
Herpes Zoster NEJM
Disseminated zoster. B02.7 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2024 edition of ICD-10-CM B02.7 became effective on October 1, 2023. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of B02.7 - other international versions of ICD-10 B02.7 may differ.

Ilustración de Virus Del Zoster De La Varicela De Varicela y más Vectores Libres de Derechos de
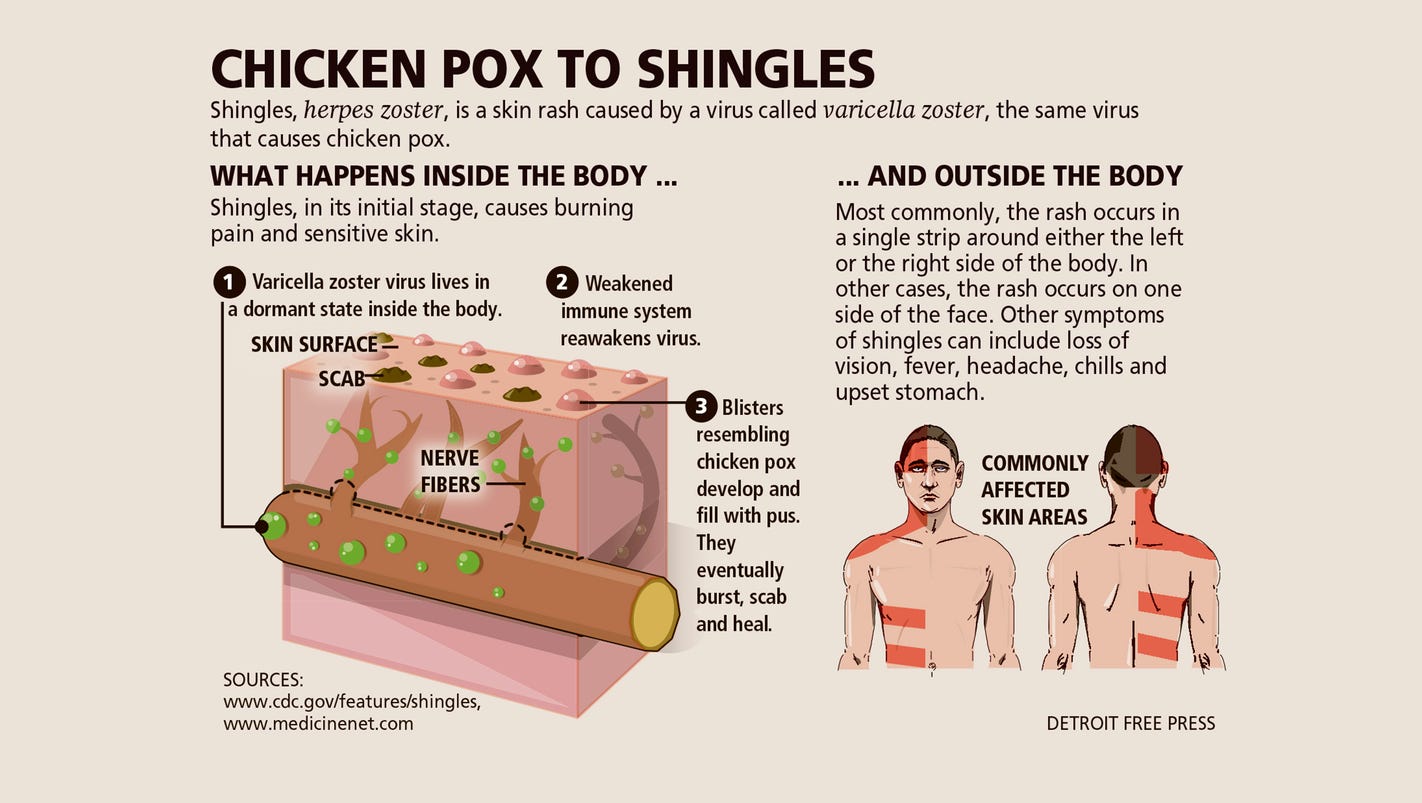
A common dermal and neurologic disorder caused by reactivation of the varicella-zoster virus that has remained dormant within dorsal root ganglia, often for decades, after the patient's initial exposure to the virus in the form of varicella (chickenpox).

Chickenpox (varicella zoster) Clinical Review
Herpes zoster, also known as shingles, is caused by reactivation of varicella-zoster virus (VZV), the same virus that causes varicella (chickenpox). Primary infection with VZV causes varicella. After a person has varicella, the virus remains latent in the dorsal root ganglia.

VaricellaZoster Virus Spread Infectious Diseases JAMA JAMA Network
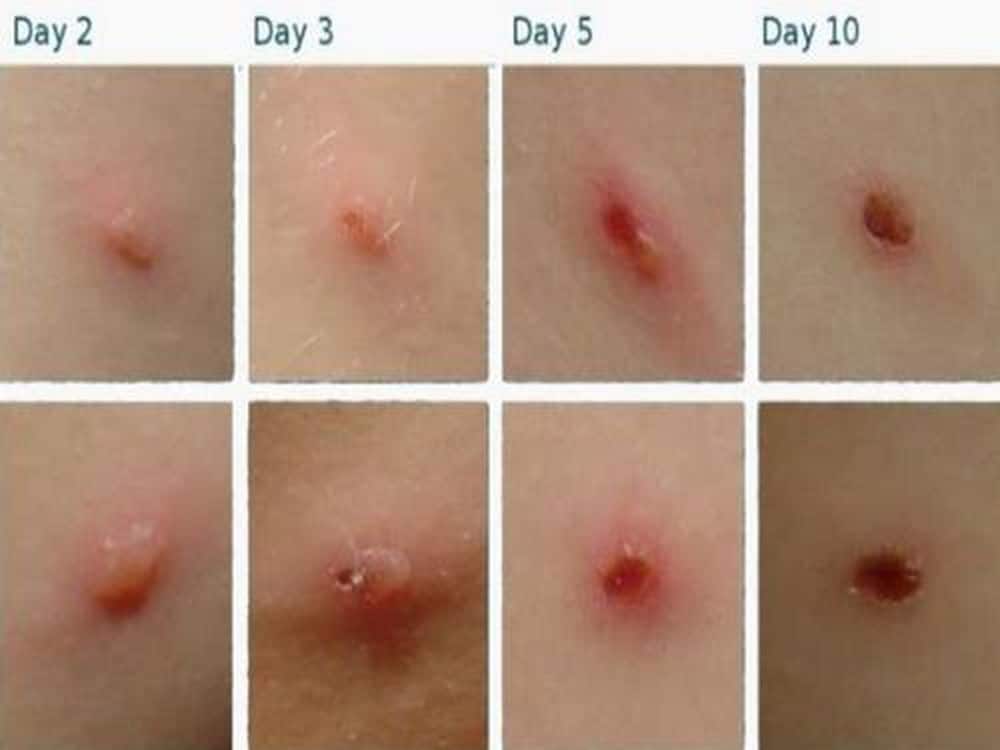
The rash caused by chickenpox appears 10 to 21 days after you're exposed to the varicella-zoster virus. The rash often lasts about 5 to 10 days. Other symptoms that may appear 1 to 2 days before the rash include: Fever. Loss of appetite. Headache. Tiredness and a general feeling of being unwell.
What you need to know about shingles infections
Chickenpox or varicella is a contagious disease caused by the varicella-zoster virus (VZV). The virus is responsible for chickenpox (usually primary infection in non-immune hosts) and herpes zoster or shingles (following reactivation of latent infection). Chickenpox results in a skin rash that forms small itchy blisters which scab over.
Varicellazoster virus American Academy of Ophthalmology
A contagious childhood disorder caused by the varicella zoster virus. It is transmitted via respiratory secretions and contact with chickenpox blister contents. It presents with a vesicular skin rush, usually associated with fever, headache, and myalgias. The pruritic fluid-filled vesicles occur 10-21 days after exposure and last for 3-4 days.

Varicella (Chickenpox) and Herpes Zoster (Shingles) Varicella (Chickenpox) and Herpes Zoster
Varicella zoster virus ( VZV ), also known as human herpesvirus 3 ( HHV-3, HHV3) or Human alphaherpesvirus 3 ( taxonomically ), is one of nine known herpes viruses that can infect humans. It causes chickenpox (varicella) commonly affecting children and young adults, and shingles (herpes zoster) in adults but rarely in children.
Varicella Zoster Virus Particle 1 Photograph by Heather Davies/science Photo Library Fine Art
Genetic causal association between Varicella-zoster virus infection and psychiatric disorders: A 2-sample Mendelian randomization study Behav Brain Res. 2024 Feb 28:114927. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2024.114927. Online ahead of print. Authors Bo Yan 1 , Pan Liao 2 , Conglin Wang 1.

Billing and Coding for Shingles A Painful Skin Condition
Herpes zoster, also known as zoster, or shingles, is caused by the reactivation of varicella-zoster virus (VZV). The term "herpes zoster" was first used by encyclopedist Celsus in c. 25 BCE to c. 50 AD.
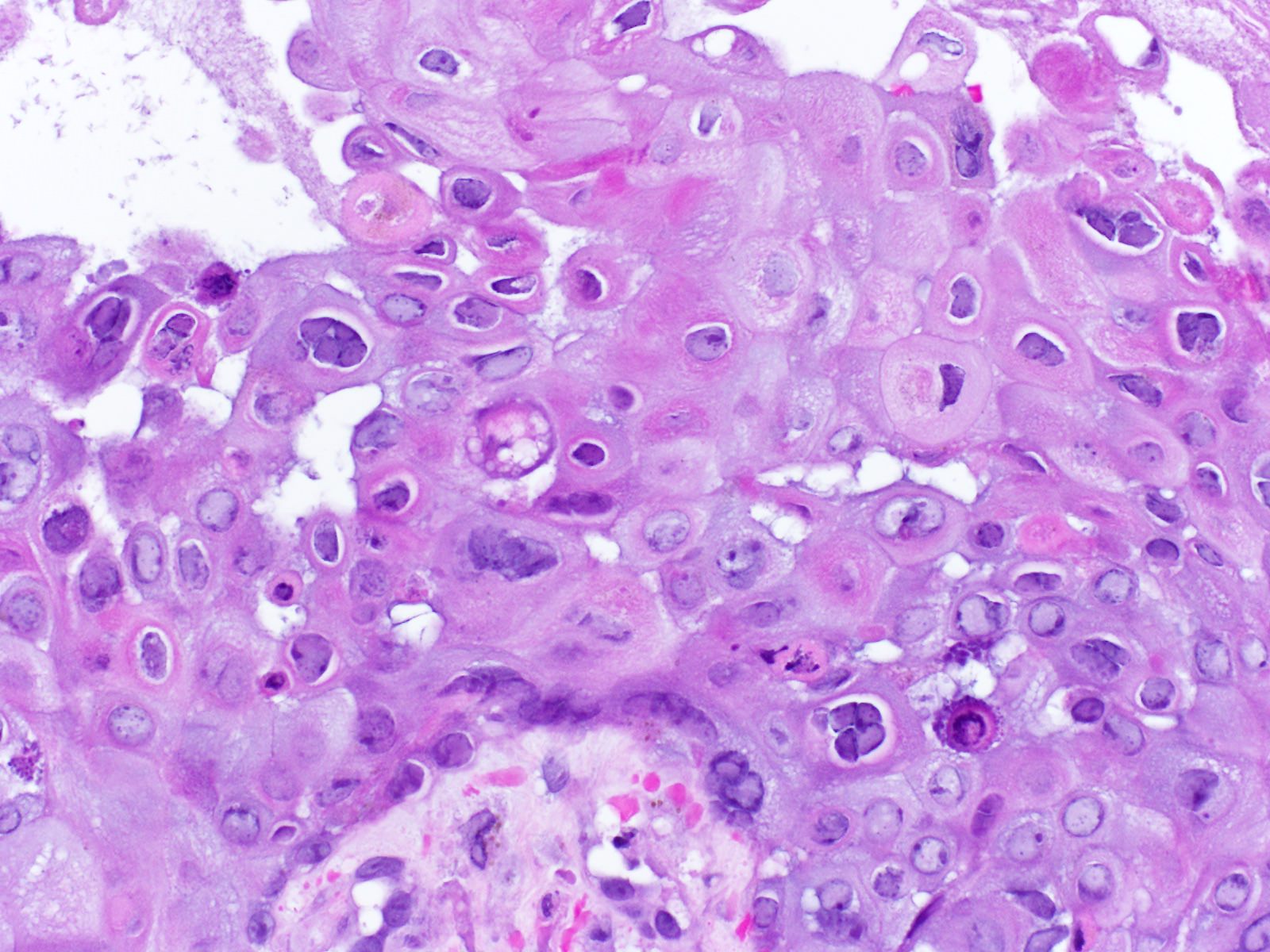
Pathology Outlines Herpes simplex or varicella zoster
Acute infectious, usually self-limited, disease believed to represent activation of latent varicella zoster virus in those who have been rendered partially immune after a previous attack of chickenpox; it involves the sensory ganglia and their areas of innervation and is characterized by severe neuralgic pain along the distribution of the affect.

Varicella (chickenpox) Immunisation Advisory Centre
Varicella-zoster virus (VZV) and herpes zoster cause infections of the central nervous system (CNS) manifesting as meningitis or encephalitis. As compared to enterovirus (EV) and herpes simplex virus 1 (HSV-1) and 2 (HSV-2), it is not often tested in CNS infections due to VZV and herpes zoster. There is a certain tendency to think that the.
Chicken Pox Kid Care Pediatrics
Varicella-zoster virus (chickenpox) is an acute febrile rash illness that was very common in children in the United States before the universal vaccination program came into existence. Luckily, the varicella-zoster virus is a vaccine-preventable disease. The FDA approves the use of the live varicella virus vaccine to provide immunity for preventing varicella in individuals 12 months older.

Disseminated varicella zoster virus encephalitis The Lancet
One-quarter of hospitalizations were due to laboratory-confirmed zoster meningitis/encephalitis (9/38, 23.7%) (Figure 1). Five of the 43 inpatient admissions identified by ICD-9 or ICD-10 codes as being VZV associated were excluded as a double clinician review deemed the code incorrect/misclassified.
VaricellaZoster Grade 2 Microbix Biosystems Inc.
The average incubation period for varicella is 14 to 16 days after exposure to a varicella or a herpes zoster rash, with a range of 10 to 21 days. A mild prodrome of fever and malaise may occur 1 to 2 days before rash onset, particularly in adults. In children, the rash is often the first sign of disease.

Disseminated Verrucous Varicella Zoster With Exclusive Follicular Involvement Dermatology
A contagious childhood disorder caused by the varicella zoster virus. It is transmitted via respiratory secretions and contact with chickenpox blister contents. It presents with a vesicular skin rush, usually associated with fever, headache, and myalgias. The pruritic fluid-filled vesicles occur 10-21 days after exposure and last for 3-4 days.
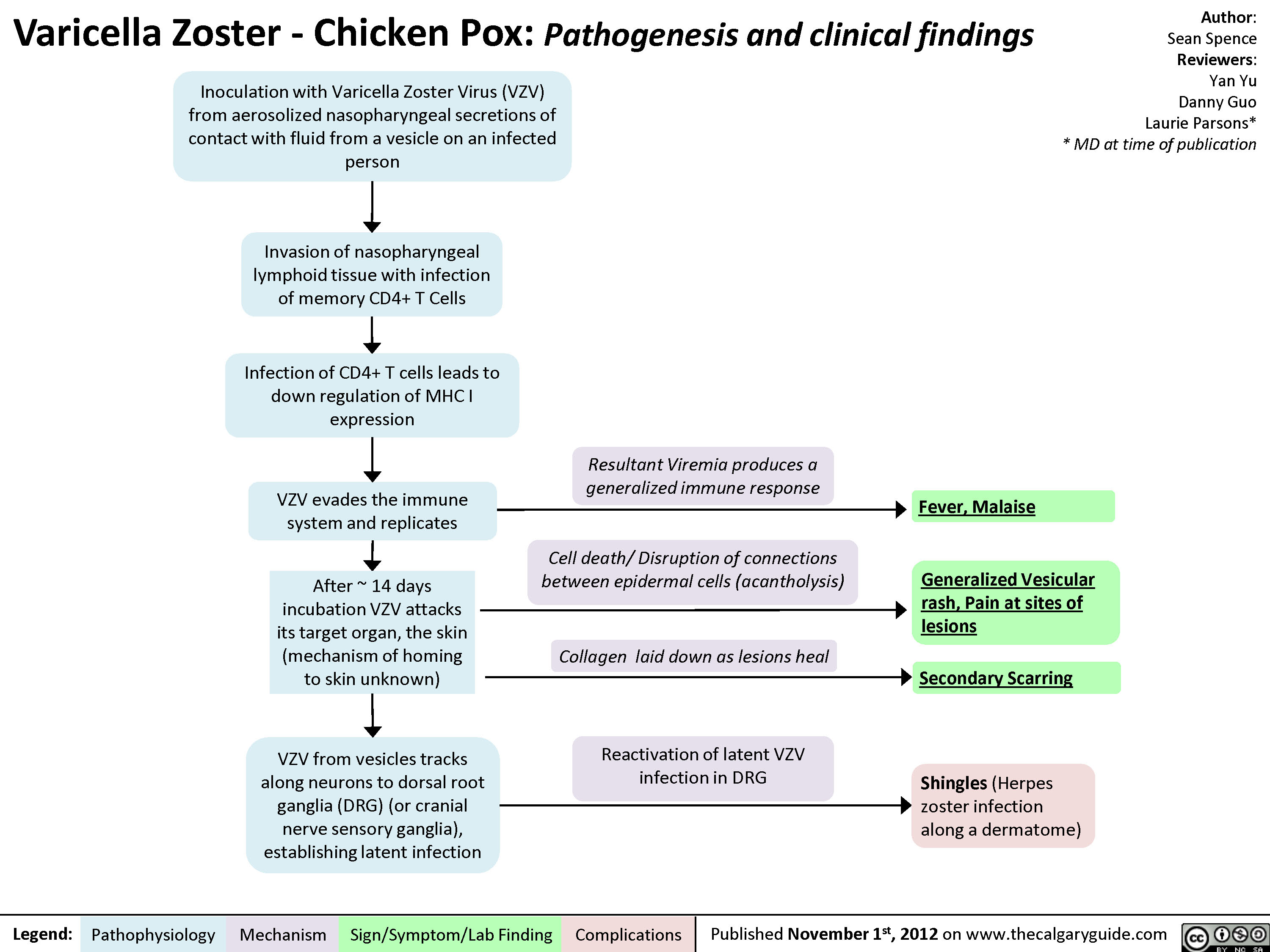
Varicella Zoster (Chicken Pox) Calgary Guide
Varicella zoster virus (VZV), a ubiquitous DNA virus, is one of eight known human herpesviruses. Primary infection occurs via aerosols from skin vesicles from an infected person with varicella or zoster, resulting in the characteristic disseminated rash of varicella. (See "Clinical features of varicella-zoster virus infection: Chickenpox" .)