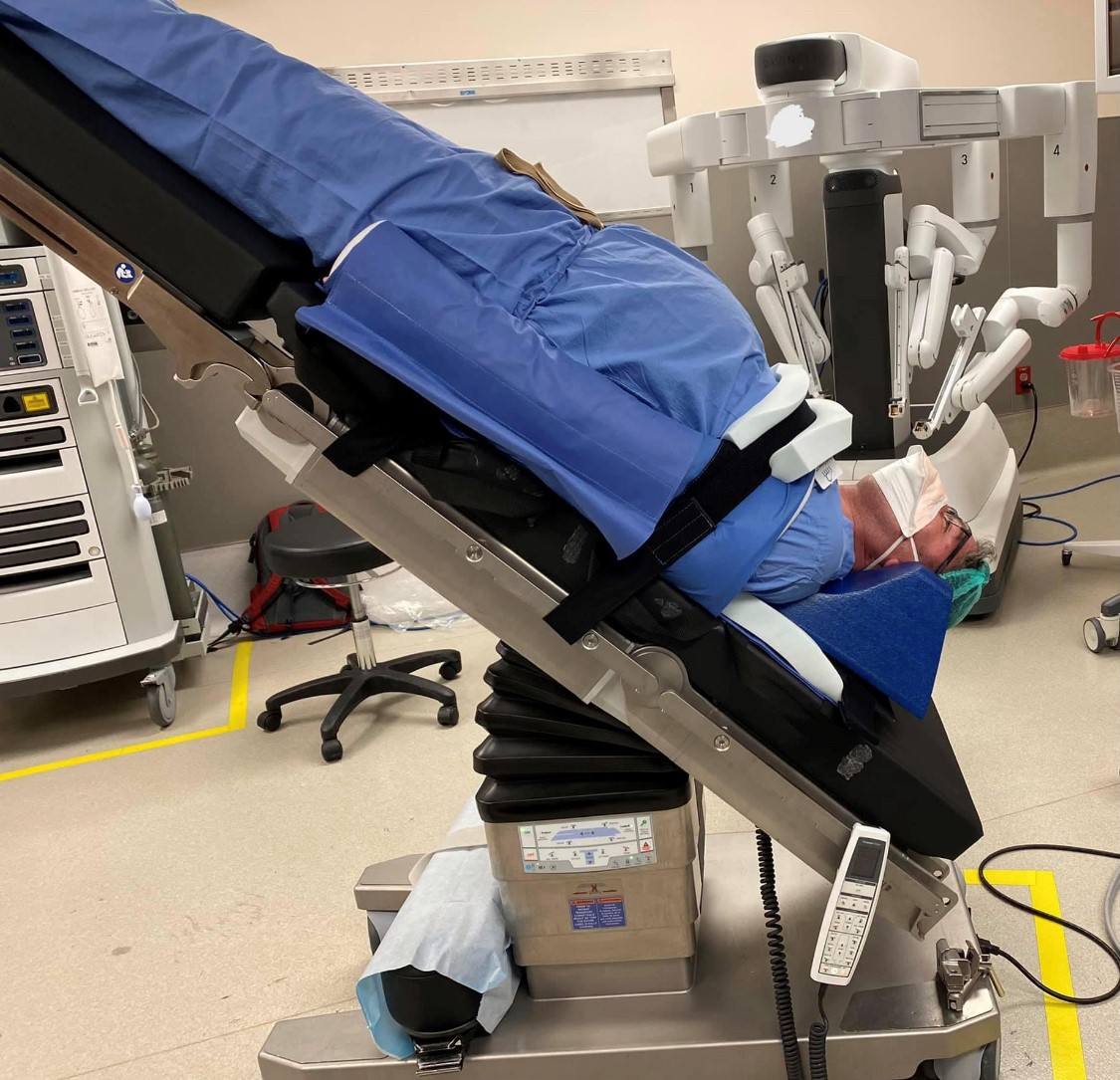
Trendelenburg Positioning System and Robotic Surgery Face Protection
The gravitational effect of the Trendelenburg position is thought to divert blood away from lower extremities and increase central blood volume . This increases cerebral blood flow and intracranial pressure by impairing venous outflow from the brain, increasing hydrostatic pressure within the cerebral vasculature and pushing fluid into the.

Trendelenburg & Reverse Trendelenburg Positions on ICU Bed YouTube
Related Posts. The Trendelenburg Position (TP) is a clinical technique where the body is tilted in the supine position so that the head is lower than the body and the legs. Clinicians usually administer TP at an angle of approximately 16°. 1 The modified Trendelenburg Position (mTP) is a full recline of the body where the head and body are.
Trendelenburg position when this patient management is relevant
After 24 h, patients were placed in a −20° Trendelenburg position with 1 to 1.5 h duration three times a day, from 9:00-11:00, 15:00-17:00, and 20:00-22:00, respectively. The treatment.
Reverse Trendelenburg Position REBEL EM Emergency Medicine Blog
In steep Trendelenburg position, the patient is angled at 30 - 40 degrees in the head-down position. This version is most often used for robotic pelvic procedures. Risks associated with steep Trendelenburg position include altered pulmonary function, airway edema, increased intracranial and intraocular pressure, and nerve injury.3

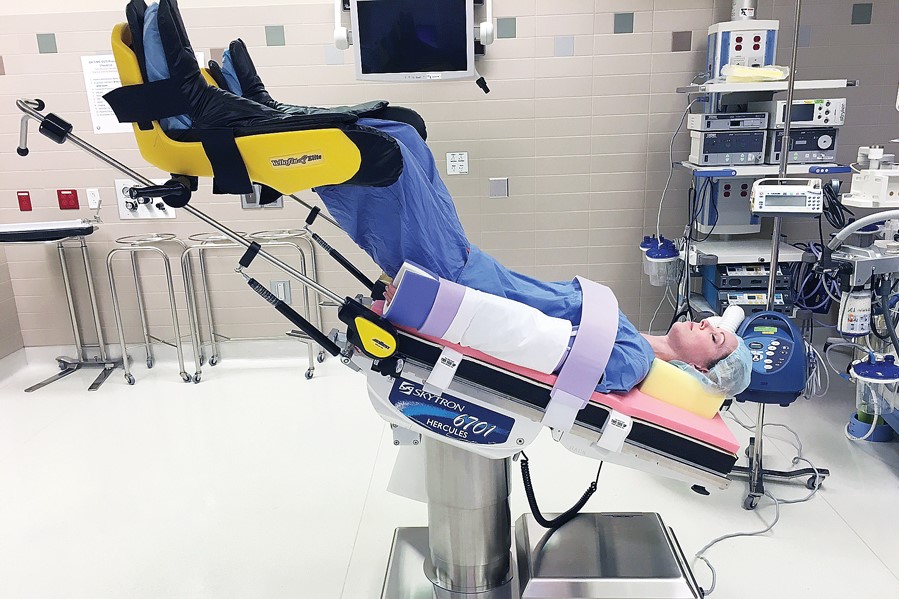
Trendelenburg Position WaffleGrip™ HotDog Patient Warming
As a result, the Trendelenburg position may have detrimental effects in patients with coronary artery disease and ischemia of the lower limbs, decreased vital capacity such as in the obese, and increased intraocular and intracranial pressure and cerebral edema.18 Because many of the studies reviewed assessed the effects of 200 or less, the.

trendelenburgs_position141de3809835da0fed2 The Nurses Post
The Trendelenburg position is still a pervasive treatment for shock despite numerous studies failing to show effectiveness. The authors of this study replicated what another study did in 2005.

Pengaturan Posisi Pasien di Tempat Tidur (Panduan Lengkap) Nerslicious
The Trendelenburg position is named after the German surgeo n Friedrich Trendelenburg, who was an innovator in the medical profession in the late 1800's and the early 1900's. Among many of his medical innovations was the Trendelenburg position. The position was originally used for accessing the pelvic organs during surgery.

Trendelenburg Position WaffleGrip™ HotDog Patient Warming
The Trendelenburg position involves placing the patient head down and elevating the feet. It is named after German surgeon Friedrich Trendelenburg (1844-1924), who created the position to improve surgical exposure of the pelvic organs during surgery. In World War I, Walter Cannon, the famous American physiologist, popularized the use of.
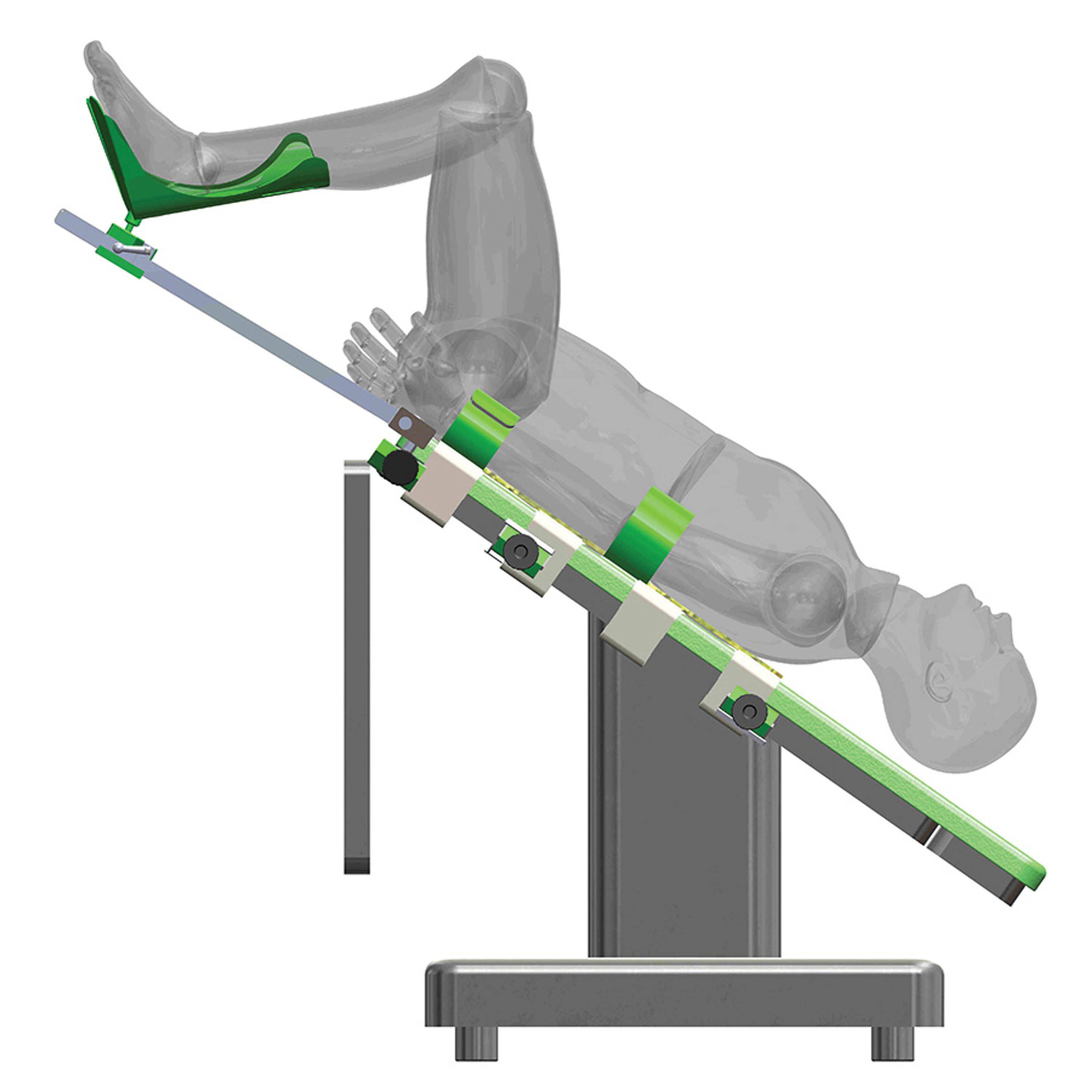
Trendelenburg Position Hysterectomy
The Trendelenburg position is achieved by elevating the feet and legs of the patient above the level of the heart in the supine position. This position continues to be used to redirect blood from the lower extremities into the central circulation. Vertical distance between the veins in the neck and the right atrium increases, leading to.